Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
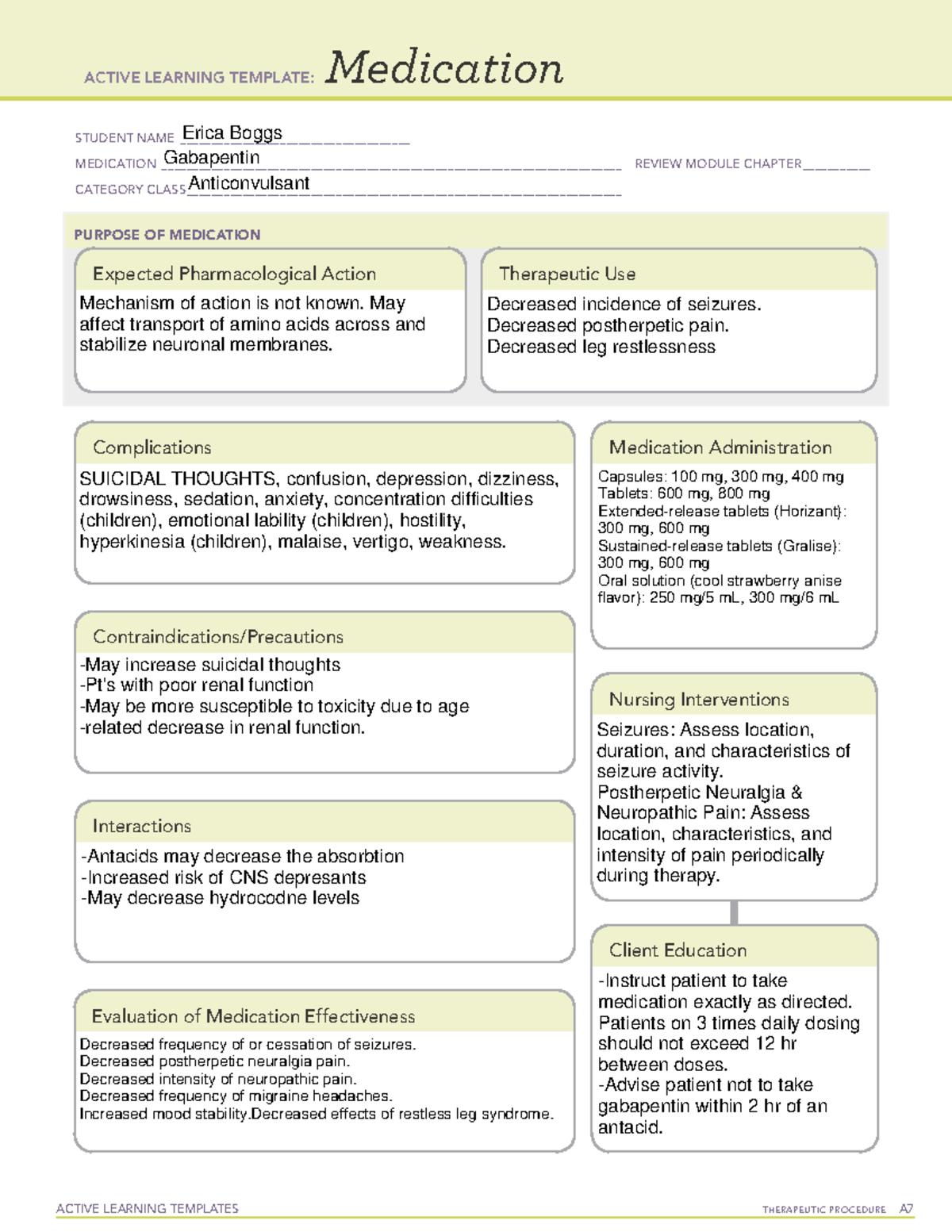
Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. The exact mechanisms through which gabapentin exerts its analgesic and antiepileptic actions are unknown however, according to ; information on the FDA-approved label for the gabapentin, gabapentin has no effect on GABA binding, uptake or degradation. In, vitro studies have shown that gabapentin binds to auxiliary α2-δ subunits of voltage- Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Therapeutic class: Anti-epileptic, Anticonvulsant Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid, Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue FDA Approved: December 30, 1993 Driving performance studies conducted with a prodrug of gabapentin (gabapentin enacarbil tablet, extended-release) indicate that gabapentin may cause significant driving impairment. Prescribers and patients should be aware that patients' ability to assess their own driving competence, as well as their ability to assess the degree of somnolence Gabapentin and gabapentin enacarbil are used for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. Considered one of several first-line therapies for PHN; more effective than placebo, but evidence suggests that only a small proportion of patients will derive a clinically meaningful benefit. Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs known as anti-seizure drugs. Take gabapentin by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once a day with the evening meal. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Swallow gabapentin whole. Do not crush or chew sustained-release tablets. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin helps to stabilize cell membranes by changing cation (sodium, calcium, and potassium) transport, reducing excitability, and suppressing seizure focus or discharge. VET: In general, avoid the use of the commercially available human oral solution (Neurontin) in dogs as it reportedly contains 300 mg/mL xylitol.As the threshold dose that can cause hypoglycemia in dogs is approximately 100 mg/kg doses of up to 15 mg/kg in dogs using the solution should be safe, but further data is needed to confirm this Additionally, xylitol may be hepatotoxic in dogs. The following tables describe changes to the AHFS Pharmacologic-Therapeutic Classification© that will be published in the 2021 edition of AHFS Drug Information® (February 1, 2021), as well as any new classes added after the publication of the 2020 edition. This is only a partial listing of the AHFS PTC. The full classification system, along with Continue reading AHFS Classification Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Based on the American Psychiatric Association (APA) guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of patients with alcohol use disorder, gabapentin is suggested for patients with alcohol use disorder (moderate to severe) who want to decrease or abstain from use of alcohol and either prefer gabapentin or are unable to tolerate or are unresponsive Gabapentin readily enters the brain and prevents seizures in a number of animal models of epilepsy. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels and it is proposed that binding to the α2δ subunit may be involved in gabapentin’s anti-seizure effects in animals. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8,10 Gabapentin has •Divided into a therapeutic classification hierarchy •As you increase the amount of couplets, more specific subgroup of drugs are being identified. •Defines equivalent drug products having the same active ingredients, strength, route, form, and therapeutic use •Example: •58-20-00-60-10-01-05 •Nortriptyline HCL Capsule 10 mg Neurontin; Ther. Class. analgesics. anticonvulsants. mood stabilizers. Pharm. Class. gamma aminobutyric acid gaba analogues. Controlled Substance Schedule: V(only schedule V in some states) There's more to see -- the rest of this topic is available only to subscribers. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gralise (gabapentin) is only used for pain after having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It should not be used for any other medical condition.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |