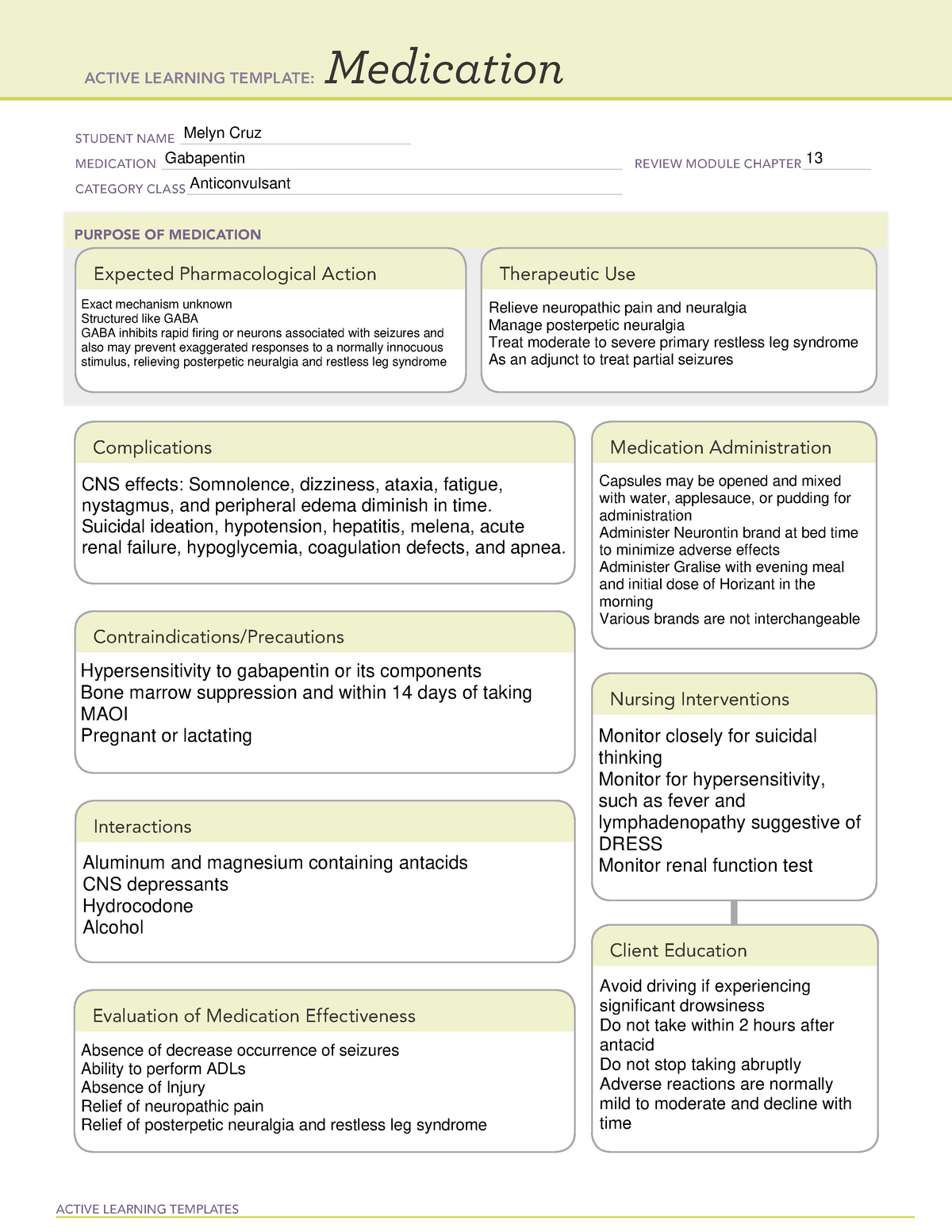
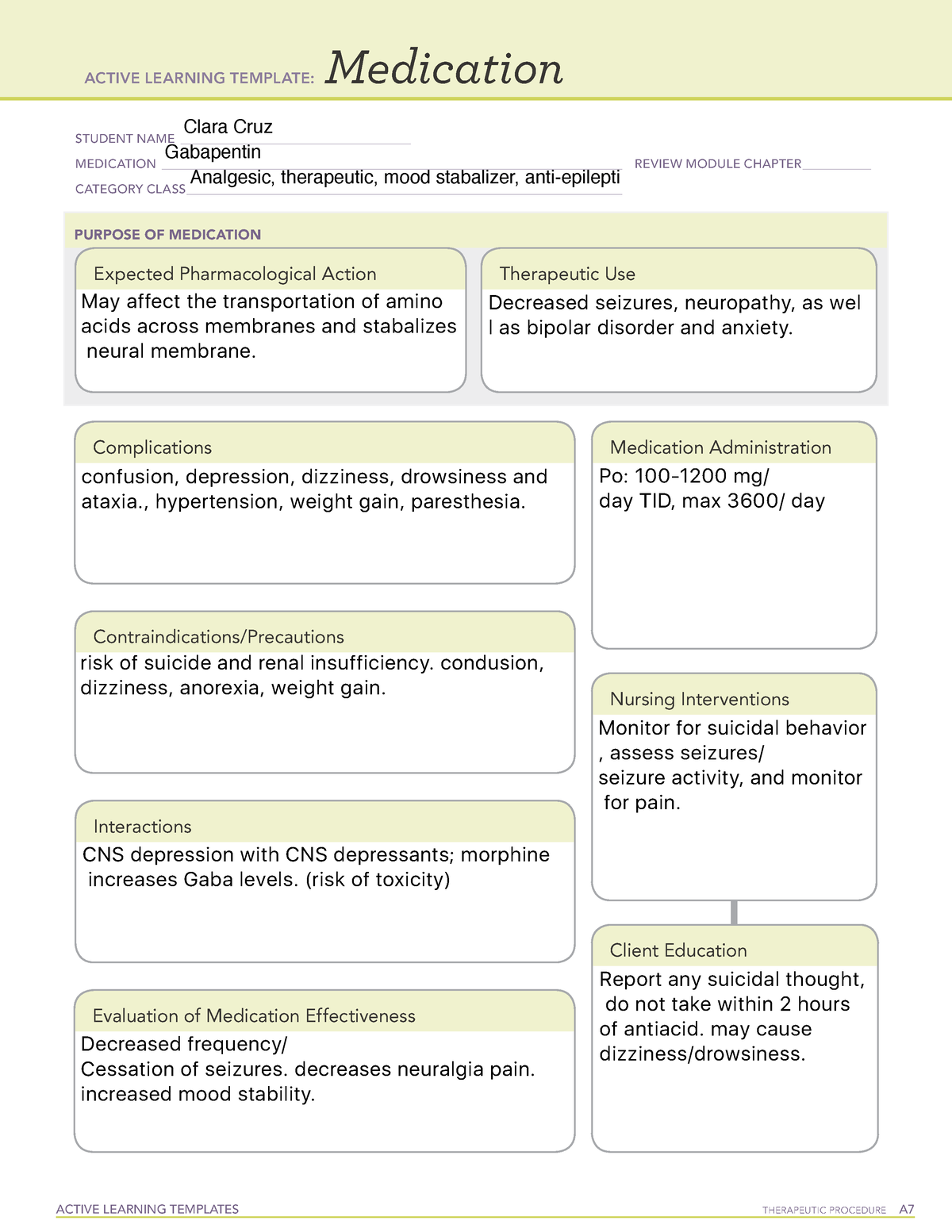
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
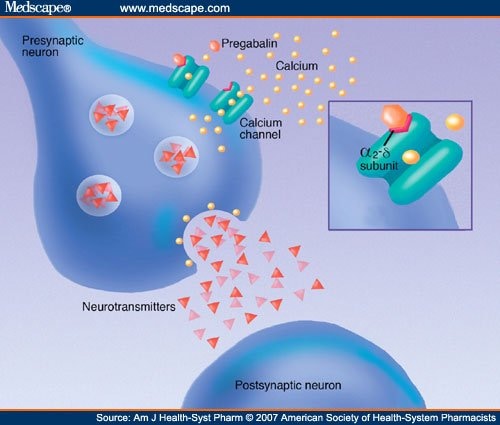
The National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines on the management of neuropathic pain recommend gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline or duloxetine as the initial choice of treatment for neuropathic pain with the exception of trigeminal neuralgia. 1 The guideline development group found that gabapentin was the most cost Gabapentin is FDA approved for pain management of a limited number of neuropathic pain conditions; Gabapentin is widely used off-label for various chronic pain conditions and for the treatment of acute pain, making it now one of the most commonly described analgesic drugs; The liberal use of gabapentin for both acute and chronic pain management Gabapentin (GBP) is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy Several case reports note analgesia when gabapentin was used for treatment of chronic pain. 14,15 And in a clinical study on postoperative pain in dogs undergoing mastectomy, although pain scores did not differ, dogs receiving NSAIDs plus gabapentin required fewer opioid rescue doses than dogs receiving NSAIDs alone; thus, the gabapentin did The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at understood. The analgesic effect in neuropathic pain is well evidenced but the role in postoperative pain is less certain. Medline and EMBASE database searches were conducted to identify studies relating to mechanisms of action and effects in experimental animal models of inflammatory and postoperative pain and human models of experimental In randomized open clinical trial, the combination of gabapentin with opioid analgesics was shown to provide better relief in neuropathic pain in cancer patients as compared to opioid analgesics alone in terms of reduction in pain intensity for burning and shooting pain at different days of the study. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific binding to this subunit is described to produce Its mechanisms of action appear to be a complex synergy between increased GABA synthesis, non-NMDA receptor antagonism and binding to the α, δ subunit of voltage dependent calcium channels. The latter action inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Gabapentin is especially effective at relieving allodynia and hyperalgesia in animal models. It has been shown to be efficacious in numerous small clinical studies and case reports in a wide variety of pain syndromes. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. In general, gabapentin treatment appears to be more effective in reducing paroxysmal pain with throbbing, pricking, and cramping quality than dull aching pain in MS patients. These findings suggest that a large-scale, controlled clinical trial may be warranted to determine the effectiveness of gabapentin in improving pain in MS patients. In a meta-analysis of trials evaluating the treatment of neuropathic pain, including painful polyneuropathy and spinal cord injury pain, gabapentin was shown to be safe and effective IASP [Finnerup 2015]. Data from meta-analyses support the use of IR gabapentin for reducing pain by more than 50% in diabetic neuropathy Moore 2014, Rudroju 2013. The Mechanism for Pain Relief. The same mechanism that makes gabapentin effective for seizures also plays a role in pain management. Specifically, gabapentin reduces the hyperexcitability of nerves that can cause neuropathic pain, such as pain associated with post-herpetic neuralgia (shingles) and diabetic neuropathy. By decreasing abnormal Key Takeaways: Gabapentin for Pain Relief Mechanism of Action: Gabapentin modulates nerve signals to alleviate pain. Conditions Treated: Effective for neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and more. Dosing Guidelines: Start low and increase dosage based on individual response. Side Effects: Common effects include dizziness and fatigue; monitor Pain relief mechanism. Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used for the management of pain. It works by targeting the pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord, which helps to reduce the sensation of pain. Gabapentin works by binding to specific receptors in the brain called alpha-2-delta subunits. The number-needed-to-treat (NNT, defined as the number of patients needed to be treated for one patient to receive at least 50% pain relief) for the analgesic effects in neuropathic pain with gabapentin in this study was 3.8 . This compares with a NNT of 2.3 for carbemazepine and 2.1 for phenytoin in other randomised controlled trials . Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Here we review the current understanding of the pathophysiological role of the α 2 δ ‐1 subunit, the mechanisms of analgesic action of gabapentinoid drugs and implications for efficacy in the clinic. Despite widespread use, the number needed to treat for gabapentin and pregabalin averages from 3 to 8 across neuropathies. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |