Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
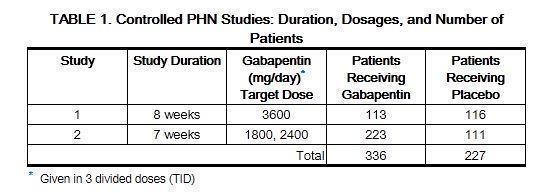 |  |
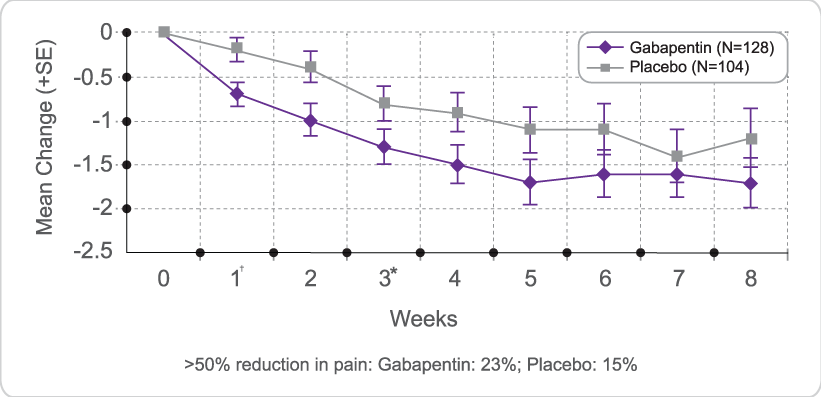
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Naproxen: Coadministration appears to increase the amount of gabapentin absorbed. Hydrocodone: Coadministration decreases hydrocodone. Cimetidine: Appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. Renal Dose : Dose in Renal Impairment GFR (mL/min) Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously e vident in the . In particular, although glomerular filtration rate is the metric used to guide dose adjustment, kidney Pharmacologic treatment of mild to moderate CKD (eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2) Pharmacologic treatment of advanced CKD (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) - Principles for dosing and administration - Drug selection - Specific pain syndromes. Nociceptive pain - Acetaminophen - Opioids; Neuropathic pain - Gabapentin and pregabalin - Tricyclic antidepressants Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended Gabapentin dosing ranges from 100 to 3600 mg daily and pregabalin dosing is 25 to 600 mg daily. 1,2 Gabapentin and pregabalin exhibit greater than 90% kidney elimination and adjustments to dose and frequency are recommended for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 1,2 For patients with a creatinine clearance (CrCl) below 60 mL/min, a The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study equation is now widely recognized as providing more accurate estimates of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) than the CG equation and has been reexpressed for use with standardized serum creatinine values, enabling consistent performance across clinical laboratories after standardization of serum creatinine assays, anticipated to be 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES ; CAPD :Probably dialysed. Dose as in GFR15 mL/min. HD :Dialysed. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each ; HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Given these risks, it is imperative for healthcare providers to adjust gabapentin dosage based on a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of kidney function. Generally, patients with mild to moderate CKD require lower doses or less frequent dosing of gabapentin compared to those with normal kidney function. Notwithstanding, most reports of toxicities were associated with concentrations higher than 15 mg/L for gabapentin and concentrations higher than 13 mg/L for pregabalin, whereas individuals with normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of ~5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The index, the total daily maintenance dose may be reduced either by decreasing the dose or by increasing the dosing interval, or sometimes by a combination of both. Dosing guidelines for varying degrees of renal impairment are stated accordingly. • Dose in renal replacement therapy: Details are given for dosing in automated peritoneal dialysis/ The half-life of gabapentin immediate-release formulation is 5–7 hours in patients with normal renal function and is prolonged up to 52 hours in patients with CrCl<30 mL/min. 26 The half-life of pregabalin is 16.7 hours in patients with CrCl 30–59 mL/min, 25 hours in patients with CrCl 15–29 mL/min, and 48.7 hours in patients with CrCl<15 In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |