Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
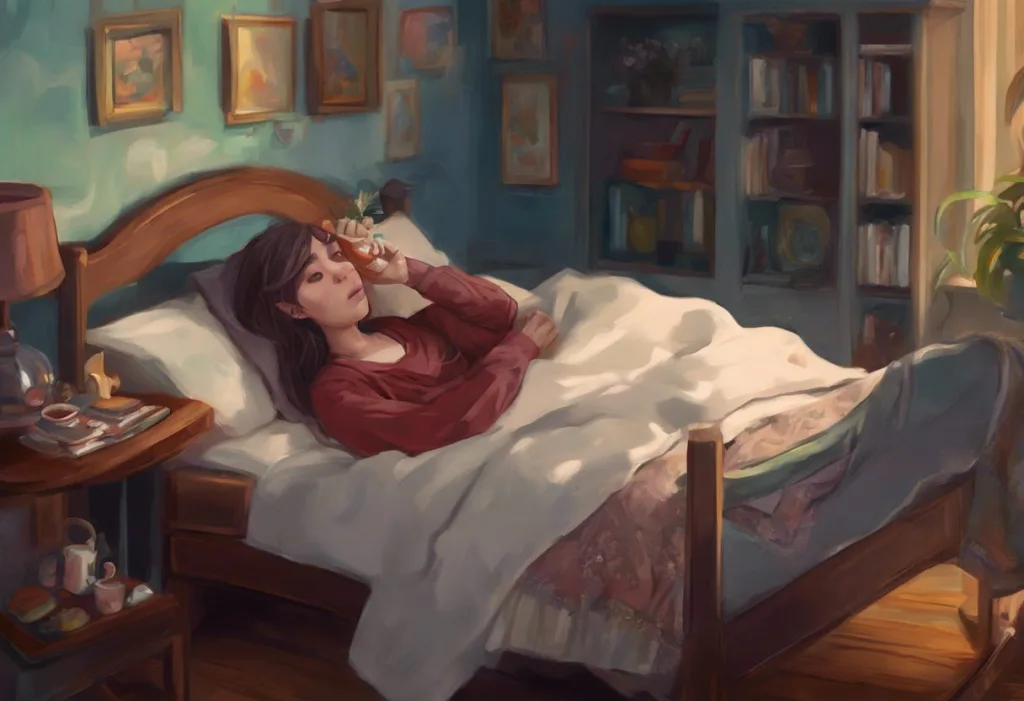
Gabapentin for Sleep: Optimal Timing and Usage Guidelines can provide valuable insights into maximizing the sleep-promoting effects of gabapentin while minimizing potential interactions with other sleep medications. Gabapentin For Sleep. Gabapentin, also referred to as Neurontin, is a medication that’s often prescribed by doctors for quite a few different purposes. Primarily, it’s known as an anticonvulsant, a medication that helps prevent or stop seizures resulting from epilepsy. Taking gabapentin with other drugs that make you drowsy or slow your breathing can cause dangerous side effects or death. Ask your doctor before taking opioid medication, a sleeping pill, a muscle relaxer, or medicine for anxiety or seizures. Tell your doctor about all your current medicines. Many drugs can affect gabapentin, especially: naproxen; A range of medications and substances are used to treat insomnia in adults, spanning the following categories: Medications with regulatory approval for treatment of insomnia Off-label prescription medications prescribed for insomnia Over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids (eg, diphenhydramine and doxylamine, alone or in "PM" formulated medications) Combining an opioid with sleeping pills can be dangerous. The combination increases the sedative effects of the pills and can lead to slowed breathing or unresponsiveness. It can even cause you to stop breathing. Take sleeping pills strictly as prescribed by your health care provider. Some prescription sleeping pills are for short-term use only. "I've had chronic insomnia for 20 years. I can't fall asleep and then when I do, I wake up after a couple of hours and can't fall back to sleep for several hours. I still take trazodone to get to sleep and use the Gabapentin to stay asleep. I take 100 mg of the trazodone and 1500 mg of the Gabapentin. I sleep great and feel great the next day. sedatives or sleeping pills; tramadol. Alcohol may worsen the side effects of gabapentin such as drowsiness and dizziness. Note that this list is not all-inclusive and includes only common medications that may interact with gabapentin. You should refer to the prescribing information for gabapentin for a complete list of interactions. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that’s FDA approved to treat a certain type of seizure and nerve pain from shingles. It’s often used “off-label” for a wide range of conditions, including anxiety, hot flashes, and sleep. Some research shows gabapentin may be effective for sleep. For those who have difficulty staying asleep, low-dose doxepin and the z-drugs should be considered. Benzodiazepines are not recommended because of their high abuse potential Insomnia Medications (Sleeping Pills) Other names: Difficulty sleeping; Dyssomnia; 141 reviews for gabapentin to treat Insomnia: Rx: C N: X: Generic name: The short answer is yes, you can take a sleep aid with gabapentin. However, it is important to talk to your doctor or pharmacist before doing so. This is because there are some potential risks and side effects associated with taking these two medications together. Sleep aids, such as Ambien and Lunesta, can cause drows Gabapentin, a medication originally developed to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain, has recently captured the attention of sleep researchers and clinicians alike. In two separate large population studies, both benzodiazepines (a category that includes medications for anxiety and sleeping pills) and anticholinergics (a group that encompasses medications for allergies and colds, depression, high blood pressure, and incontinence) were associated with an increased risk of dementia in people who used them for Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Gabapentin and sleep. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. This is why it’s best to avoid combining tramadol with sedatives or other sedative-like medications. Examples include: Gabapentin (Neurontin) Benzodiazepines like alprazolam (Xanax) Sleep medications like zolpidem (Ambien, Edluar, and ZolpiMist) Barbiturates like phenobarbital. Muscle relaxers like tizanidine and methocarbamol
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |