Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
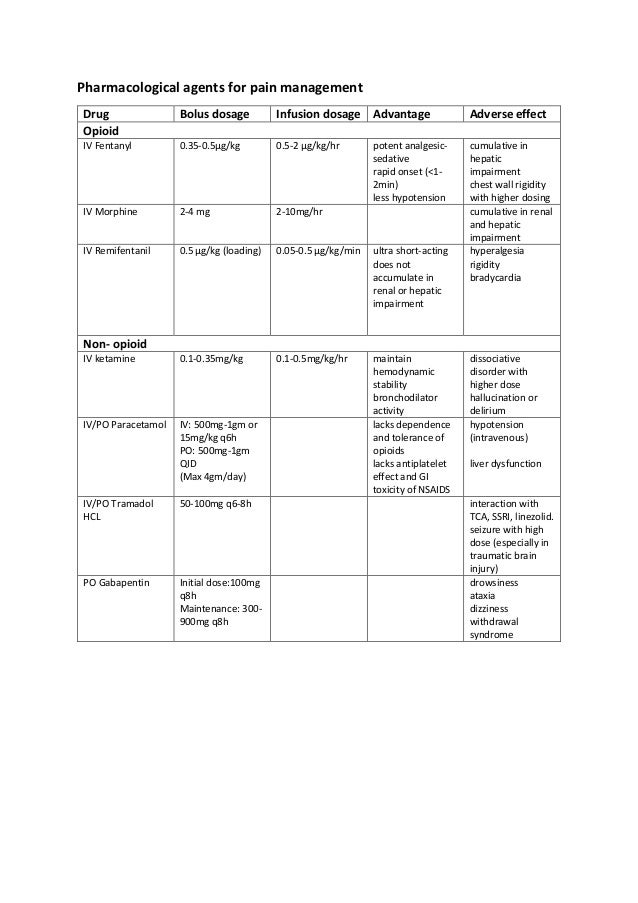
Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. The TID group received equal doses of gabapentin 3 times per day, while the QID group received 4 different doses of gabapentin per day. The pain score, frequency of breakthrough pain (BTP), Administration of 4 different doses of gabapentin during the initial titration in outpatients with neuropathic pain resulted in a significant reduction in awakening from breakthrough pain and a reduction in the adverse effects of the medication. In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg QID (N=12), the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus, cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. Learn how to take gabapentin for epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. Find out the usual, maximum, and adjusted doses for different ages, conditions, and renal functions. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. Menu. Drugs TABLE 1. NEURONTIN Dosage Based on Renal Function; TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose * For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg QID (N=12) the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. Estimates for k a, k el, and V d were obtained from a non-linear least-squares regression analysis (Heinzel et al., 1993) of mean plasma gabapentin concentration-time data obtained from a 300-mg single dose bioavailability study in healthy volunteers (data on file, Study 945-055-0, Parke-Davis Pharmaceutical Research, Division of Warner-Lambert). Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. QID and Q6H are both medical abbreviations used on prescription medications. QID medications should be taken four times a day, while Q6H should be taken every six hours. While this may seem redundant, it's not. There's a key difference. With QID medications, you need to space out your doses, but not Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Cimetidine: In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg QID (N=12) the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Adults: Increase by 4-8 mg at 1W intervals to a maintenance dose of 32-56 mg/day divided BID-QID Children: Increase to 8 mg daily in 2 divided doses for 1W; then increase by 4-8 mg weekly to response Cimetidine: In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg QID (N = 12) the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus, cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. Gabapentin (GBP) is a non-metabolized antiepileptic drug that is eliminated by renal excretion and displays saturable, dose dependent absorption. The recommended dosing schedule for GBP is t.i.d. At large daily doses, oral bioavailability (F) may be improved by giving the daily dose more frequently. In present study, gabapentin was initiated and titrated at the same total daily dose as the standard schedule, but it was administered in unequal four times a day (QID).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |