Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
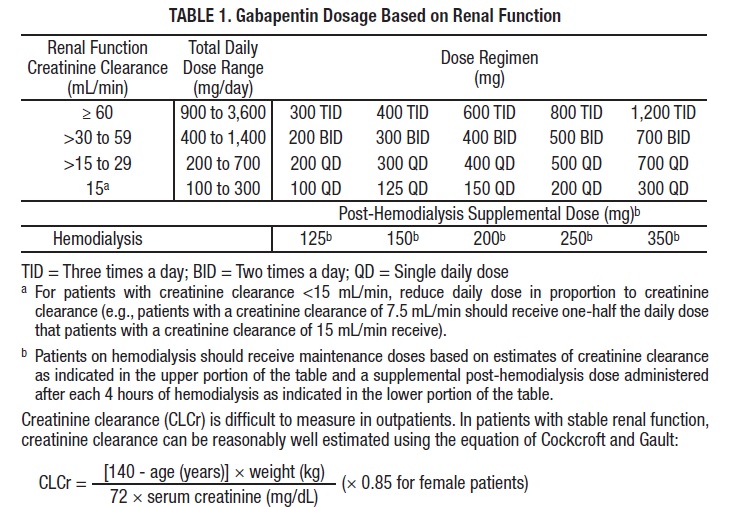
The functional tolerance seen with phenobarbitone makes regular monitoring particularly important, as a previously well-controlled patient may relapse during the course of treatment. Repeated serum samples should ideally be collected around the same time of day in an individual patient to avoid comparing peak and trough serum concentrations. Peak & Trough (2 samples) Bromide (Potassium/Sodium) Cyclosporine: Digoxin: Gabapentin: Leflunomide (Teriflunomide) Levetiracetam (Keppra®) Mycophenolate (MPA, MMF) Phenobarbital: Theophylline: Zonisamide: Other Test : Continue ONSET, PEAK AND DURATION OF COMMON PAIN MEDICATIONS Medication Onset of Action (minutes)* Peak Effect (hours)* Duration of Action (hours)* Route of Admin. Comments Non-Opioid Analgesics Acetaminophen 30 -45 0.5 -1 4 -6 Oral Headache, nausea, vomiting May cause hepatic complications in doses over 3000mg/24hr in the elderly Plasma gabapentin peak-to-trough and percent fluctuation of GBP-IR were 63% and 76% higher, respectively, when compared to GEn (Figure 3A, B). Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is an oral antiepileptic agent that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but it does not interact with GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it has properties in common with other anticonvulsant medications. Experience to date indicated that gabapentin is safe and relatively nontoxic. Therapeutic ranges are based on specimens collected immediately before the next dose (ie, trough). Most epileptic patients show a response to the drug when the trough concentration is in the range of 2 to 20 mcg/mL. Gabapentin - Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug commonly used as adjunctive therapy to treat partial seizures. Therapeutic drug monitoring is useful to optimize dose and to avoid toxicity. Draw sample 2 hours after last dose. Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. GBP-GR resulted in substantially (~ 4-fold) higher peak-to-trough ratio and percent fluctuation compared to GEn. GEn resulted in more sustained and less fluctuating daily exposure relative to Although the analyzable sample size was small, impressive is the large effect of GPN on CP pain responses in this sample (Cohen’s d = 1.01 [threshold peak methadone]; 1.73 [threshold trough methadone]; 1.11 [tolerance peak methadone]; 0.30 [tolerance trough methadone]). Like the hyperalgesia of neuropathic pain, OIH appears to respond to GABA Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin vary widely among patients, particularly those with compromised renal function. Adverse effects may include somnolence, dizziness, ataxia, and fatigue. Methodology: Interpretation. Therapeutic ranges are based on specimens collected immediately before the next dose (ie, trough). Most epileptic patients show a response to the drug when the trough concentration is in the range of 2 to 20 mcg/mL. Therapeutic drug monitoring may be useful due to inter-individual variation in pharmacokinetics and dose-dependent bioavailability; specimens for measurements Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is commonly used to determine whether measured drug levels are within the therapeutic range. 1,2 The therapeutic range is the concentration range over which, for most patients, the probability of a beneficial clinical response is high and the probability of toxic effects is low. In a medicine that is administered periodically, the trough level should be measured just before the administration of the next dose in order to avoid overdosing. It should be contrasted with a "peak level", which is the highest level of the medicine in the body, and the "average level", which is the mean level over time. One sample (sometimes referred to as the measured peak) should be drawn no earlier than 1 hour after the end of a 30-minute, at minimum, infusion. 156 A second sample may be drawn any time later but is usually drawn within 30 minutes of the start of infusion of the next dose (assumed to be the trough). 42,152,154 If it is expected that the Peaks and troughs are the highest and lowest concentrations of a medication in an individual’s body. They are used to determine dosing intervals, or how much time should pass between each new administration of the drug. Food has no effect on the rate or extent of absorption of gabapentin. In patients with epilepsy, gabapentin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid are approximately 20% of corresponding steady-state trough plasma concentrations. In addition to their use in managing neuropathic pain, gabapentinoids are increasingly being used for off-label conditions despite the lack of evidence. Prescription rates for off-label conditions have overtaken that for on-label use. Peak Trough Single Peak & Trough ; Cyclosporine: 0.5 mL EDTA. whole blood (purple top) 1.5–2 hrs Preferred sample if only one is submitted. BND: W, F: $75: $115: Immunoassay: No: Do not use a gel barrier tube. Recommend peak & trough the first time to establish a half-life. A level may be too low to detect if a sample is drawn >12 hours post Peak & Trough (2 samples) Bromide (Potassium/Sodium) Cyclosporine: Digoxin: Gabapentin: Leflunomide (Teriflunomide) Levetiracetam (Keppra®) Mycophenolate (MPA, MMF) Phenobarbital: Theophylline: Zonisamide: Other Test : Continue
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |