Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
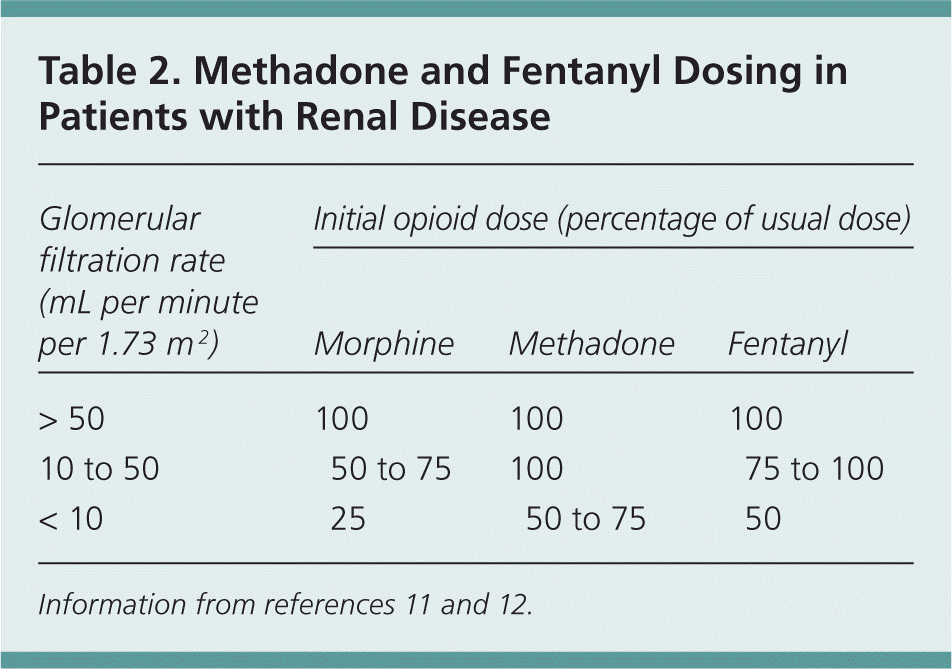
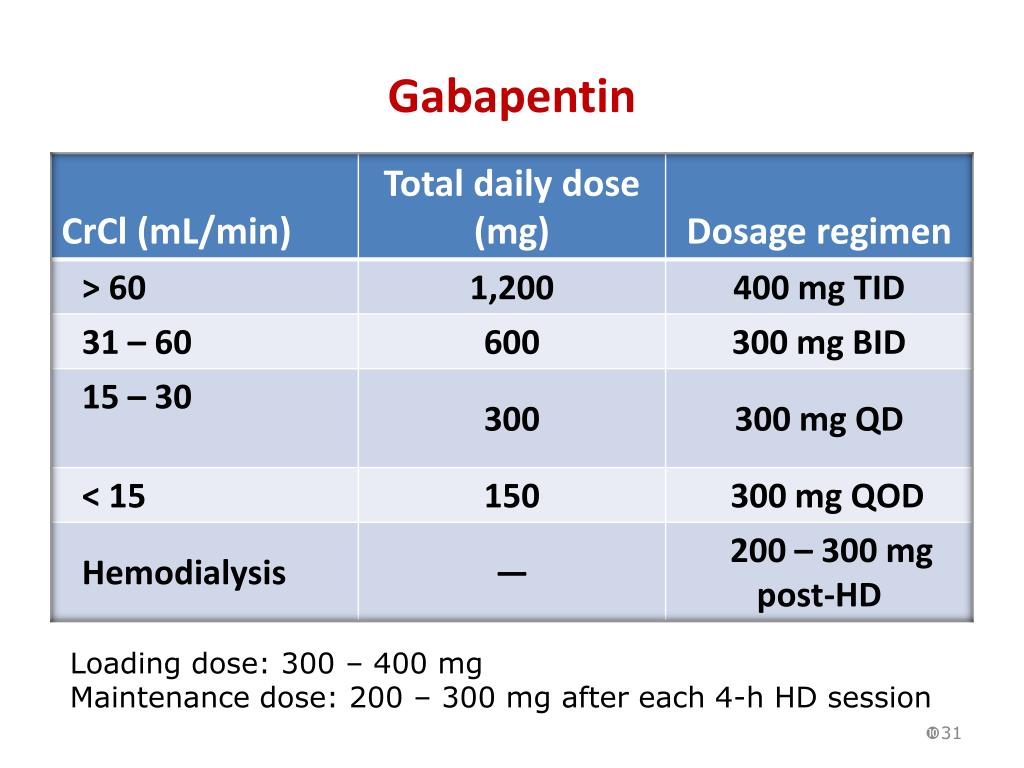
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS . 7.1 Other Antiepileptic Drugs 7.2 Opioids . 7.3 Maalox ® (aluminum hydroxide, magn esium hydroxide) 7.4 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions . 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS . 8.1 Pregnancy . 8.2 Lactation 8.4 Pediatric Use . 8.5 Geriatric Use 8.6 Renal Impairment . 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE . 9.1 Controlled Substance . 9.2 Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentin 340 Galantamine 341 Ganciclovir 342 Gemcitabine 343 Gemfibrozil 344 Vinorelbine 776. The Renal Drug Handbook . The Renal Drug Handbook. renal excretion must be considered when prescribing the parent drug in patients with renal impairment. • Dose in renal impairment: The level of renal function below which the dose of a drug must be reduced depends largely on the extent of renal metabolism and elimination, and on the drug’s toxicity. Uremic pruritus (UP) is a common discomfort of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease. Some studies suggest a neuropathic cause of UP. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, has shown promising results as an emerging drug to treat this condition. An Following concerns about abuse, gabapentin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Healthcare professionals should evaluate patients carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing gabapentin, and observe patients for signs of abuse and dependence. Panebianco M, Bresnahan R, Marson AG. Pregabalin add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2022;3:CD005612. 10.1002/14651858.CD005612.pub5 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 12. Panebianco M, Al-Bachari S, Hutton JL, Marson AG. Gabapentin add-on treatment for drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Impairment of kidney function alters the pharmacokinetics of many medications prescribed in both the acute and chronic settings. The Guidance for Industry: Pharmacokinetics in Patients With Impaired Renal Function—Study Design, Data Analysis, and Impact on Dosing and Labeling from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), published in 1998 and herein referred to as the FDA Guidance for The Renal Dosage is an educational tool designed by an experienced physician, Dr. Safwan Sayyal in consultation with nephrologists to ascertain the appropriate medication dosage based on a patient's kidney function. This will help to eliminate dosing errors in individuals with renal impairment. DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES ; CAPD :Probably dialysed. Dose as in GFR15 mL/min. HD :Dialysed. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each The Renal Drug Handbook Third EdiTion. The Renal Drug Handbook Third EdiTion Edited by Gabapentin 340 Galantamine 341 Ganciclovir 342 Gemcitabine 343 Gemfibrozil 344 Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. The Renal Drug Datbase is an easy-to-use digital tool for pharmacists, clinicians, and other healthcare professionals prescribing for patients with renal disease or those who receive renal replacement therapy. Reductions in renal function impair the renal excretion of many drugs and their metabolites, leading to accumulation and increased risks of toxicity and adverse events. In addition, altered drug absorption, protein binding and drug distribution can increase risk of toxicity, or impair the effectiveness of some medications. 1, 2 of the drug, its class, chemistry and pharmacokinetics in patients with normal renal function. • Sensitivity to some drugs is increased, even if elimination is unimpaired. • Many side-effects are particularly poorly tolerated by renally impaired patients. • Some drugs are ineffective when renal function is reduced. General Renal Dosing Guidelines and a specialized list of renal medication dosing - simple renal dosing guidelines - GlobalRPH Drug-food and drug-drink interactions: Food and drinks can change how medicines work or worsen side effects when they are combined. Examples include beverages like grapefruit juice and statins causing muscle pain, or alcohol and opioids leading to dangerously slowed breathing. Provides access to the latest drug monographs submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Please review the latest applicable package insert for additional information and possible updates. A local search option of this data can be found here . Renal Drug Handbook and Renal Drug Database. The Renal Drug Database (subscription required) is available online and as a handbook. Both contain: individual medicine monographs on how to prescribe, prepare and administer the medicine in various types of renal impairment; practice-based information for medicine dosing and administration in renal Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |