Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
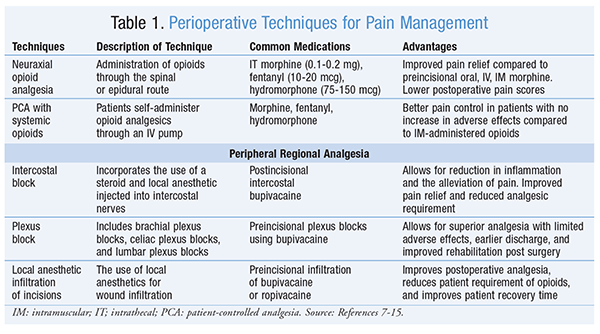
Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, has recently been suggested as an effective postoperative ‘analgesic’ agent. The objective of the present study was to examine the analgesic effectiveness, opioid-sparing effects and side effects associated with the use of gabapentin in a perioperative setting. Increasing numbers of randomized trials indicate that gabapentin is effective as a postoperative analgesic. This procedure-specific systematic review aims to analyse the 24-hour postoperative effect of gabapentin on acute pain in adults. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. In 2006, Sihoe et al. evaluated gabapentin in the treatment of chronic pain after chest surgery (6). Twelve patients were chest trauma victims, 22 were status post video assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), 8 had undergone open thoracotomies, and 3 had median sternotomies. Patients were started on a dose of gabapentin 300 mg daily The shift towards multimodal pain regimens, including gabapentin, has taken place without attention to ensuring that they, like opioids, are appropriately discontinued soon after surgery. The prevalence of prolonged use of post-operative gabapentin among older adults is unknown, as are the factors associated with prolonged use. The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. Recent findings: Recent meta-analyses have revealed that prior data likely have overestimated the beneficial effects of gabapentinoids in acute perioperative This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Given the significant differences between the studies and the possibility of Background: Perioperative pain treatment often consist of combinations of non-opioid and opioid analgesics, 'multimodal analgesia', in which gabapentin is currently used. The aim was to document beneficial and harmful effects of perioperative gabapentin treatment. The efficacy of preoperative gabapentin in spinal surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Phys. 2017; 20(7):649-661. Medline, Google Scholar; 17. . Gabapentin for post-operative pain management—a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2016; 60(9):1188-1208. Crossref Perioperative gabapentin may reduce the incidence and intensity of postoperative pain up to 6 months after otolaryngology, orthopedic, mastectomy, and abdominal/pelvic operations. 12-15 Professional guidelines advocate for perioperative administration of gabapentin as a component of multimodal analgesia, 16 but its efficacy in the context of Gabapentin appears safe and well tolerated when used for persistent post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients, although minor side effects do occur. Gabapentin may relieve refractory chest wall pain in some of these patients, particularly those with more severe pain. Gabapentin 250 mg is statistically superior to placebo in the treatment of established acute postoperative pain, but the NNT of 11 for at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours with gabapentin 250 mg is of limited clinical value and inferior to commonly used analgesics. some outcomes indirectness. Firm evidence for use of gabapentin is lacking as clinically relevant beneficial effect of gabapentin may be absent and harm is imminent, especially when added to multi-modal analgesia. Editorial Comment In this trustworthy systematic review, use of gabapentin for post-operative pain management was scrutinized. But gabapentinoids also have risks and there is little evidence to support their use for postoperative pain relief, according to a large new study by a team of Canadian researchers. “No clinically significant analgesic effect for the perioperative use of gabapentinoids was observed. 300 mg on day 1, 600 mg on day 2, and 900 mg from day 3 to day 30 after surgery: Acute post-operative pain intensity in gabapentin group was significantly lower than the placebo group p<0.05). The rate of PLP at the last follow-up was lower in the gabapentin group (43.48%) compared to placebo (77.27%, p=0.033). Hah et al., 2018 25 Pain management after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Some randomized controlled studies have carried out to evaluate the effects of gabapentin on pain relief after TKA. However, no solid result was Compared with controls, gabapentinoids were associated with a lower postoperative pain intensity (100-point scale) at 6 h (mean difference, -10; 95% CI, -12 to -9), 12 h (mean difference, -9; 95% CI, -10 to -7), 24 h (mean difference, -7; 95% CI, -8 to -6), and 48 h (mean difference, -3; 95% CI, -5 to -1). The coprimary outcomes were postoperative acute pain at 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h after surgery measured by any quanti-tative pain scale.58 Secondary outcomes were postoperative subacute pain (defined as pain intensity during postopera-tive weeks 4 to 12); incidence of postoperative chronic pain Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. In response to the opioid crisis, surgeons nationwide have sought to decrease opioid use by adopting opioid-sparing multimodal medication regimens to treat perioperative pain. 1 For example, gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) are now commonly administered during the perioperative period as part of “enhanced recovery after surgery
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |