Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
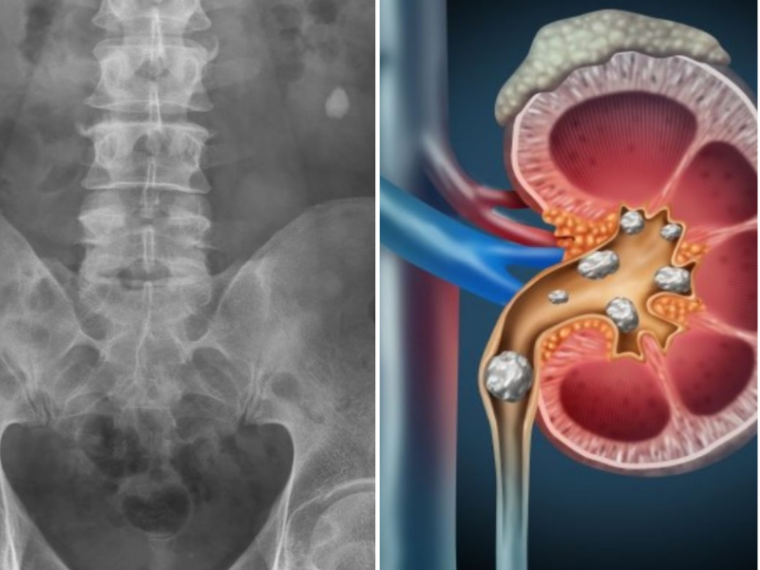
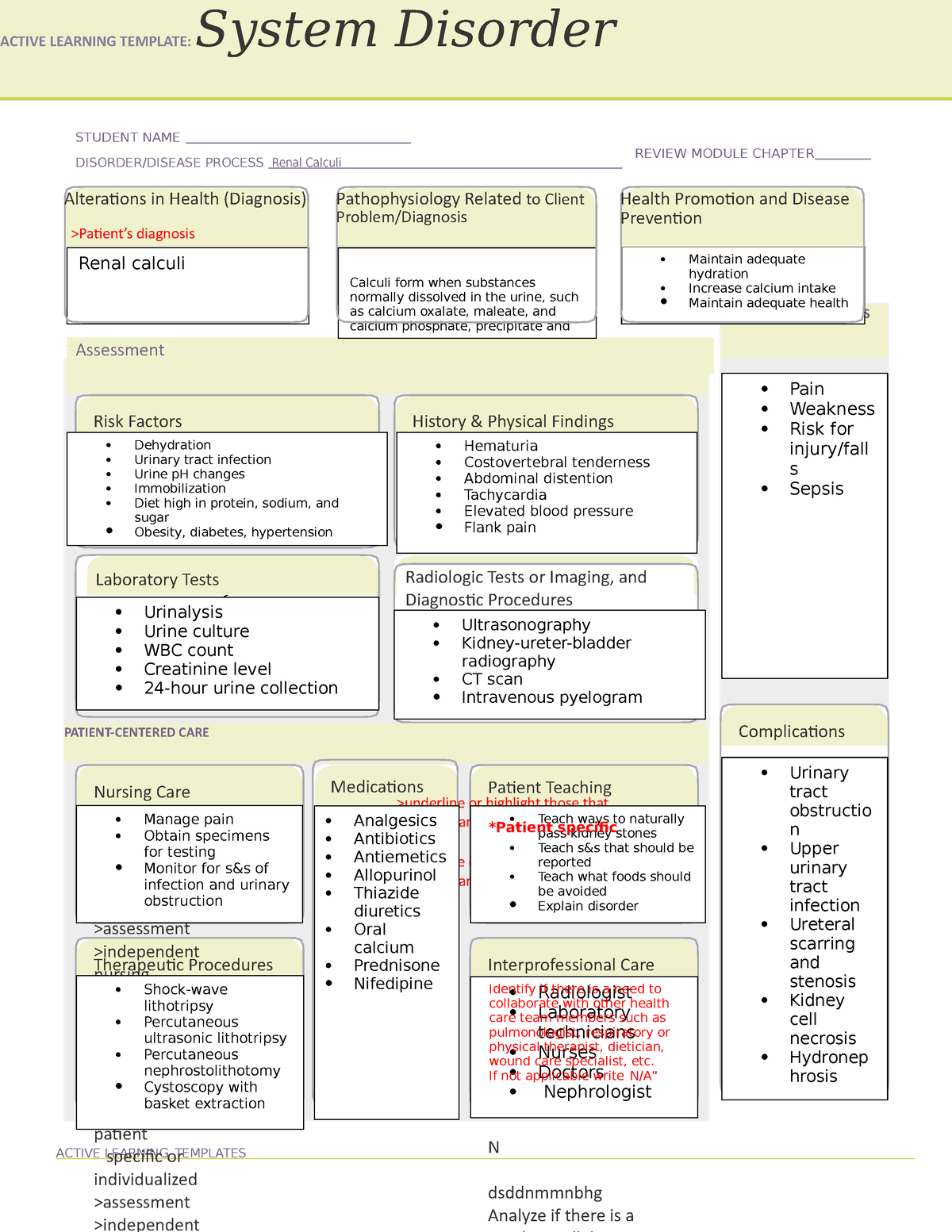
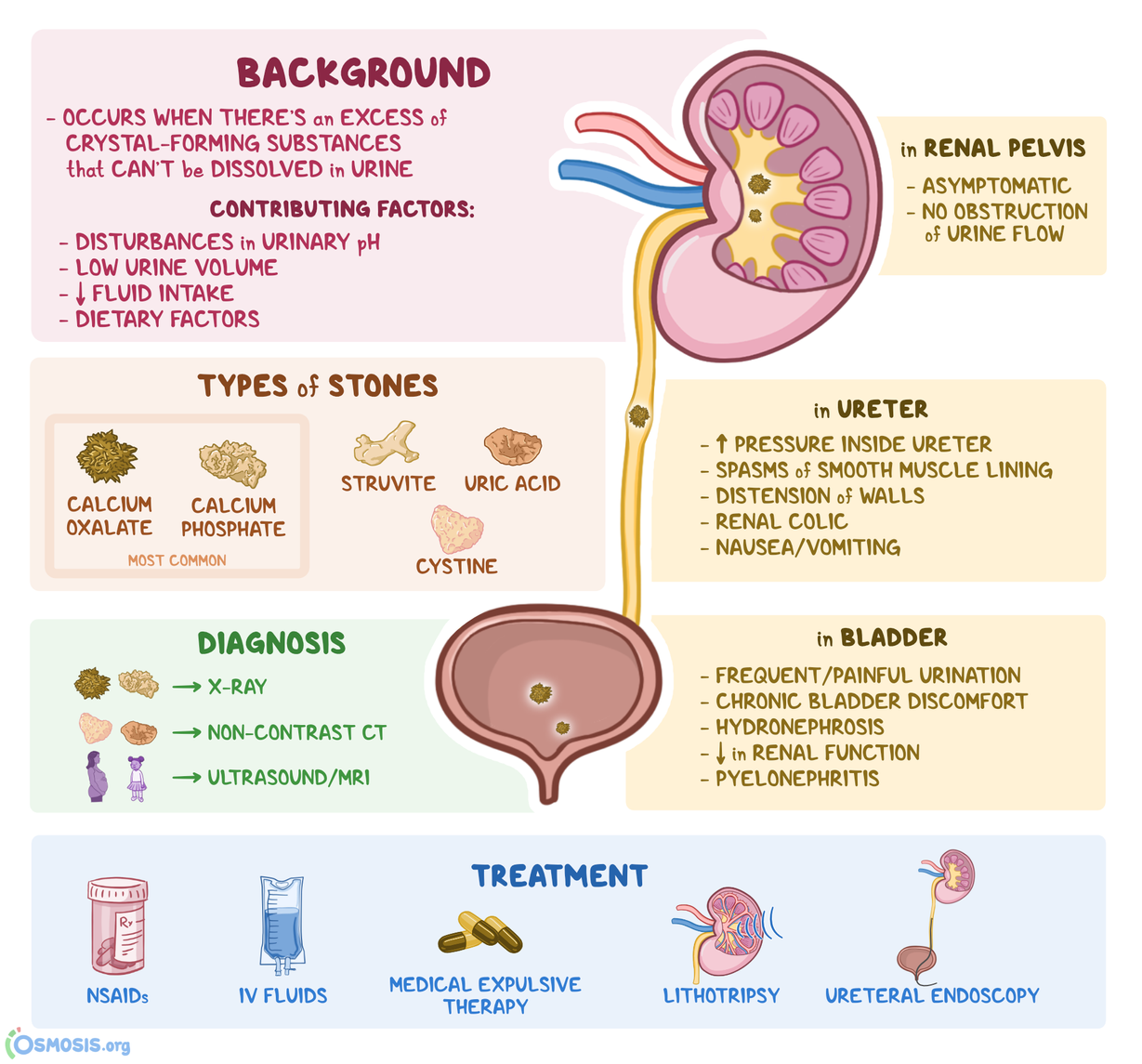
Kidney stones in Gabapentin; How the study uses the data? The study is based on gabapentin (the active ingredients of Gabapentin). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs) are considered. Dosage of drugs is not considered in the study. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Renal calculi have been noted in up to 64% of low-birth-weight infants receiving furosemide therapy. 1 Furthermore, the hypercalciuric effect of furosemide in infants is enhanced by a reduced glomerular filtration rate and immature hepatic function, which contribute to significantly prolonging the half-life of this drug. 2 The calculi isolated Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 However, patients on hemodialysis may be particularly vulnerable to complications from the use of gabapentin and pregabalin due to reduced clearance of these agents, which are dependent on renal excretion for their elimination. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Potentially, these medications could prevent kidney stones from causing such severe pain in humans. The problem with kidney stones. Prof. Michael Cima, the study’s senior author, notes, “We Understanding Kidney Stones. Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. They can cause severe pain when passing through the urinary tract. The most common types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate stones, uric acid stones, struvite stones, and cystine stones. Factors contributing to their Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. We conducted a population-based study to answer this question. For every 250 patients who star-ted gabapentin or pregabalin at a higher dose (>300 It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin treatment, especially when the drug is used off-label, is associated with increased risk for adverse events among patients on hemodialysis, even at low doses, investigators reported at Kidney stones is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 50-59 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Celebrex, and have Migraine. Modular program-based one-time assessment of incident use of eight antiepileptic drugs (lamotrigine, levetiracetam, topiramate, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, zonisamide, gabapentin, and phenytoin) and a diagnosis of kidney stones. Each product was analyzed by two unique incidence definitions and two unique kidney stone definitions. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease J Pain Res. 2017 Jan 27:10:275-278. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S130942. eCollection 2017. Authors We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. Several years ago, Cima and Brian Eisner, who co-directs the Kidney Stone Program at MGH and is also an author of the paper, began thinking about ways to improve the treatment of kidney stones. While some larger stones require surgery, the usual treatment plan is simply to wait for the stones to pass, which takes an average of 10 days.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |