Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
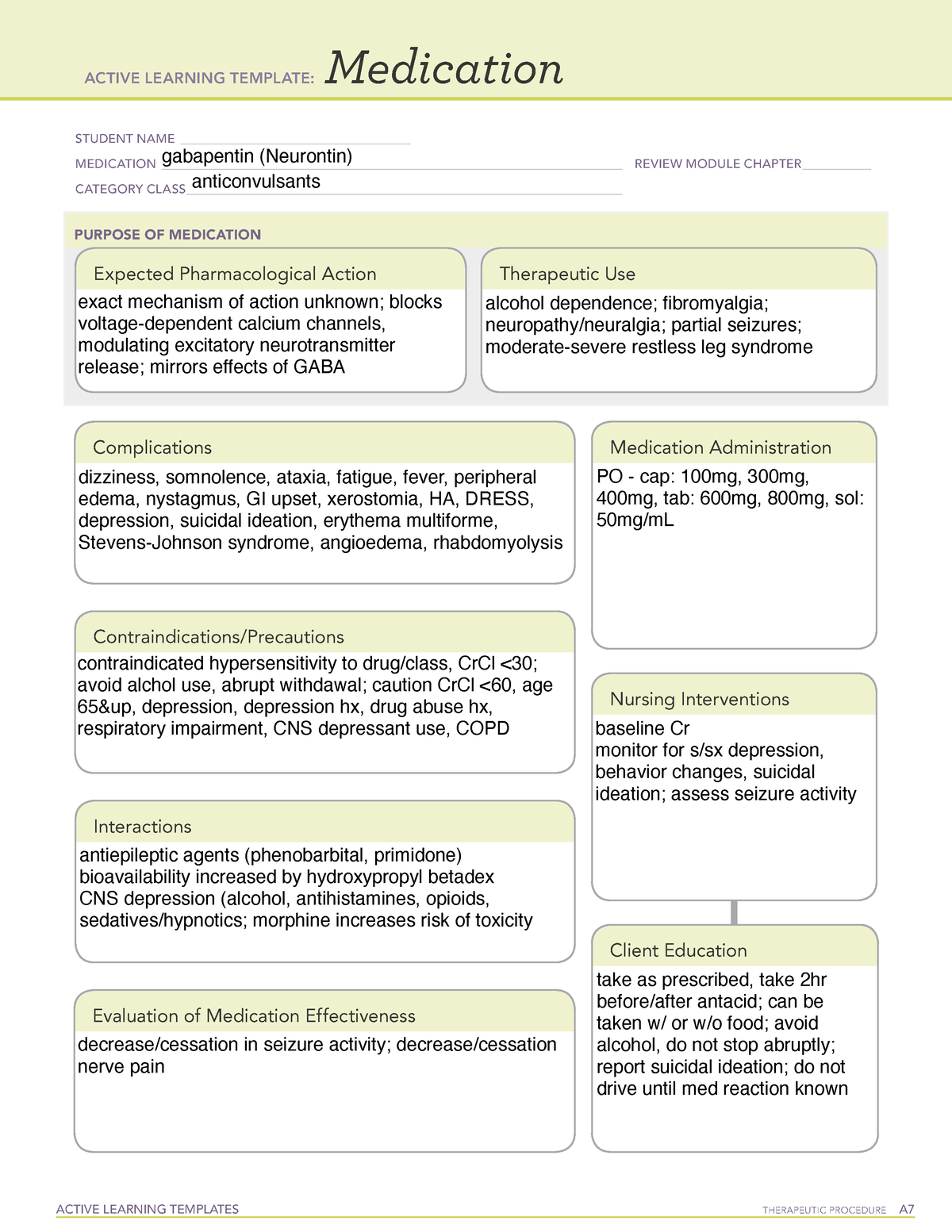 |  |
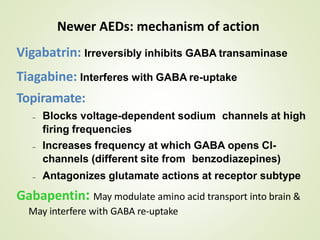
All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Oral Bioavailability . Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Gabapentin is a structurally related to GABA that binds to voltage-gated calcium channels. It is used for various indications, such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, restless legs syndrome, and postoperative pain. Learn about its dosage, pharmacokinetics, contraindications, and interactions. Gabapentin, like other gabapentinoid drugs, acts by decreasing activity of the α 2 δ-1 protein, coded by the CACNA2D1 gene, first known as an auxiliary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. [13][14][15] However, see Pharmacodynamics, below. Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes), and to treat and prevent hot flashes (sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating) in women who are being treated for breast cancer or who have experienced menopause (''change of life'', the end of monthly menstrual periods). All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Oral Bioavailability. Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin ®) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed.It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinical practice. This article has summarised these key differences. In addition to their use in managing ne Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally related compounds with recognized efficacy in the treatment of both epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The pharmacological mechanisms by which these agents exert their clinical effects have, until recently, remained unclear. While gabapentin's mechanism of action is generally understood, it appears to be a pharmacologic option for treating issues involving the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor system. Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed. Patients on 3 times daily dosing should not exceed 12 hr between doses. Take missed doses as soon as possible; if less than 2 hr until next dose, take dose immediately and take next dose 1-2 hr later, then resume regular dosing schedule. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Learn Gabapentin - Analgesic Agents (Pain Management) - Pharmacology - Picmonic for Medicine faster and easier with Picmonic's unforgettable videos, stories, and quizzes! Picmonic is research proven to increase your memory retention and test scores. Start learning today for free! Gabapentin is regarded as safe and tolerable with a promising pharmacokinetic profile and an extensive therapeutic index. 10 Also, gabapentin have been approved in Japan as adjunctive drug therapy for medically intractable seizures. 4 Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant.It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder.It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. All pharmacological actions following gabapentin administration are due to the activity of the parent compound; gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Oral Bioavailability: Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 60% Mechanism of action. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, thereby blocking the excitatory influx of calcium; (2) reducing the expression and phosphorylation of CaMKII via modulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation; (3) i Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |