Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
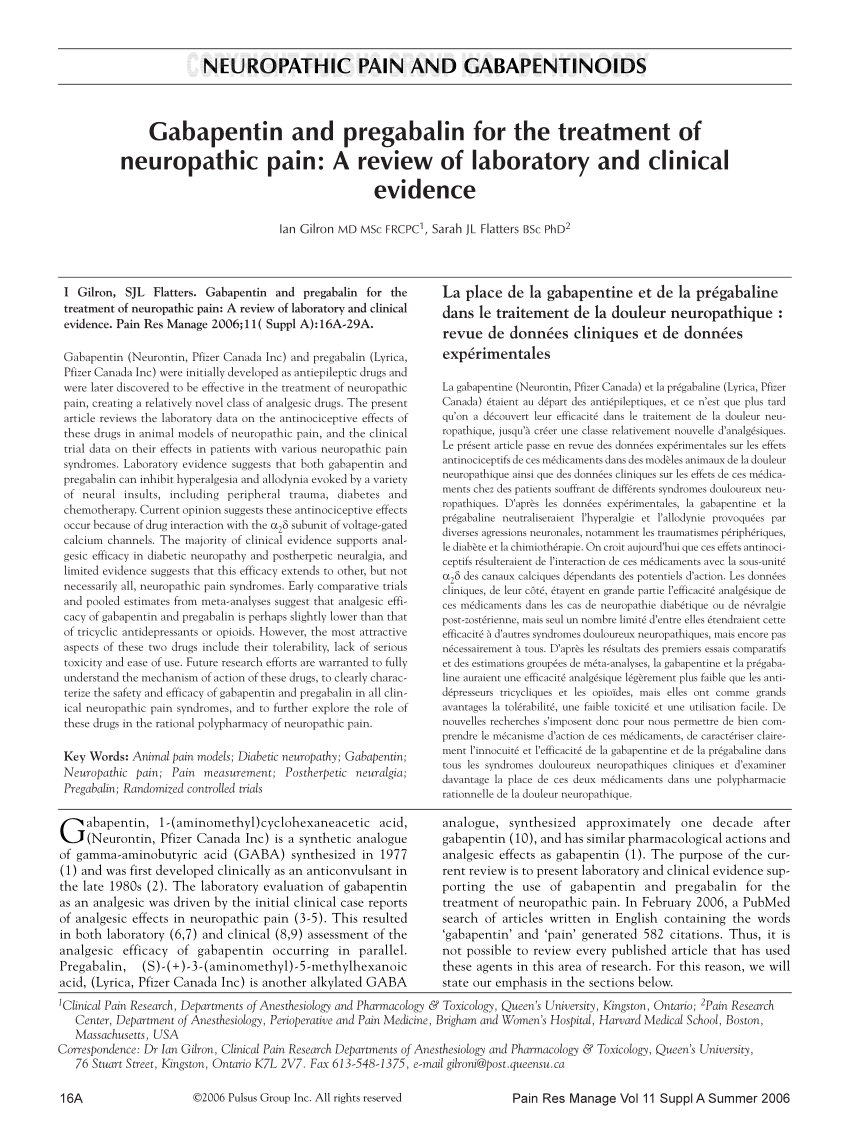
Gabapentin is not the same as pregabalin, even though they both belong to the same class of medicine, called gabapentinoids, and work similarly. Lyrica and Lyrica CR are the only brands of pregabalin. Neurontin is a brand name for gabapentin. Other brands of gabapentin include Gralise and Horizant. Absorption and distribution. Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as compared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. From midnight on 1st April 2019, gabapentin and pregabalin will be reclassified as Schedule 3 controlled drugs, under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations (2001), and Class C of the Misuse of Drugs Act (1971), as is already the case with Tramadol. Having originally been developed as an anti-seizure medication, gabapentinoids include gabapentin and pregabalin, which are now prescribed primarily for neuropathic pain, seizures and anxiety, but also for fibromyalgia, restless legs syndrome and complications of MS (Chan et al, 2023). Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar orally administered drugs but differ in their indications and dosages. Regarding safety, pregabalin is a controlled substance; gabapentin is not. Both drugs are used to treat certain types of nerve-related pain in adults. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Pregabalin is used in the treatment of nerve pain and also to prevent seizures. Gabapentin and pregabalin are members of a class of anti-convulsive and anti-epileptic drugs called gabapentinoids. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and pregabalin followed in 2004. They’ve been widely prescribed to treat certain types of pain as well. Conditions gabapentin and pregabalin are approved to treat include: The ACMD recommended that gabapentin and pregabalin be controlled as Class C drugs under the 1971 Act, and placed in Schedule 3 to the 2001 Regulations. For more information about these compounds As of 1 April 2019, pregabalin and gabapentin are controlled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 as Class C substances and scheduled under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001 as Schedule 3. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) both belong to a class of drugs called gabapentinoids, which means they work in similar ways. They're both used to treat chronic pain in certain Pregabalin was originally FDA approved in 2004 as an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It works by slowing down impulses in the brain that cause seizures . Pregabalin also affects chemicals in the brain that send pain signals across the nervous system. Following concerns about abuse, pregabalin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Healthcare professionals should evaluate patients carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing pregabalin, and observe patients for signs of abuse and dependence. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic medications that bare structural resemblance to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though neither agent has activity in GABA’s neuronal systems. Gabapentin contains the active ingredient gabapentin. Both Lyrica and gabapentin belong to a class of drugs known as anticonvulsants. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Lyrica Gabapentin and pregabalin both work to increase the amount of GABA (a pain-fighting transmitter) in your central nervous system. These two medications are in the same drug class. They are gabapentinoids or more generally called anticonvulsants. However, there are differences between them. Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which bind selectively to the α 2 δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). [1][2][3][4][5] Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. In 2016, the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) raised concerns over medicinal misuse, illegal diversion of the drugs and addiction, and recommended that pregabalin and gabapentin Pregabalin and gabapentin can both provide relief from pain and be effective ways to manage seizure disorders. However, it’s important to consider the differences between them. Pregabalin is more rapidly absorbed compared to gabapentin, which has a slower absorption rate. Gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs commonly used for neuropathic pain management and pain reduction in adults. Both medications are classified as antiepileptic medications, but they have differences in pharmacokinetics, safety profile, and clinical applications.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |