Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
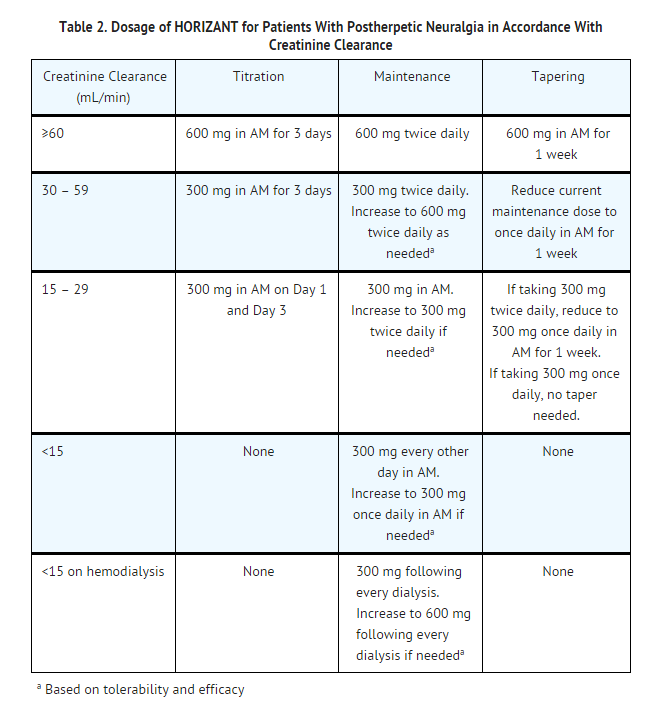
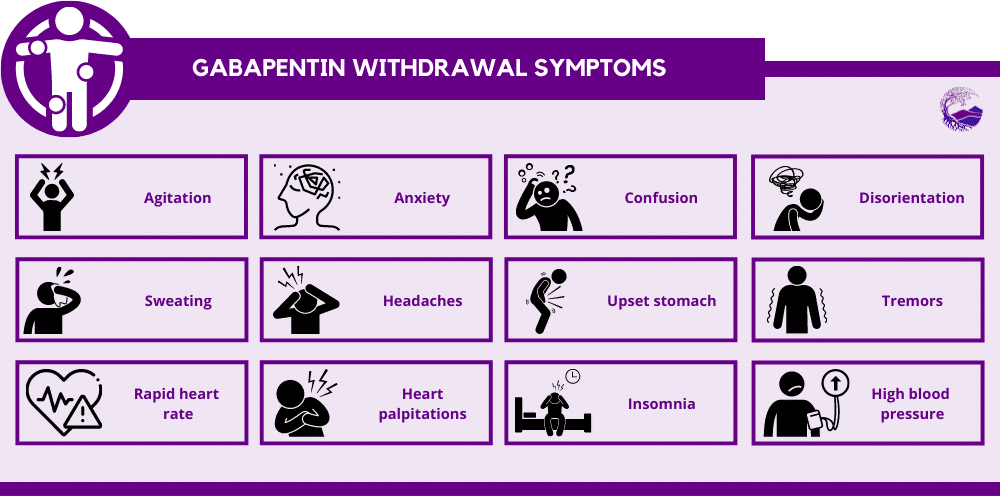
Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, UpToDate Alcohol-related disorders cause significant physical, psychological, and societal harm. Diagnostic criteria have Mild symptoms can be treated with carbamazepine or gabapentin. Benzodiazepines are A double blind trial of gaba pentin vs lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawl. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Sep; 33(9): 1582–1588. PMID: 19485969; ↑ Myrick, H et al. A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Sep;33(9):1582-8. PMID: 19485969; ↑ Barrons R et We hypothesized that patients treated with fixed-dose gabapentin taper would experience shorter clinically significant alcohol withdrawal with equivalent safety compared with those treated with CIWA-triggered benzodiazepines. Days 4 through 7: taper to 300 mg to 600 mg per day: Voronin K, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol withdrawal symptoms: a We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from reduced Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. The propensity score for being treated with gabapentin was estimated using a logistic regression model incorporating the following pretreatment variables: age, sex, number of prior admissions with alcohol withdrawal, prior documented alcohol withdrawal seizures or delirium tremens, prior treatment of alcohol withdrawal with gabapentin, prior Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. CIWA protocol adapted from San Francisco General Hospital CIWA protocol form. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. ⦁ Gabapentin is advantageous for withdrawal because (unlike benzos) it can be continued for long-term treatment to prevent future alcohol relapse Moderate Outpatient Withdrawal With Benzodiazepines Clonazepam (Klonopin) is usually the first-choice benzodiazepine for outpatient withdrawal due to a lower likelihood of causing euphoria. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Gabapentin dependence and withdrawal requiring an 18-month taper in a patient with alcohol use disorder: a case report. Stanford Health Care delivers the highest levels of care and compassion. SHC treats cancer, heart disease, brain disorders, primary care issues, and many more. How does Gabapentin work for alcohol dependence? This medication works by increasing the production of GABA, the brain’s primary calming neurotransmitter. Since alcohol binds to GABA receptors, heavy drinkers develop a deficiency in GABA. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |