Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/drinkbeforebed-e6800d7f121e438ab8f0299a4e26afb5.jpg) |
/GettyImages-901219888-46d9e0b1e7f44006b5470df27123a0fd.jpg) |  |
 | /apnea-treatment-171576486-5c01c810c9e77c0001dc4e66.jpg) |
 |  |
 | /Stocksy_txpaf520c291ri100_Medium_1398059-59fea1cdec2f640037d55a5d.jpg) |
/sleep-apnea-syndrome-585990356-594bb1315f9b58f0fcd0cc3c.jpg) |
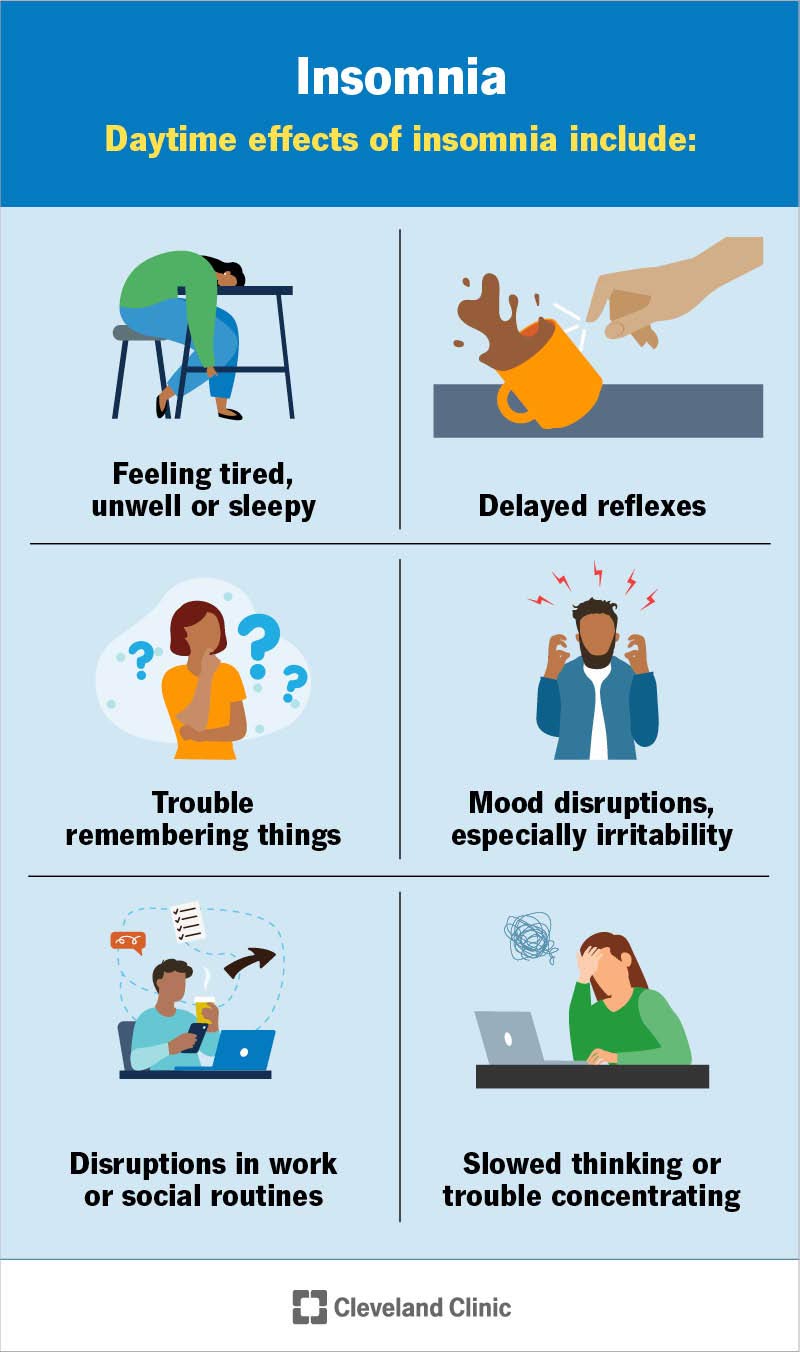
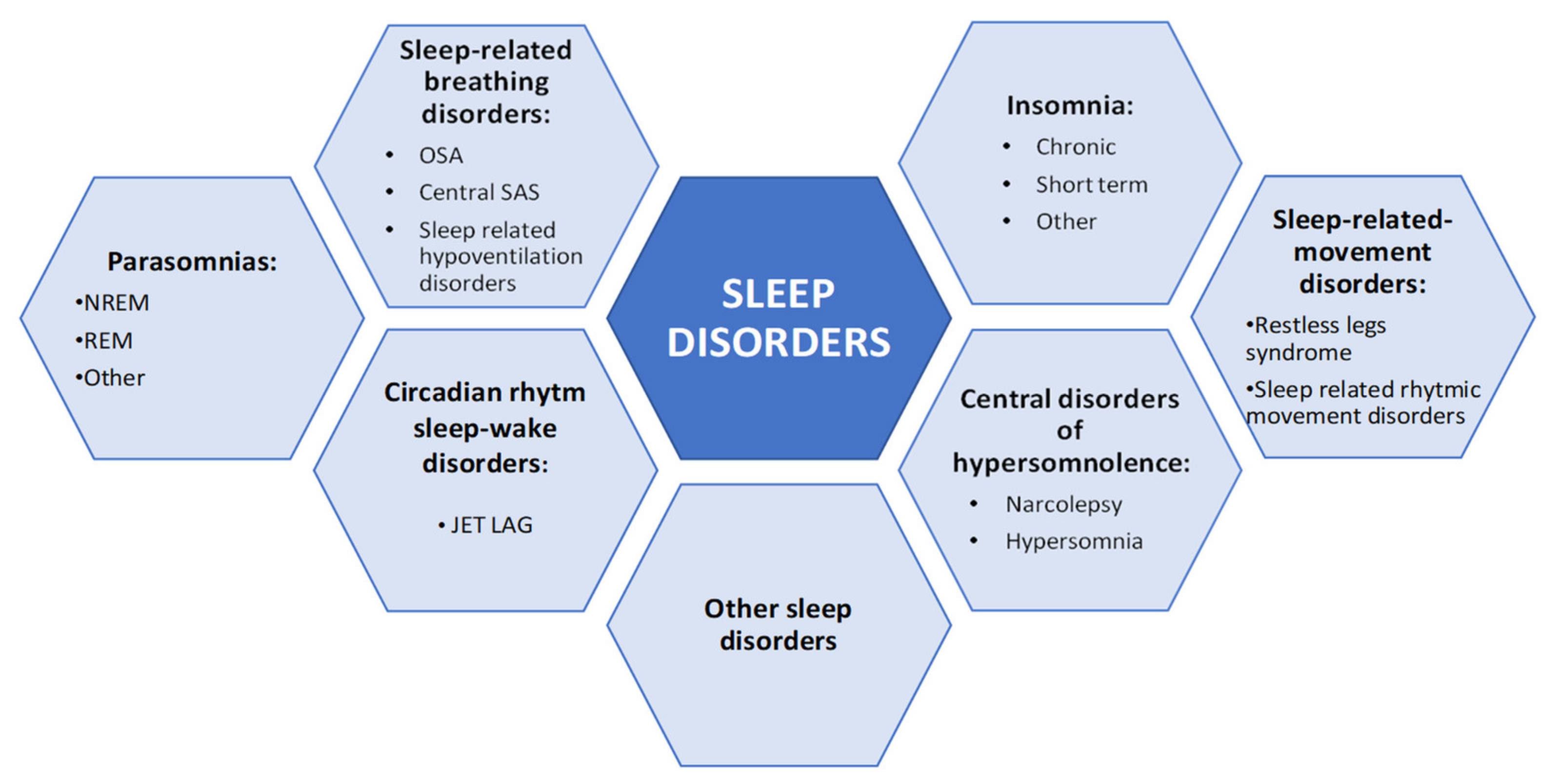
We hypothesized that gabapentinoids might be associated with sleep apnea syndrome. A recent pilot study reported a higher apnea–hypopnea index with gabapentin, supporting our hypothesis [5]. Like baclofen, some studies have shown that gabapentin might be of interest in alcohol dependence management [2]. In this context, baclofen is linked to sleep apnea syndrome [3, 4], aggravating sleep-disordered breathing by depressing central ventilatory drive and/or increasing upper airway obstruction. We investigated the acute effects of gabapentin (GABA) on sleep breathing in older men without sleep apnea. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled cross-over pilot study using a bedtime dose of gabapentin 300 mg was conducted in eight non-obese older men. Polysomnography measured the effects of the intervention. While sleep medications may seem like an optimal sleep solution, the long-term effects can harm your sleep health and exasperate sleep apnea symptoms. Locations Call Today (615) 893-4896 | Schedule An Appointment Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a potentially serious and under-recognized adverse reaction of opioids, baclofen, valproic acid, sodium oxybate, gabapentin, and ticagrelor. CSA may be associated with impaired sleep quality, insomnia, nonrestorative sleep, impaired quality of life, fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and increased morbidity and mortality Medication-induced central sleep apnea (CSA) is one of the eight categories of causes of CSA but in the absence of awareness and careful history may be misclassified as primary CSA. While opioids are a well-known cause of respiratory depression and CSA, non-opioid medications including sodium oxybat The other trial showed gabapentin alone increased pauses in breathing during sleep. The three observational studies at one academic medical center showed a relationship between gabapentinoids given before surgery and respiratory depression occurring after different kinds of surgeries. This study is the first to systematically assess the clinical value of gabapentin for the treatment of sleep disorders. We found that regardless the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin displayed stable treatment efficacy for sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness. Two patients (2%, 95% CI 0-7%) had sleep-related hypoxemia in the absence of sleep apnea or hypoxemia during wakefulness. CONCLUSIONS Patients on chronic opiate therapy for chronic pain have an extremely high prevalence of sleep apnea and nocturnal hypoxemia. Hypoxemia can occur during quiet wakefulness in patients on chronic opioid medications Understanding how gabapentin may affect sleep patterns is crucial in assessing its impact on sleep apnea symptoms and overall sleep quality. Gabapentin has been shown to influence sleep architecture in several ways. Gabapentin: Understanding the Side Effects and Risks Are you struggling with sleep apnea and wondering if gabapentin could be the cause? You’re not alone. Many people have reported experiencing sleep apnea while taking gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed for various conditions including seizures, nerve pain, and mood disorders. We investigated the acute effects of gabapentin (GABA) on sleep breathing in older men without sleep apnea. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled cross-over pilot study using a bedtime dose of gabapentin 300 mg was conducted in eight non-obese older men. Some studies have found that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical restoration and cognitive function. Additionally, it may reduce sleep fragmentation, leading to fewer nighttime awakenings and improved sleep continuity. J Clin Sleep Med 10: 1101-1109. Moore RA, Philip JW, Sheena D, Andrew SC (2014) Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD007938. Marvisi M, Balzarini L, Mancini C, Ramponi S, Marvisi C (2015) Fibromyalgia is frequent in obstructive sleep apnea and responds to CPAP therapy. gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR) When used with CNS depressants or in patients with lung problems . in breathing during sleep. The three Central sleep apnea (CSA) in adults encompasses a group of sleep-related breathing disorders, categorized into six distinct entities in the third edition of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3) []: primary CSA, CSA with Cheyne-Stokes Breathing (CSB), CSA due to a medical disorder without CSB, CSA due to high altitude periodic breathing, treatment-emergent CSA, and CSA
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/drinkbeforebed-e6800d7f121e438ab8f0299a4e26afb5.jpg) |
/GettyImages-901219888-46d9e0b1e7f44006b5470df27123a0fd.jpg) |  |
 | /apnea-treatment-171576486-5c01c810c9e77c0001dc4e66.jpg) |
 |  |
 | /Stocksy_txpaf520c291ri100_Medium_1398059-59fea1cdec2f640037d55a5d.jpg) |
/sleep-apnea-syndrome-585990356-594bb1315f9b58f0fcd0cc3c.jpg) |