Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
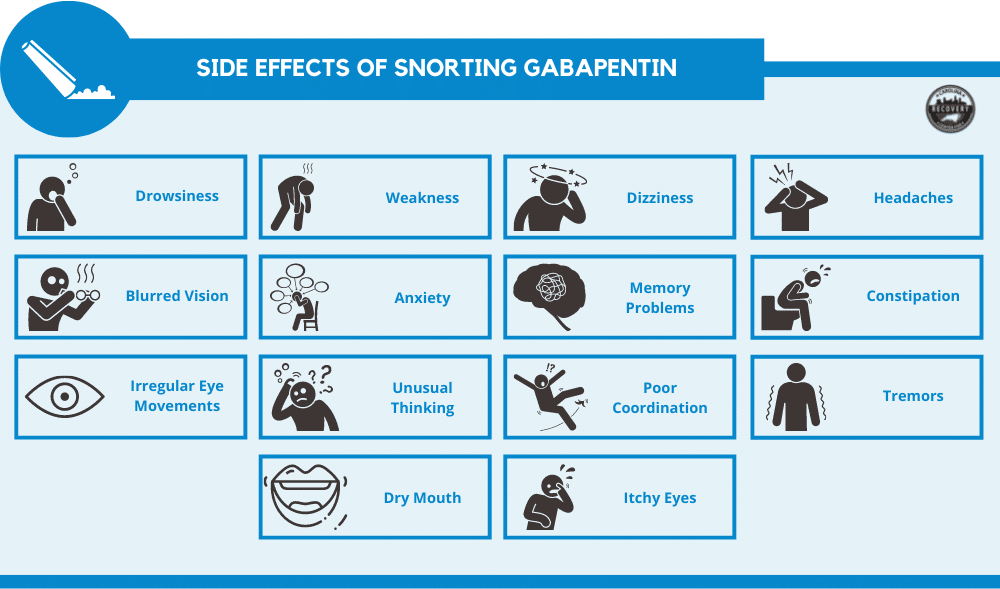
The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Gabapentin may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have: drowsiness, dizziness, weakness; problems with balance or muscle movement; or. increased seizures. Common gabapentin side effects may include: fever, chills, sore throat, body aches, tiredness; headache; swelling of your legs and feet; trouble speaking; Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Common gabapentin side-effects . What can I do if I experience this? Feeling sleepy, tired, unsteady or dizzy; blurred vision and other eyesight problems. Do not drive and do not use tools or machines. Headache. Drink plenty of water and ask your pharmacist to recommend a suitable painkiller. If the headaches continue, let your doctor know However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Neuropathic pain, which occurs as a result of damage to neural tissue, includes phantom limb pain, compression neuropathies, peripheral neuropathies (e.g. due to Diabetic complications, chronic excessive alcohol intake, HIV infection, chemotherapy, idiopathic neuropathy), trauma, central pain (e.g. pain following stroke, spinal cord injury, and syringomyelia), and postherpetic neuralgia Some drug monographs in the BNF include information that is common across the drug class. If a side-effect is associated with at least 60% of the drugs in a class then it will appear as a class side-effect for all drugs in the class, and the frequency of the side-effect will be the highest of all the drugs in that class. Side-effects, further information. The risk of side-effects is reduced by titrating slowly to the minimum effective dose (every 2–3 days). Consider using a lower starting dose in elderly patients. Overdose. Overdosage with amitriptyline is associated with a relatively high rate of fatality. View pregabalin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. These common side effects of gabapentin may happen in more than 1 in 100 people. They're usually mild and go away by themselves. There are things you can do to help cope with them: As your body gets used to gabapentin, these side effects should wear off. What are the serious side effects of gabapentin? If you have any of these symptoms, call your healthcare provider right away: Signs of an allergic reaction: If you have a skin rash, hives, itching or swollen, blistered or peeling skin with or without fever contact your healthcare provider. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. NHS medicines information on gabapentin – what it's used for, side effects, dosage, and who can take it. Sevelamer — absorption of gabapentin may be reduced if taken concurrently with sevelamer. Gabapentin should be taken at least 1 hour before, or 3 hours after, sevelamer if the reduction in gabapentin levels is clinically significant. Morphine — interaction of gabapentin with morphine sulphate increases risk of respiratory depression. Most people who take gabapentin do not get any side effects. But some people may feel sleepy, tired and dizzy. Common side effects are usually mild and go away by themselves. Side Effects Common side effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin can cause several common side effects, including dizziness, drowsiness, and fatigue. Other commonly reported side effects include headache, nausea, and blurred vision. These side effects are usually mild and tend to improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication. Category 3. Brivaracetam, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lacosamide, levetiracetam, pregabalin, tiagabine, vigabatrin.For these drugs, it is usually unnecessary to ensure that patients are maintained on a specific manufacturer’s product as therapeutic equivalence can be assumed, however, other factors are important when considering whether switching is appropriate. Use the interactions A to Z to look up a drug and see which other drugs it interacts with and the severity of these interactions. What are the common side effects of Gabapentin? The common side effects are drowsiness, unsteadiness, and giddiness. Some patients may tire more easily, or suffer from visual side-effects, weight gain or memory loss, nausea, and vomiting It is important to give this medicine a fair trial, and to give your body a chance to get used to the side Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |