Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
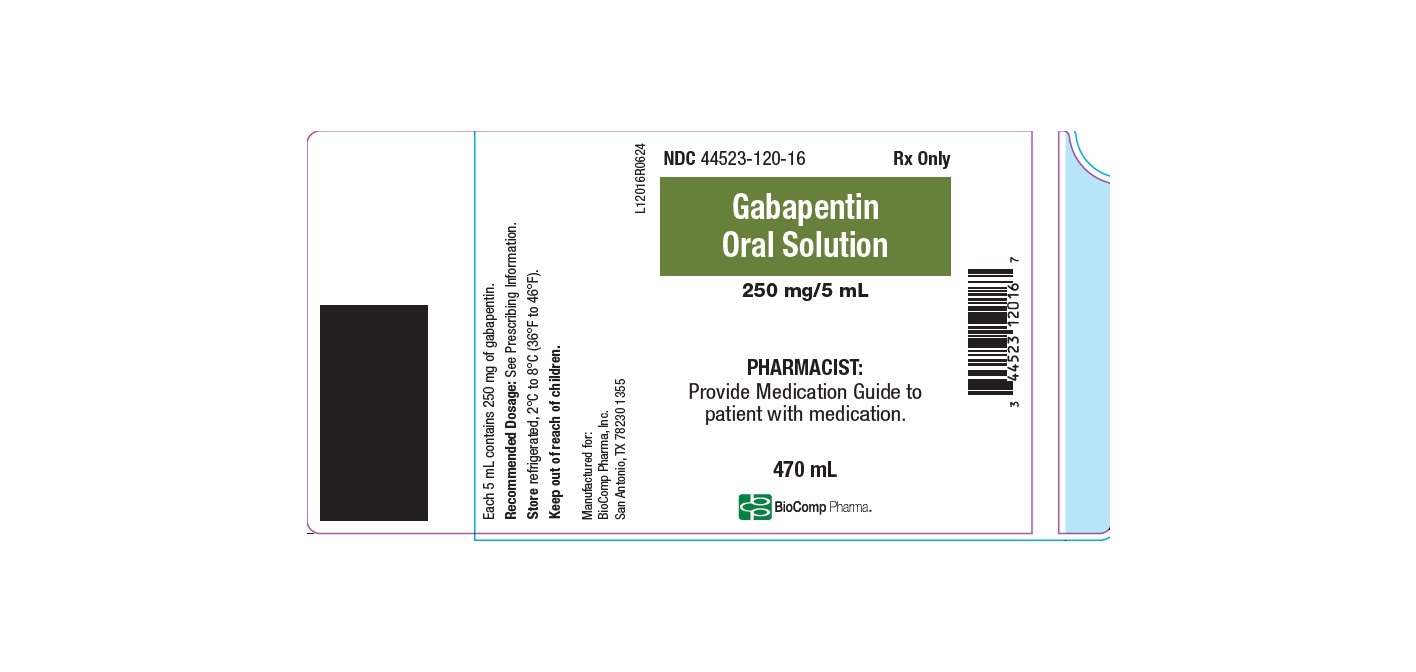
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GABAPENTIN ORAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GABAPENTIN ORAL SOLUTION. GABAPENTIN oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Gabapentin oral solution is indicated for: Postherpetic neuralgia in adults (1) Neurontin was evaluated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies; N=563 patients in the intent-to-treat (ITT) Gabapentin is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with and without secondary generalization in adults and children aged 6 years and above (see section 5.1). Gabapentin readily enters the brain and prevents seizures in a number of animal models of epilepsy. Gabapentin does not possess affinity for either GABAA or GABAB receptor nor does it alter the metabolism of GABA. It does not bind to other neurotransmitter receptors of the brain and does not interact with sodium channels. (gabapentin) Oral Solution DESCRIPTION Neurontin ® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution What is Gabapentin Oral Solution? Gabapentin Oral Solution is a prescription medicine used to treat: Pain from damaged nerves (postherpetic pain) that follows healing of shingles (a painful rash that comes after a herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin oral solution may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been administered in a long-term clinical study. Gabapentin readily enters the brain and prevents seizures in a number of animal models of epilepsy. Gabapentin does not possess affinity for either GABA A or GABA B receptor nor does it alter the metabolism of GABA. It does not bind to other neurotransmitter receptors of the brain and does not interact with sodium channels. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Stopping gabapentin oral solution suddenly can cause serious problems. Gabapentin oral solution can cause serious side effects including: 1. Suicidal Thoughts. Like other antiepileptic drugs, gabapentin oral solution may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500. Gabapentin. is most commonly used in veterinary medicine to relieve chronic. pain and in some pets, to reduce fear and anxiety associated with veterinary. appointments. Gabapentin may be used alone or in combination with other drugs. Gabapentin is available as capsules, tablets and as an oral solution. GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Gabapentin (gabapentin) Oral Solution DESCRIPTION Neurontin ® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution Administer the required dose of Gabapentin Oral Solution with a suitable measuring device. The oral syringe included in the pack is only for patients who are able to swallow the medicine. HCPs must use another suitable device. Each ml of oral solution contains 50mg gabapentin. Excipients with known effect: Each ml of oral solution contains 1.2mg methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), 0.12mg ethyl parahydroxybenzoate (E214), 17.2mg propylene glycol (E1520) and 0.949mg sodium. Gabapentin oral solution is indicated for: Postherpetic neuralgia in adults ( 1) Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary NEURONTIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEURONTIN. NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 ----- Warnings and Pr ecautions, Respiratory Depression (5.7) 04/2020 Gabapentin is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of part seizures with and without supplementary generalization in grown-ups and kids aged six years and over (see section 5. 1). Your doctor will prescribe Gabapentin Teva for you to help treat your epilepsy when your current treatment is not fully controlling your condition. You should take Gabapentin Teva in addition to your current treatment unless told otherwise. Gabapentin Teva can also be used on its own to treat adults and children over 12 years of age. (gabapentin) Oral Solution . DESCRIPTION . Neurontin ® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution Gabapentin can be given with or without food and should be given with sufficient fluid-intake (e.g. a glass of water). If necessary, Gabapentin oral solution can be administered via intragastric feeding tubes (nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes). For further information see section 6.6.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |