Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
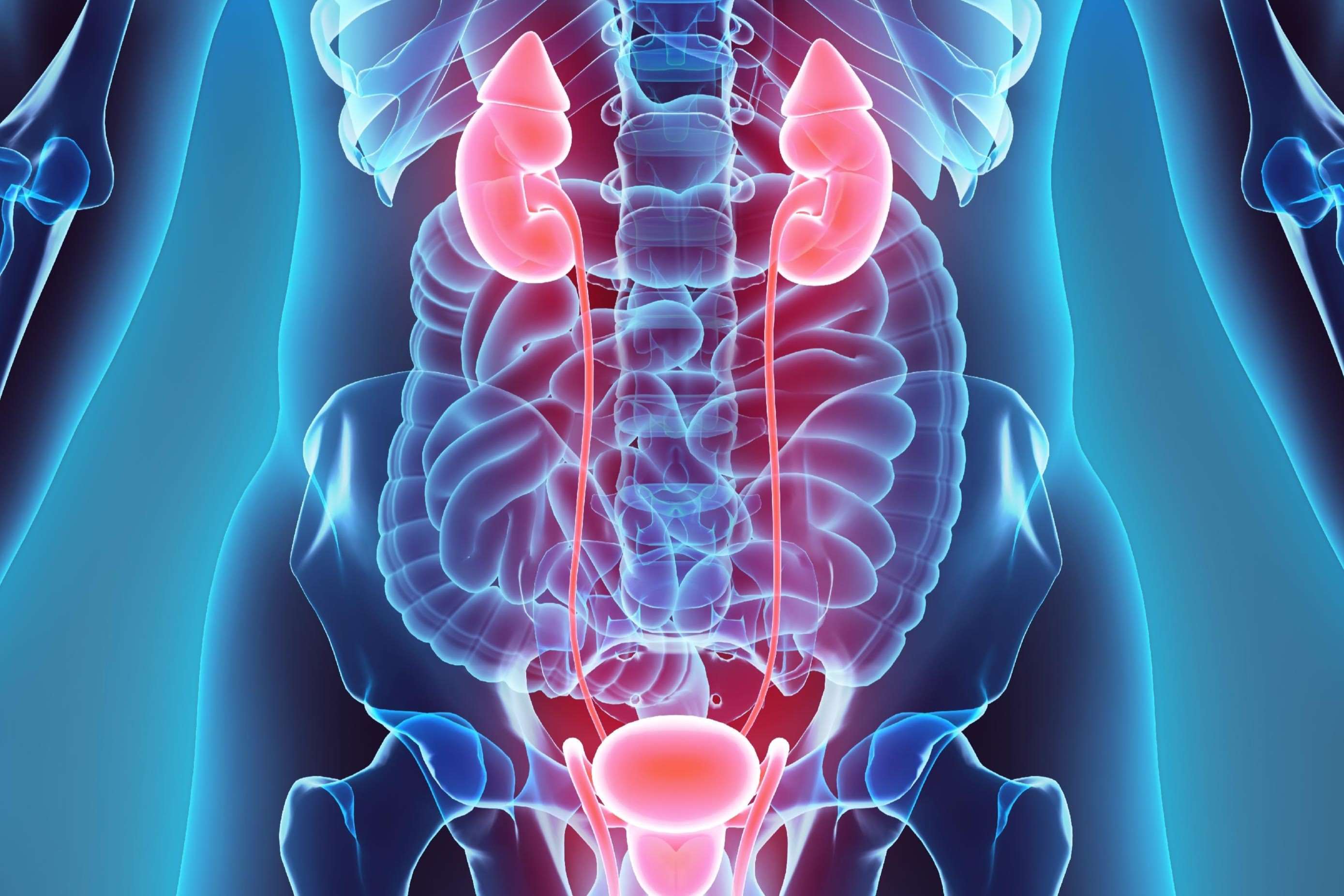
Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. If even mild renal impairment is considered likely on clinical grounds, renal function should be checked before prescribing any drug which requires dose modification. General guidance Drugs eliminated via the kidneys can accumulate during acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) and this can lead to further renal impairment or The Renal Drug Handbook Third EdiTion. The Renal Drug Handbook Third EdiTion Edited by Gabapentin 340 Galantamine 341 Ganciclovir 342 Gemcitabine 343 Gemfibrozil 344 In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Dosing recommendations for individual drugs can be found in Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Dosing Guidelines for Adults. 4 The guidelines are divided into three broad GFR categories (less than The Renal Drugs Handbook (4th ed) recommends giving dialysis patients an initial loading dose of Gabapentin 300-400mg. Glycopyrrolate (Robinul) Respiratory secretions (Terminal) No data D = 48.5% renal remainder unchanged in bile No data 200-400mcg q 2 - 4 hrs sci No data No data No data No Recommended for terminal secretions in renal Gabapentin 340 Galantamine 341 Ganciclovir 342 Gemcitabine 343 Gemfibrozil 344 Vinorelbine 776. The Renal Drug Handbook . The Renal Drug Handbook. Each medication is listed alphabetically in the book followed by 1–2 pages of renal-related information that is concisely organised into bolded categories. This streamlined design enhances the book's utility and allows for quick identification of clinically relevant information. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/ min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption.1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. renal excretion must be considered when prescribing the parent drug in patients with renal impairment. • Dose in renal impairment: The level of renal function below which the dose of a drug must be reduced depends largely on the extent of renal metabolism and elimination, and on the drug’s toxicity. **Patients with renal impairment are more sensitive to neurological side effects of these drugs and should be carefully monitored** Gabapentin. HD: 100mg after each dialysis session. If required the dose may be titrated in 100mg increments every 7 days to 300mg post HD, according to response and tolerability. PD and CrCl <30mL/min: Gabapentin Dosage Guide as per Renal Function The Renal Dosage is an educational tool designed by an experienced physician, Dr. Safwan Sayyal in consultation with nephrologists to ascertain the appropriate medication dosage based on a patient's kidney function. renal excretion must be considered when prescribing the parent drug in patients with renal impairment. • Dose in renal impairment: The level of renal function below which the dose of a drug must be reduced depends largely on the extent of renal metabolism and elimination, and on the drug’s toxicity. accordingly. Information on dosage adjustment can be obtained from the renal drug handbook or renal pharmacist. Patients with severe renal failure taking gabapentin or pregabalin have a higher incidence of neurological side effects and should be monitored regularly. Amitriptyline Each of the over 900 monographs provides guidance on Clinical Use, Dose in Normal Renal Function, Dose in Renal Impairment, Important Drug Interactions, Metabolism and Administration, with information validated under the governance of the UK Renal Pharmacy Group. The Renal Drug Handbook. 2nd ed. United Kingdom: Radcliffe Medical Press Ltd, 2004 Shann, Frank. Drug Doses. 14th ed. Intensive Care Unit. Royal Children’s Hospital, Parkville, Victoria 3052, Australia, 2008 McClintock, Alan et al. Notes on Injectable Drugs. 5th ed. New Zealand. New Zealand Healthcare Pharmacists’ Association, 2004 Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 200–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |