Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
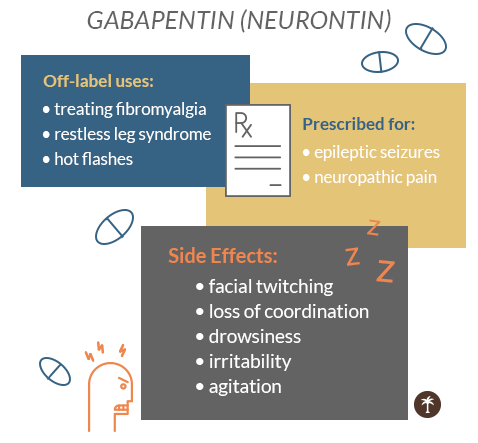
These symptoms can occur as early as 12 hours to 7 days after stopping the medication. Additionally, the long-term effects of high-dose Gabapentin treatments in clinical settings remain uncertain, with concerns about side effects such as dizziness and euphoria, which may be related to pain relief. Gabapentin Side Effects. Misuse of gabapentin can also occur, particularly in individuals seeking a euphoric effect or those with a history of substance abuse. As with euphoria achieved from gabapentin misuse, sedation/relaxation/calmness was experienced in combination with other substances (e.g., quetiapine, alcohol, cannabis, buprenorphine/naloxone) (29, 31, 32) or by taking gabapentin alone (28, 50), and over a range of dosages (e.g., 600–4800 mg). The “fun” effects reported by some gabapentin users are a dangerous side effect of misusing the medication, and a reason for caution. While some may experience euphoria or relaxation, these aren’t the intended outcomes of the medication and often come with risks. Side Effects of Gabapentin. Thirty-five percent of people on gabapentin had to stop taking it due to side effects, particularly dizziness and gastrointestinal problems. While gabapentin can be helpful in a number of conditions, it also causes side effects that can be debilitating for many people, and even deadly for some. Misuse of gabapentin can reportely cause the following effects in users: Decreased anxiety; Euphoria; A similar "high" to marijuana; Sedative reactions; At very high doses, gabapentin is reported to have dissociative and psychedelic effects in some users. One theory behind the euphoric effects of gabapentin is that it increases the release of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brain, which has a calming effect and can lead to feelings of relaxation and euphoria. Gabapentin misuse has been reported to produce anxiolytic effects and a euphoria similar to that of opioid misuse. 3 Gabapentin is known to cause respiratory depression, particularly when combined with other central nervous system depressants. 1 – 3 Long-term use can cause physiologic dependence and withdrawal syndrome on cessation Timing: Take gabapentin at the same times each day. You can take gabapentin with or without food. Try taking it with food if it makes you feel sick (nauseous). Swallow the capsules whole, with a glass of water: If you have problems swallowing the capsule, you can open it and mix the contents with apple sauce or orange juice, just before taking it. Individuals describe varying experiences with gabapentin abuse, including: euphoria, improved sociability, a marijuana-like ‘high’, relaxation, and sense of calm, although not all reports are positive (for example, ‘zombie-like’ effects). Gabapentin can produce feelings of relaxation, calmness and euphoria. Some users have reported that the high from snorted gabapentin can be similar to taking a stimulant. It can also enhance the euphoric effects of other drugs, like heroin and other opioids, and is likely to increase the risks when taken in this way. Individuals may abuse gabapentin for its ability to produce feelings of relaxation or calmness. They may take it at high doses (above 800 mg or more) for its ability to produce euphoria. Gabapentin is also used recreationally because it does not show up on most standard drug screens. Euphoric mood is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 40-49 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Amisulpride, and have Schizophrenia. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. The effects of gabapentin, as described by participants, were varied. Participants’ descriptions were roughly evenly split among the following themes: feelings of intoxication, sedative-type effects, euphoria reminiscent of opioids, pain relief, and unpleasurable or no noticeable effects. The majority of adverse events pertained to the nervous system (7 effects) or psychiatric (3 effects) disorders. There were more adverse effects reported with pregabalin (36 effects) than with gabapentin (22 effects). Six pregabalin studies reported euphoria as a side effect, while no studies reported euphoria with gabapentin. There were more adverse effects reported with pregabalin (36 effects) than with gabapentin (22 effects). Six pregabalin studies reported euphoria as a side effect, while no studies reported euphoria with gabapentin. This was the only side effect that may correlate with addictive potential. If you just down a bunch of pills, chances are you won't be feeling much of anything, besides a very subtle high. However, if you dose correctly, you'll be feeling fucking amazing for a long duration, and be 100% functional. It becomes a very nice opiate without the side effects and addiction. HOW TO PROPERLY USE GABAPENTIN: Abnormal behaviour consisted of elevated mood, euphoria, and increased energy in both patients, and pressure of speech and decreased need for sleep in one of them. These symptoms were transient and fully reversible. There were more adverse effects reported with pregabalin (36 effects) than with gabapentin (22 effects). Six pregabalin studies reported euphoria as a side effect, while no studies reported euphoria with gabapentin. This was the only side effect that may correlate with addictive potential.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |