Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
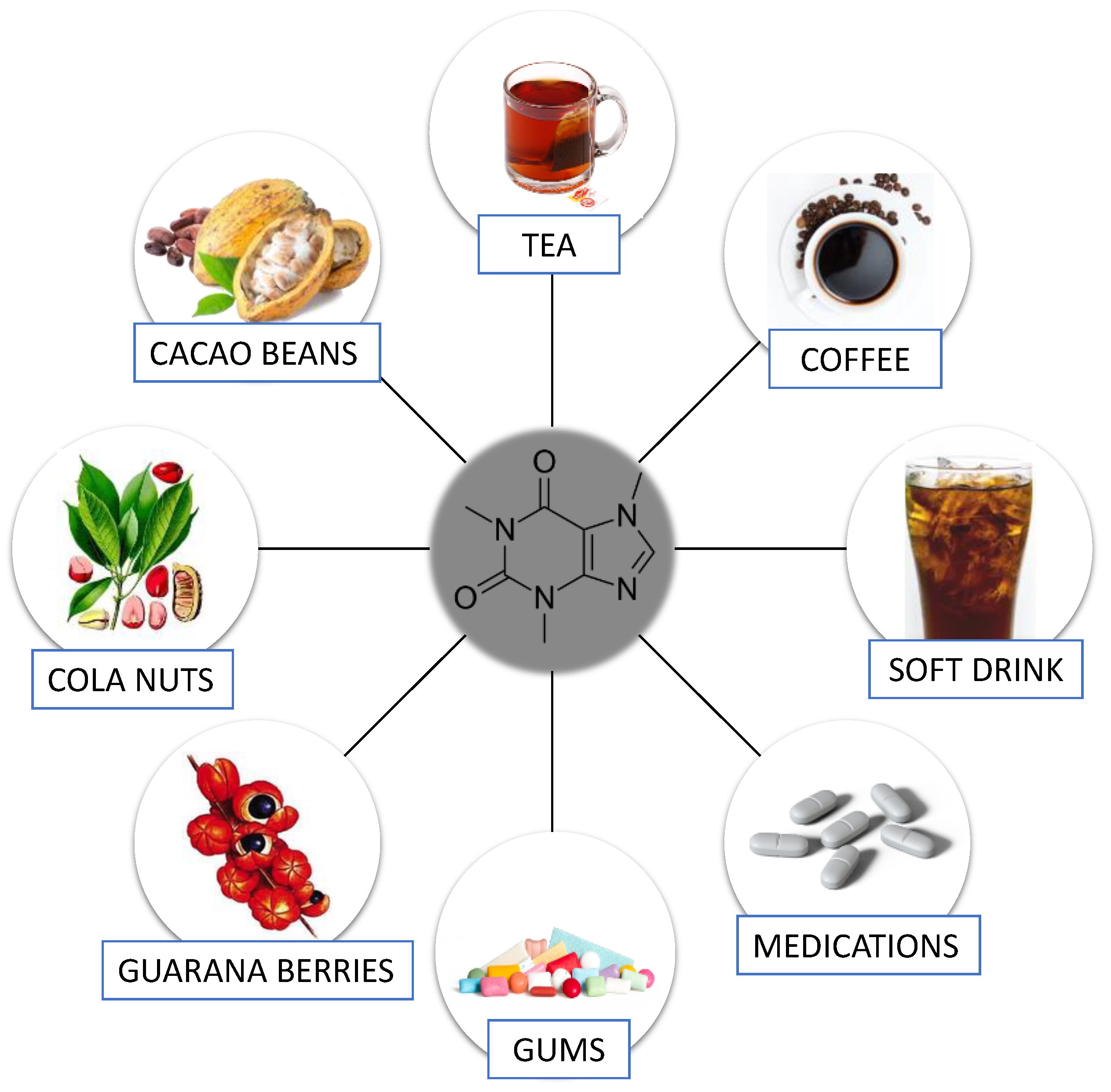
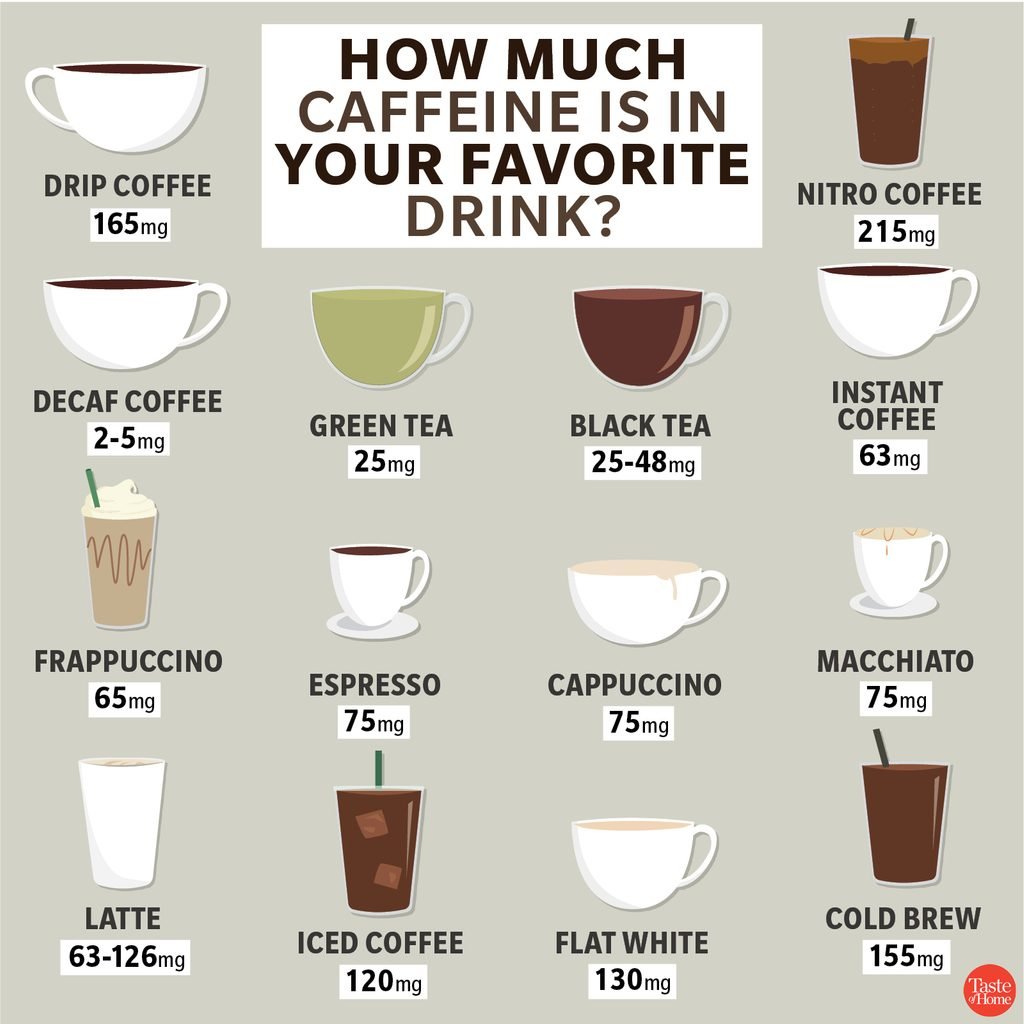
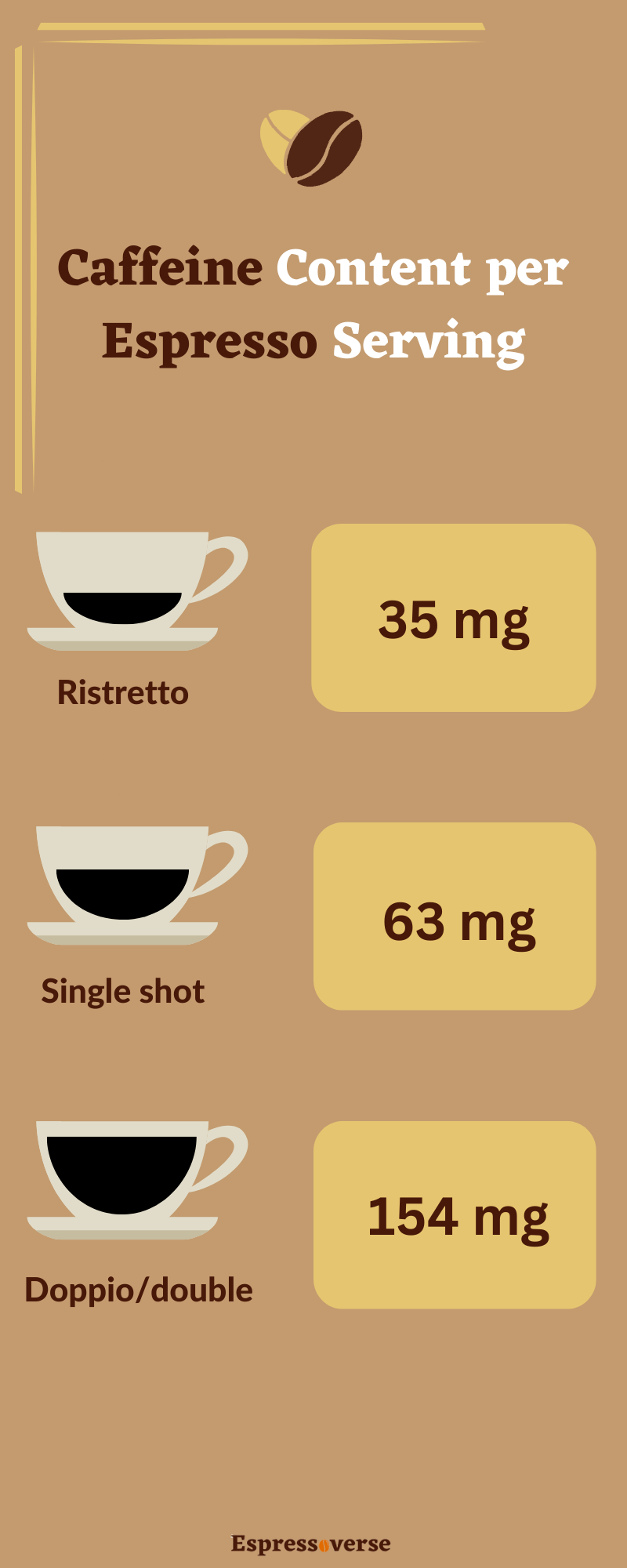
You may experience side effects from the medication, including drowsiness, tiredness, weakness, dizziness or headaches. Caffeine may have the opposite effect because it stimulates the central nervous system, increasing energy and improving concentration. While not generally considered dangerous, caffeine can potentially interfere with gabapentin’s anticonvulsant effects, making it less effective for seizure control. It’s advisable to limit or avoid caffeine, especially if you are taking gabapentin for seizures. Caffeine is a naturally occurring central nervous system stimulant belonging to the methylxanthine class and is widely recognized as the most utilized psychoactive stimulant worldwide. Although this drug is most commonly sourced from coffee beans, it can also naturally occur in certain types of tea and cacao beans and as an additive to soda and energy drinks. Caffeine consumption primarily Some people consider coffee to be a health drink, but like most foods, over indulging can cause side effects. For example, too much caffeine can give you headaches. This is primarily linked to Caffeine is a stimulant and the most commonly used drug in the world. Benefits can include increased alertness, energy, and concentration. However, it can also lead to insomnia and headaches. Caffeine can have negative side effects in some people, including anxiety, restlessness, and trouble sleeping. Recommended dosages. Both the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the European Caffeine is provided under a freeware license on Windows from Windows boot software with no restrictions on usage. Download and installation of this PC software is free and 1.98 is the latest version last time we checked. What version of Windows can Caffeine run on? Caffeine can be used on a computer running Windows 11 or Windows 10. Caffeine: Caffeine may interact with antiepileptic drugs like gabapentin, potentially reducing their anticonvulsant effects. It’s best to avoid excessive caffeine intake while taking gabapentin to ensure its effectiveness in managing conditions like seizures. Caffeine: While not a contraindication in the strictest sense, caffeine can interfere with gabapentin’s mechanism. This is especially true when taking it for seizure control, as caffeine can potentially reduce the anticonvulsant effects of gabapentin. This medication, used to open up bronchial airways, tends to have some caffeine-like effects. So taking it with caffeine might increase the adverse effects of caffeine, such as nausea and heart palpitations. Echinacea. This herbal supplement, which is sometimes used to prevent colds or other infections, may increase the concentration of Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, but it does come with some potential side effects. These can include dizziness, drowsiness, and coordination problems. As caffeine can also cause similar side effects, combining gabapentin and coffee may increase the likelihood and severity of these issues. Caffeine Interferes – Caffeine can reduce gabapentin’s effectiveness and benefits. Increased Side Effects – Mixing caffeine may lead to anxiety, dizziness, and nausea. Monitor Intake – Patients should closely monitor caffeine consumption with gabapentin. Communication is Key – Discuss dietary habits with healthcare providers for Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Consuming caffeine regularly, such as drinking a cup of coffee every day, can promote caffeine tolerance in some people so that the side effects from caffeine may decrease over time. Although we tend to associate caffeine most often with coffee or tea, the research below focuses mainly on the health effects of caffeine itself. High caffeine consumption in energy drinks (at least one liter or 320 mg of caffeine) was associated with short-term cardiovascular side effects including hypertension, prolonged QT interval, and heart palpitations. These cardiovascular side effects were not seen with smaller amounts of caffeine consumption in energy drinks (less than 200 mg). Caffeine is in milligrams (mg). Keep in mind that the caffeine content of a cup of coffee or tea can vary. Factors such as how the product is grown and brewing time affect the caffeine level. Also, caffeine is in many products and foods you might not expect, such as medicines and processed foods. So you might be getting more than you think. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Gabapentin can interfere with the way one’s body breaks down caffeine. This results in significantly increased caffeine levels in the system, which can lead to serious issues such as an increased heart rate, insomnia, and even headaches and vomiting. Drug interactions are reported among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) and Caffeine (caffeine). Common drug interactions include agitation among females and completed suicide among males. The phase IV clinical study analyzes what interactions people have when they take Gabapentin and Caffeine, and groups them by gender, age and more. Some of the main substances that interact with gabapentin are morphine, caffeine, losartan, ethacrynic acid, phenytoin, mefloquine and magnesium oxide. Some of the side effects caused by gabapentin are teratogenicity, hypoventilation, respiratory failure and myopathy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |