Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
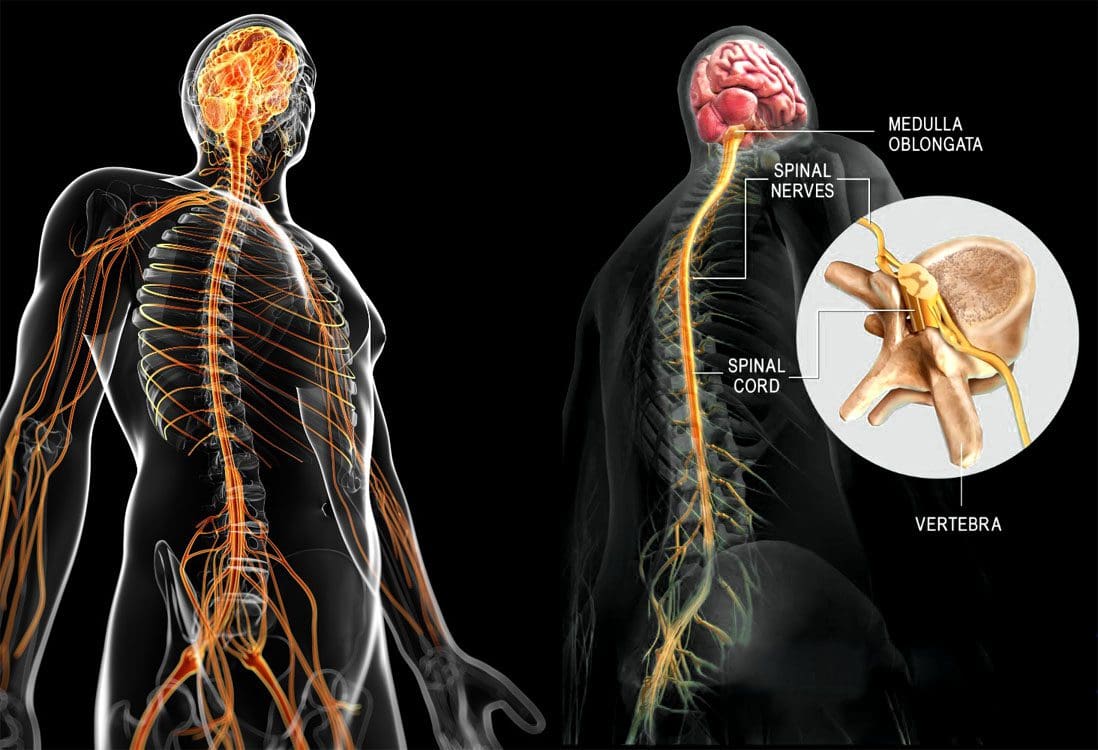
The pooled results of two trials of corticosteroids (mean difference in overall and leg pain −12.2, 95% confidence interval −20.9 to −3.4) and a single trial of the anticonvulsant gabapentin for chronic sciatica (mean difference in overall pain relief −26.6, −38.3 to −14.9) showed some benefits but only in the short term. The pharmacological management of back pain, including referred pain, was included in ‘Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s: assessment and management’ (NG59). People with sciatica typically have severe pain at onset and a slower and less complete recovery than people with back pain without sciatica. Drugs like gabapentin, duloxetine, nortriptyline and pregabalin can be useful for managing severe pain or pain that makes it hard to sleep. Corticosteroids are another treatment option. These potent anti-inflammatory drugs are delivered via an injection that places the medication just where it is needed. While opioids can provide initial sciatic pain relief, gabapentin is now favored for chronic use given the high risk of dependency and side effects with opioids. Gabapentin gives more consistent neuropathic pain relief compared to NSAIDs or steroids alone according to recent systematic reviews. Robertson K, Marshman LAG, Plummer D, Downs E. Effect of Gabapentin vs Pregabalin on Pain Intensity in Adults WIth Chronic Sciatica: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Oct 15. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3077. Sciatica pain originates from the compression, irritation, or damage of the sciatic nerve, resulting in aching in the lower back that extends through the leg. This condition is often accompanied by limitations in physical functionality and sensory symptoms like numbness or a prickling feeling. There is currently an absence of high-grade evidence regarding the treatment of chronic sciatica (CS). Whilst gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are both currently used to treat CS, equipoise exists regarding their individual use. In particular, no head-to-head study of GBP and PGB in CS exists. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Previous trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients with chronic low back pain or sciatica did not show a beneficial effect over placebo. 10,11 Our trial extends this finding by the inclusion How Gabapentin Helps with Sciatica Pain. Gabapentin’s ability to alleviate sciatica pain lies in its mechanism of action. By modulating the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception, Gabapentin can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain signals traveling from the sciatic nerve to the brain. In this review, no evidence has been found to support the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for sciatica pain or low back pain, since the effect is not superior to placebo. In addition, adverse effects of different considerations associated with their use have been reported. Gabapentin work for sciatic pain as follows: Gabapentin, when absorbed into the body, binds to the calcium channels in the nerve endings that transmit pain signals. It stops the pain signals that help a person feel the pain. Reducing the transmitting frequency decreases the intensity to which pain can be felt. How does gabapentin work to relieve sciatic nerve pain? In general, gabapentin calms down neurons (nerve cells) to relieve nerve pain. It does this by lowering the amounts of excitatory chemicals, like norepinephrine and glutamate, in the nervous system. FindingsThis randomized clinical trial of pregabalin vs gabapentin in 18 patients with chronic sciatica found that gabapentin was superior to pregabalin with greater reduction of leg pain intensity and fewer adverse events. Surgical diskectomy can be offered to patients with refractory sciatica, but there is only modest, short-term improvement in leg pain and disability scores. Epidural steroid injections may be Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and Then the disappointment of the shot only lasting 3 weeks was horrible. My MD then prescribed gabapentin 300mg 3x a day. It took a day or so to really kick in, but once it did WOW, the pain in my R buttocks and down the front of my right leg were almost gone. Gabapentin is widely prescribed for management of peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes. To our knowledge, however, these two case reports are the first to describe sciatica successfully controlled with gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |