Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
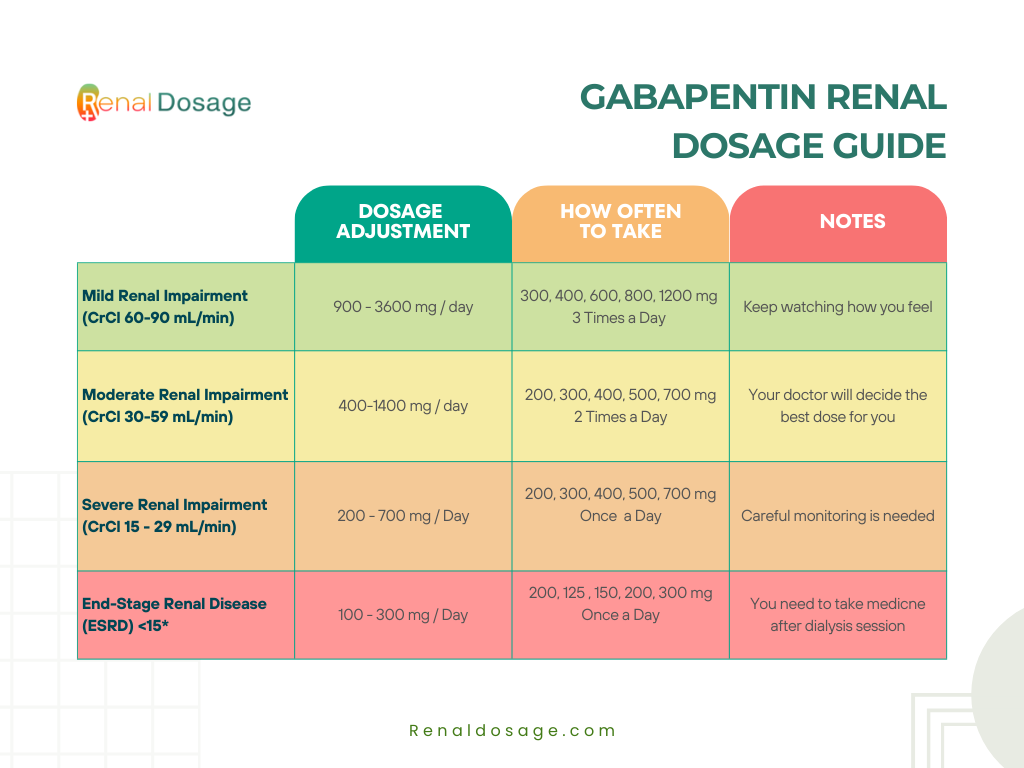
Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. We conducted a population-based study to answer this question. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Gabapentin is secreted in human milk following oral administration; effects on breastfed infant and on milk production are unknown; developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with mother's clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed infant from treatment or from underlying maternal Compared with the adverse effects of star fruit (Averrhoa carambola) in patients with impaired renal function, gabapentin and carambola both cause acute alteration of consciousness and other central nervous system disorientation such as dizziness, nausea and vomiting within hours to days. Haemodialysis is effective in both conditions. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. renal dosing [immediate-release form] CrCl 30-59: 200-700 mg bid; CrCl 16-29: 200-700 mg qd; CrCl 15: 100-300 mg qd; CrCl 15: decr. dose proportionately from CrCl 15 Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. The substitution of gabapentin with pregabalin in gabapentin responders resulted in improved pain relief and fewer adverse events. 35 However, gabapentin non-responders who had adverse effects with gabapentin also experienced adverse effects with pregabalin. 35. Central nervous system effects The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin treatment, especially when the drug is used off-label, is associated with increased risk for adverse events among patients on hemodialysis, even at low doses, investigators reported Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |