Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
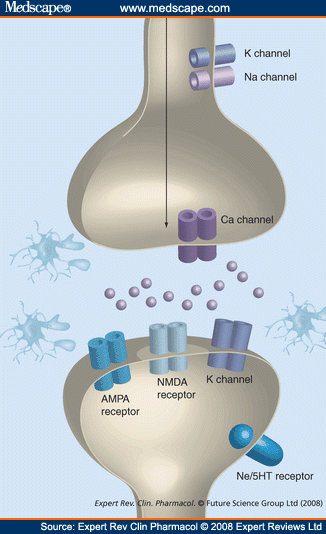 | 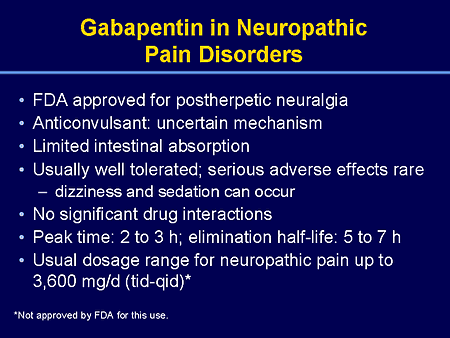 |
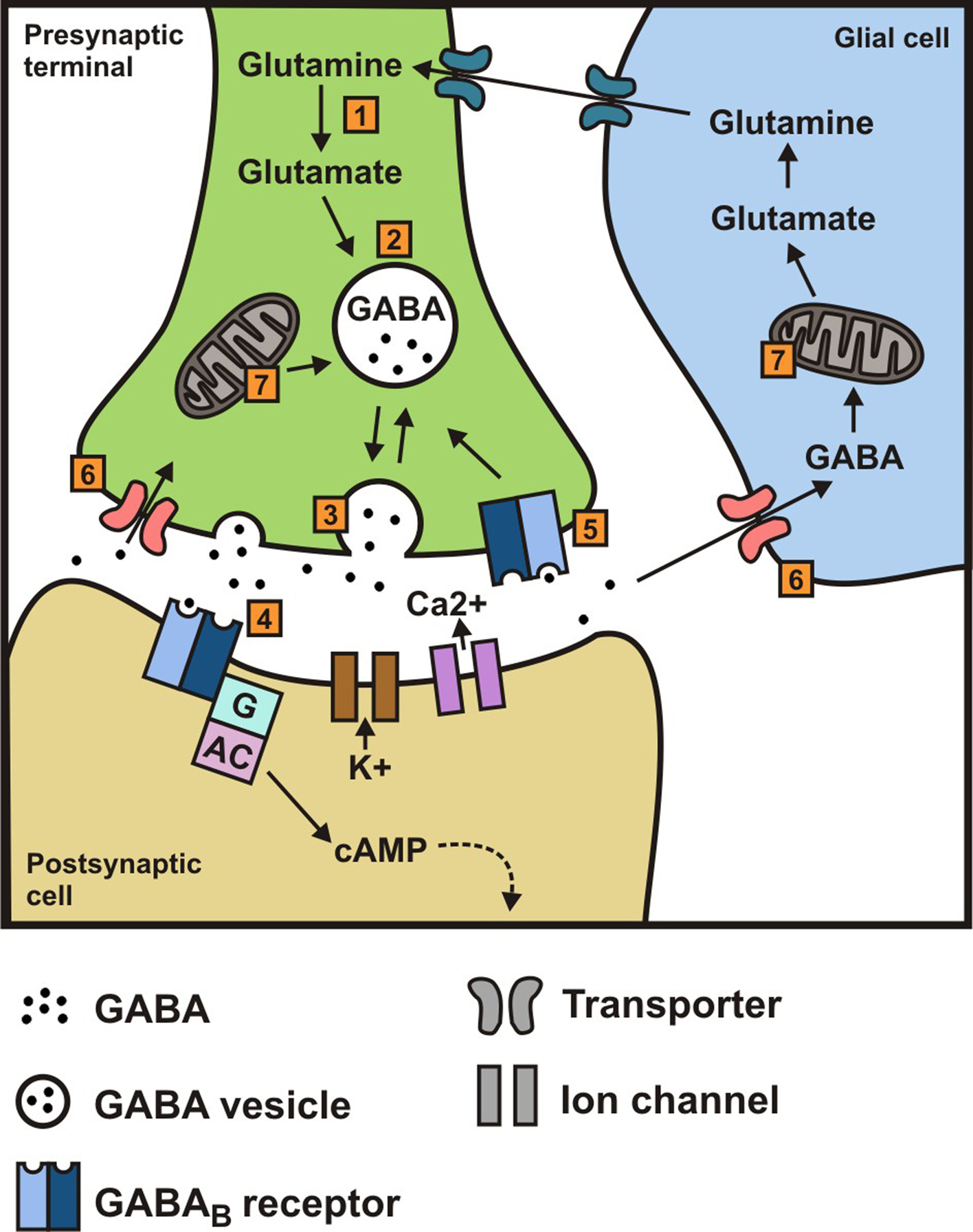
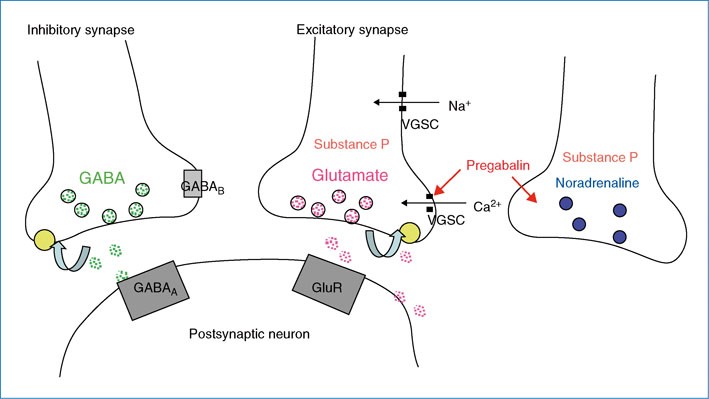
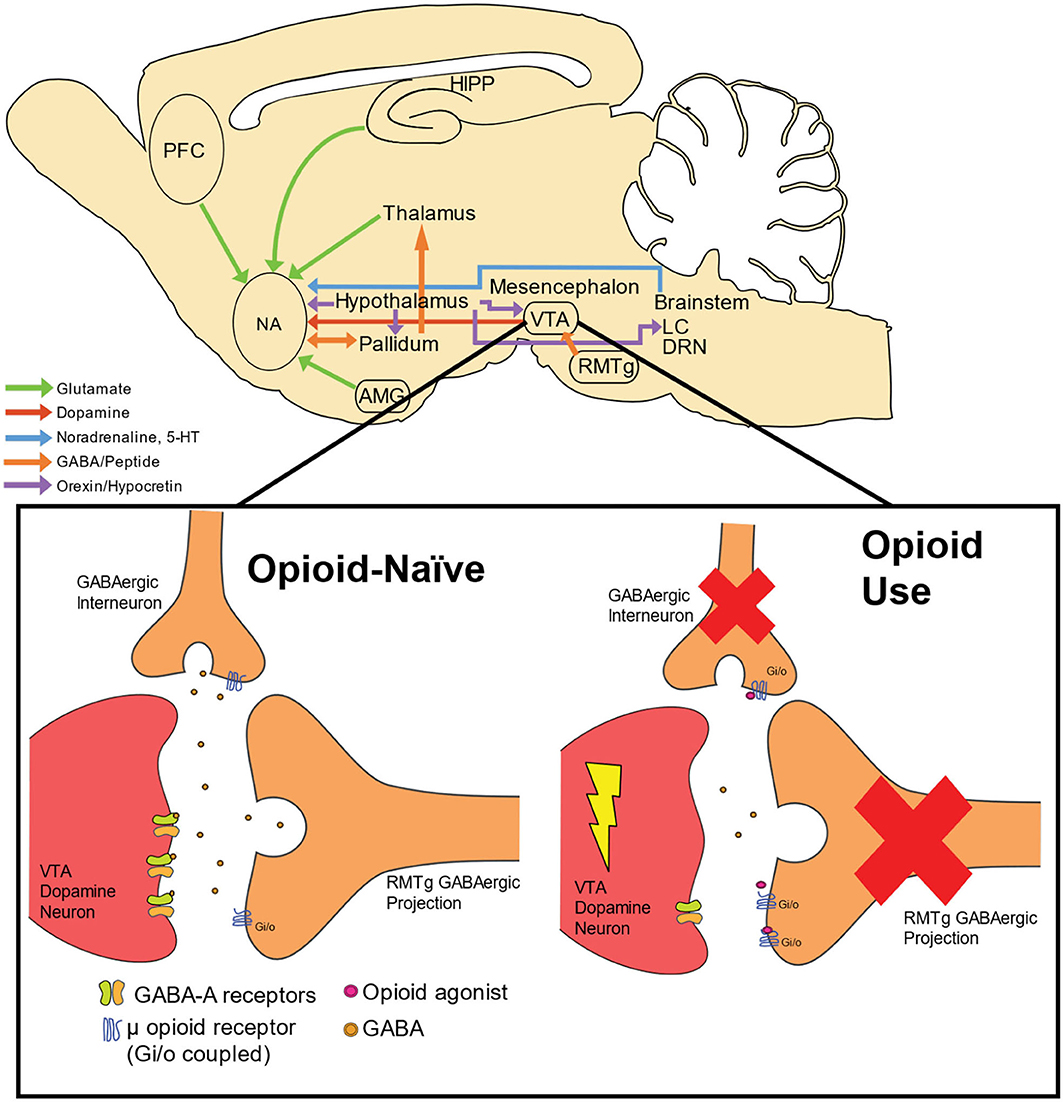
Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Furthermore, we show that the pain relief produced by gabapentin and lidocaine nerve block, treatments that are known to be analgesic in humans, depends on D1R signaling in the ACC. Gabapentin pain relief is associated with activation of VTA DAergic neurons and subsequent release of DA in the mesolimbic pathway (Navratilova et al., 2012 α2δ-1 (encoded by the <i>Cacna2d1</i> gene) is a newly discovered NMDA receptor-interacting protein and is the therapeutic target of gabapentinoids (e.g., gabapentin and pregabalin) frequently used for treating patients with neuropathic pain. Nerve injury causes sustained α2δ-1 upregulation in the d There is some evidence that gabapentin also acts on adenosine receptors 15,12 and voltage-gated potassium channels, 13 though the clinical relevance of its action at these sites is unclear. You can take 100 to 300mg sublingual GABA to treat pain flares, or 100 to 200mg of GABA simultaneously with an opioid medication or GABA surrogate for added pain relief. Forest Tennant is retired from clinical practice but continues his research on intractable pain and arachnoiditis. Ongoing pain scores are typically used as primary endpoints of efficacy in clinical trials complicating direct comparisons with animal studies where evoked stimuli are most often used, but in neuropathic rats gabapentin produces conditioned place preference, an indicator of reward and relief from ongoing pain (Griggs et al. 2015), and reduces Chen et al. show that α2δ-1, through its C terminus, physically interacts with NMDA receptors and promotes synaptic expression of α2δ-1-NMDA receptor complexes in neuropathic pain. Gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain primarily by targeting α2δ-1-bound NMDA receptors. In the present study, we examined whether gabapentin is an agonist at native GABA (B) receptors using a rat model of postoperative pain in vivo and periaqueductal gray (PAG) slices in vitro; PAG contains GABA (B) receptors, and their activation results in antinociception. Although it is known that gabapentin and pregabalin do not act on GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) receptors, it is unclear whether these side effects are due to an action of these drugs on the Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce Pregabalin is not effective in neuropathic pain due to HIV. There is limited evidence for neuropathic back pain, neuropathic cancer pain and other forms of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is effective to an extent in postherpetic neuralgia and diabetic neuropathy but the evidence in other forms of neuropathic pain is limited. Ongoing pain scores are typically used as primary endpoints of efficacy in clinical trials complicating direct comparisons with animal studies where evoked stimuli are most often used, but in neuropathic rats gabapentin produces conditioned place preference, an indicator of reward and relief from ongoing pain (Griggs et al. 2015), and reduces Gabapentin prevents pain responses in several animal models of hyperalgesia and prevents neuronal death in vitro and in vivo with models of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Gabapentin is also active in models that detect anxiolytic activity. Gabapentin has also been shown to induce modulate other targets including transient receptor potential channels, NMDA receptors, protein kinase C and inflammatory cytokines. It may also act on supra-spinal region to stimulate noradrenaline mediated descending inhibition, which contributes to its anti-hypersensitivity action in neuropathic pain. Two main drugs from this group, gabapentin and pregabalin, function by binding voltage-gated calcium channels, lowering neuronal hyperexcitability and pain signal transmission, thereby relieving neuropathic pain. Gabapentinoids depress neuronal excitability through interactions with the a2d-1 calcium channel subunit, stimulate descending inhibition, inhibit descending serotonergic facilitation, inhibit inflammatory media-tors, and influence the affective component of pain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate (GLU) play crucial roles in the control of neuropathic pain through their actions within the central nervous system (CNS). These neurotransmitters separately activate two distinct classes of receptors: ionotropic and metabotropic. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more However, with the added benefit of its effect on neuropathic pain, gabapentin may prove a useful adjunctive therapy in the dual treatment of spasticity and pain. Gabapentin starting dose is between 100–300 mg with a maximum dose of 3600 mg per day over three to four doses. It is renally excreted and requires dose adjustment for reduced
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |