Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
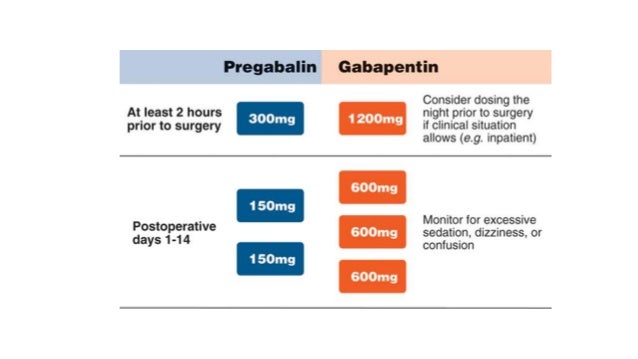
Gabapentin, Therapeutic drug monitoring, Neuropathic pain Abstract. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug prescribed for several neuropathic pain conditions. This study aimed to evaluate gabapentin (GAB) trough plasma concentration range and the applicability of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with neuropathic pain. Gabapentin (GBP) has been shown to be effective an add-on drug for the treatment of refractory partial epilepsy. We undertook an open clinical trial to test its efficacy for the first time in This study aimed to evaluate gabapentin (GAB) trough plasma concentration range and the applicability of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with neuropathic pain. Fifty-three patients with neuropathic pain, aged 20 to 75, received gabapentin as treatment for at least 7 days. Gabapentin is cleared by the kidneys and has an elimination half-life of five to seven hours. 1 Steady-state concentrations are reached after one to two days with the time between ingestion and maximal serum concentration being two to three hours. 2 For therapeutic drug monitoring, specimens should be drawn as trough levels. There are no The objective of this study was to leverage gabapentin concentrations from therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) to develop a population PK (popPK) model and characterize significant covariates that impact gabapentin PK. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of GABA used in the treatment of the partial epilepsies of adult and child of more than 12 years, in monotherapy or in association with other anticonvulsant drugs. In association, gabapentin presents the advantage of not interfering with the other anticonvulsant d The objective of this study was to leverage gabapentin concentrations from therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) to develop a population PK (popPK) model and characterize significant covariates that impact gabapentin PK. The aim of the study was to investigate the use and pharmacokinetic variability of gabapentin in epilepsy and non-epilepsy indications and to further evaluate the use of TDM in patients with restless legs syndrome (RLS). Abstract. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug prescribed for several neuropathic pain conditions. This study aimed to evaluate gabapentin (GAB) trough plasma concentration range and the applicability of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with neuropathic pain. Gabapentin PK after gabapentin enacarbil administration was consistent across studies, with low interindividual variability in bioavailability. Gabapentin enacarbil may provide more consistent and predictable exposure to gabapentin than oral gabapentin formulations. Therapeutic ranges are based on specimens collected immediately before the next dose (ie, trough). Most epileptic patients show a response to the drug when the trough concentration is in the range of 2 to 20 mcg/mL. Therapeutic drug monitoring may be useful due to inter-individual variation in pharmacokinetics and dose-dependent bioavailability; specimens for measurements should be collected TDM: from therapeutic drug monitoring towards therapeutic drug management Result interpretation is an integral part of drug monitoring and shifts the emphasis from measuring to monitoring. The test result is frequently used to adjust the dose of therapy to optimize treatment on an individual basis, resulting in a personalized healthcare The test is a definitive assay using liquid chromatography mass spectroscopy (LC/MS/MS) methodology. Therapeutic urine drug monitoring of gabapentin is important for ensuring compliance to treatment strategies. Urine or oral fluid are the specimens of choice for routine monitoring of patients taking prescription drugs. As for the newer antiepileptic drugs, including gabapentin (Neurontin), lamotrigine (Lamictal), oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), and topiramate (Topamax), there are no well-established therapeutic or Introduction. The fundamental objective of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) for antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is the prevention of seizures and the minimization of negative effects on general well-being, including cognition, mood, and endocrine function. The antiepileptic drugs with the strongest justifications for drug monitoring are lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, stiripentol, and zonisamide. Stiripentol and tiagabine are strongly protein bound and are candidates for free drug monitoring. Therapeutic drug monitoring has lower utility for gabapentin, pregabalin, and vigabatrin. Gabapentin has been increasingly used in various indications in recent years. Despite variable pharmacokinetics, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is scarcely described in other indications than epilepsy. Therapeutic drug monitoring may be useful due to inter-individual variation in pharmacokinetics and dose-dependent bioavailability; specimens for measurements should be collected before the morning dose since the short half-life may affect the interpretation of the concentration. Gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) with epilepsy and neuropathic pain indications. The purpose of this study was to investigate pharmacokinetic variability of gabapentin and pregabalin and indications for therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) in clinical practice with focus on gender aspects. Gabapentin has been increasingly used in various indications in recent years. Despite variable pharmacokinetics, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is scarcely described in other indications than epilepsy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |