Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
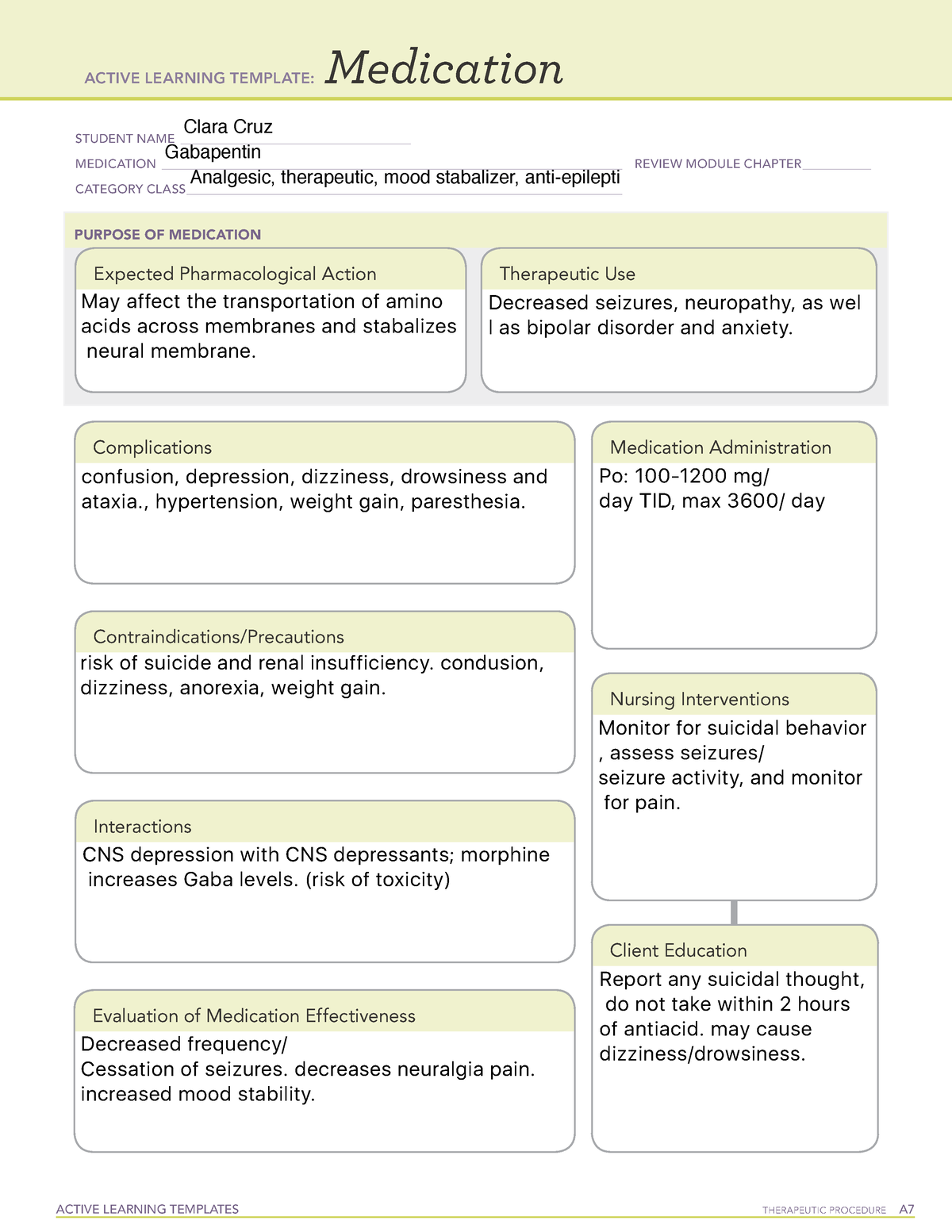
GBP has been used to treat various medical and psychiatric conditions such as fibromyalgia, chronic pain syndromes, and migraine headaches, and has been extensively prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite a lack of rigorous evidence of its effectiveness (1, 2). GBP belongs to the gabapentinoid class, used as anticonvulsants An initial bibliographic reference search for gabapentin use in psychiatric disorders was performed in PubMed and Ovid MEDLINE from January 1, 1983 (gabapentin’s appearance in medical research literature), to October 1, 2014 with no language restrictions. The first sentence of the third paragraph got my attention. The author erroneously stated: “Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).” 1 Gabapentin (Trade name: Neurontin) is an anticonvulsant. It is commonly also used off-label for anxiety disorders, restless leg syndrome, and in alcohol use disorder. It is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has a long history of being prescribed off label for various indications, including psychiatric indications. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) is an anticonvulsant medication that is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS) and posttherapeutic neuralgia. GBP is commonly prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite the lack of strong evidence. Outpatient Off-Label Gabapentin Use for Psychiatric Indications Among U.S. Adults, 2011 –2016 Brianna Costales, B.S., and Amie J. Goodin, Ph.D., M.P.P. Objective: Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with What is gabapentin and how does it differ from antipsychotic medications? Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless leg syndrome. It works by reducing the activity of certain brain chemicals that are involved in seizures and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Neurontin (generic name: gabapentin) is classified as an anti-epileptic (or anticonvulsant) medication.It is used to treat nerve pain (also known as neuropathic pain), and in some cases, restless Gabapentin, known by its brand name Neurontin, has been turning heads in the psychiatric community for its potential to address a wide range of mental health issues. But how did this anticonvulsant drug find its way into the realm of mental health treatment? I was on Neurontin at 2400 mg a day when I was first very sick and in constant extreme pain, which helped; but it can make you pass out from such an extreme dose. I had several accidents falling. If someone gives you a new medication, always go online and read everything you can about any medication before starting something new. Forms listed with a "Blank" medication name are the base form available in English and Spanish versions. Complete a blank form if no prefilled version exists for the prescribed psychotropic medication. The Client Rights Office accepts questions about these forms and suggestions for improvements. However, relevant research data have not proven success of newer antiepileptics. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results Study selection and data extraction: The resulting 988 abstracts were read by 2 reviewers; references were excluded if gabapentin was not a study compound or psychiatric symptoms were not studied. The resulting references were subsequently read, reviewed, and analyzed; 219 pertinent to gabapentin use in psychiatric disorders were retained. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures. High concomitant use of CNS-D drugs and off-label gabapentin for psychiatric diagnoses underlines the need for improved communication about safety. Objective: To determine if gabapentin is effec-tive either as adjunctive treatment or as mono-therapy for major affective disorders in a natural-istic setting. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |