Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
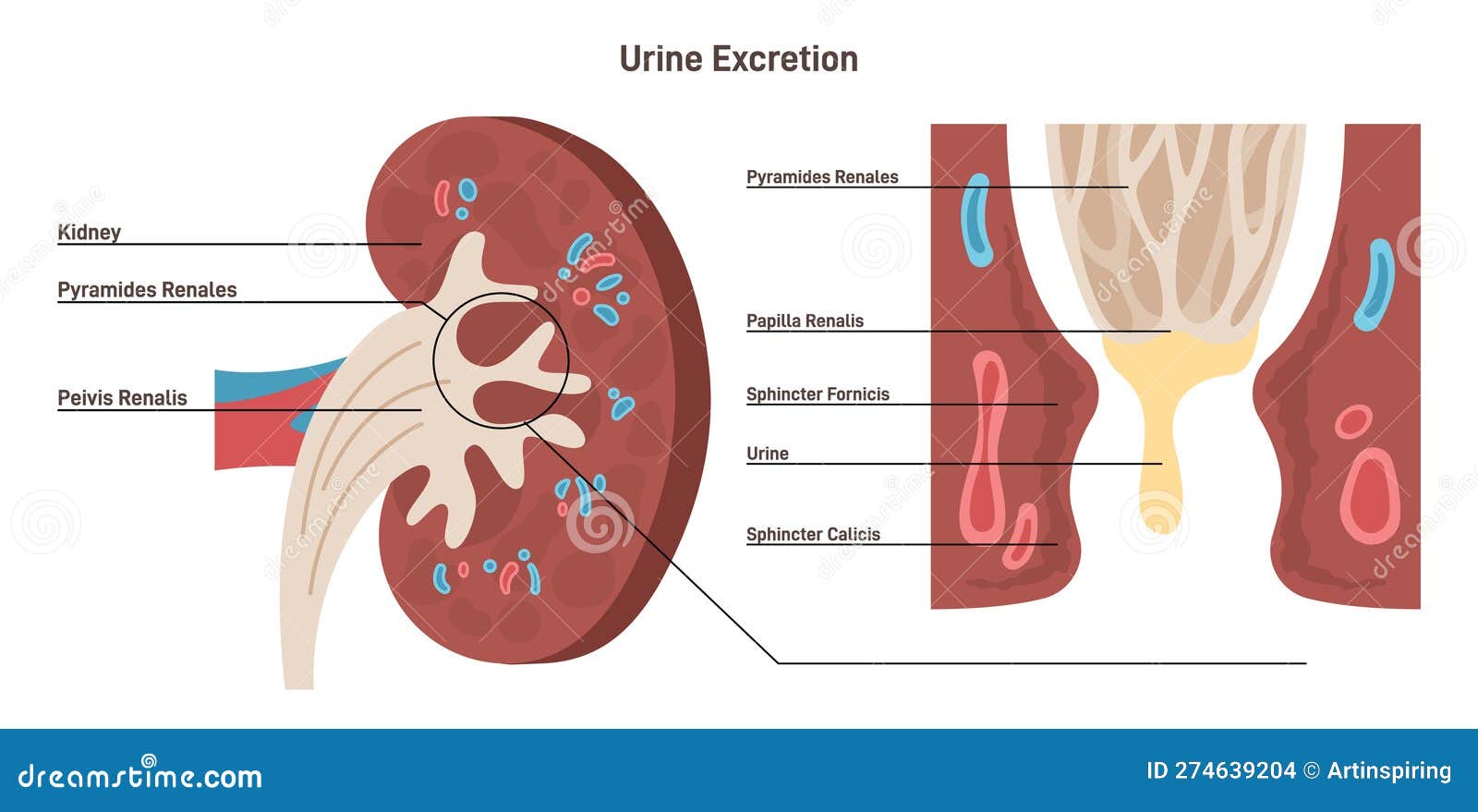
Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. The risk of respiratory depression should be assessed when initiating gabapentin in patients with respiratory comorbidities, neurological disease, renal impairment and in combination with other respiratory depressants such as opioids. Gabapentin (GBP) is a non-metabolized antiepileptic drug that is eliminated by renal excretion and displays saturable, dose dependent absorption. The recommended dosing schedule for GBP is t.i.d. At large daily doses, oral bioavailability (F) may be improved by giving the daily dose more frequently. Understanding the Risks of Gabapentin in Kidney Disease. Gabapentin’s reliance on renal excretion is the core issue for those with kidney problems. Normally, the kidneys filter waste products and medications from the blood, which are then excreted in urine. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Excretion: Renal; Mechanism of Action: GABA analogue, but has no effect on GABA binding, uptake or degradation; mech for analgesic and anticonvulsant activity unknown; See Also. Seizure; Anticonvulsants; Anticonvulsant levels and reloading; Neuropathy; References Gabapentin is cleared via renal excretion, and its elimination is proportional to creatinine clearance (CrCL); CrCL can, therefore, be used as a predictor of gabapentin renal clearance. Gabapentin produced from hydrolysis of gabapentin enacarbil is also eliminated via the renal clearance pathway. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥ 75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Elimination: Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is Excretion: Removed from your body by kidneys. If kidneys are slow, gabapentin stays longer, so dosing needs to be careful. 11. Patient Education What to Know: Take as Told: Always take gabapentin exactly as your doctor prescribed mg per day. Watch for Problems: If you feel very dizzy or confused, tell your doctor. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients greater than or equal to 75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Gabapentin enacarbil, a transported acyloxyalkylcarbamate prodrug of gabapentin, provides predictable and dose-proportional gabapentin exposure (AUC).Gabapentin is cleared via renal excretion, and its elimination is proportional to creatinine clearance (CrCL); CrCL can, therefore, be used as a predictor of gabapentin renal clearance. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥ 75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. However, other factors cannot be excluded. Metabolism and Renal Excretion. Gabapentin is not metabolized in humans and is excreted primarily as unchanged drug in the urine. Renal clearance is linearly related to creatinine clearance in both pediatric and adult populations. Therefore, dosage reductions based on declining renal function are recommended (Table 268-1).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |