Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
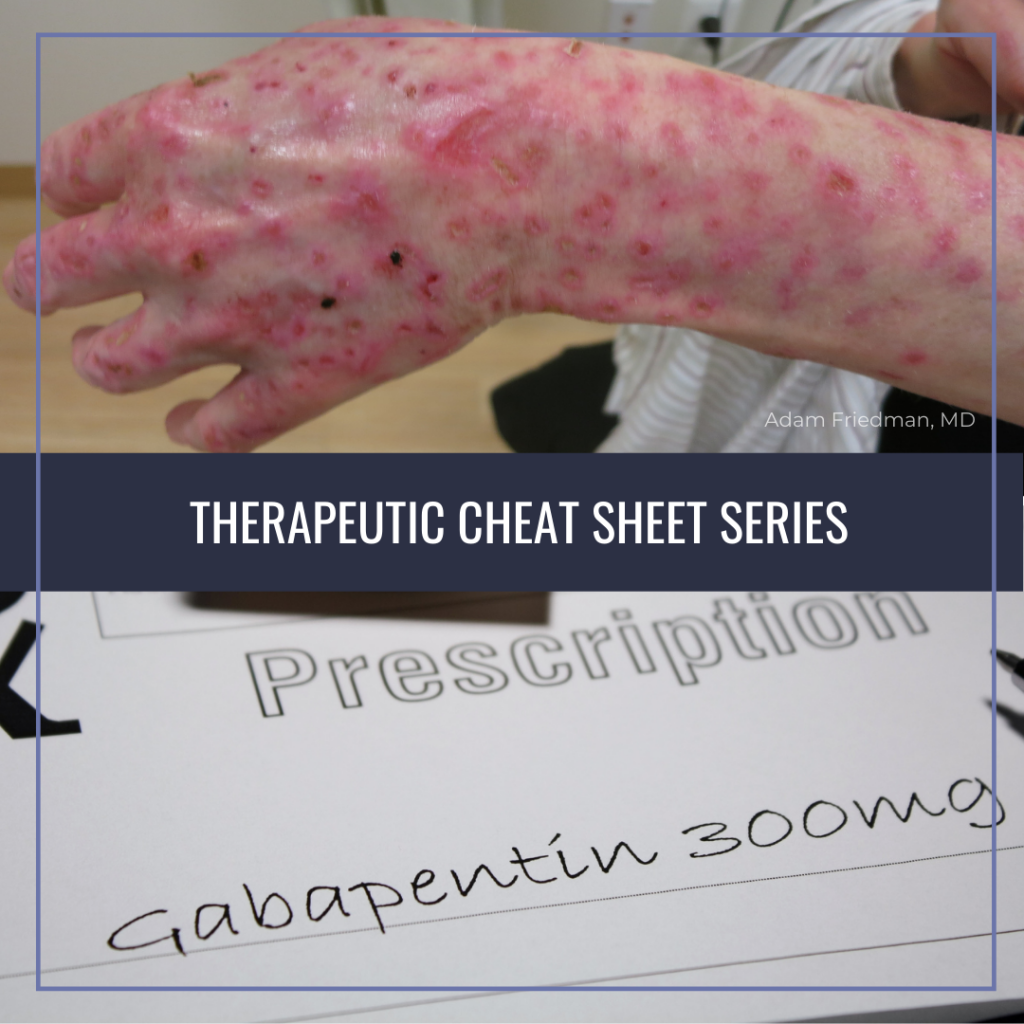
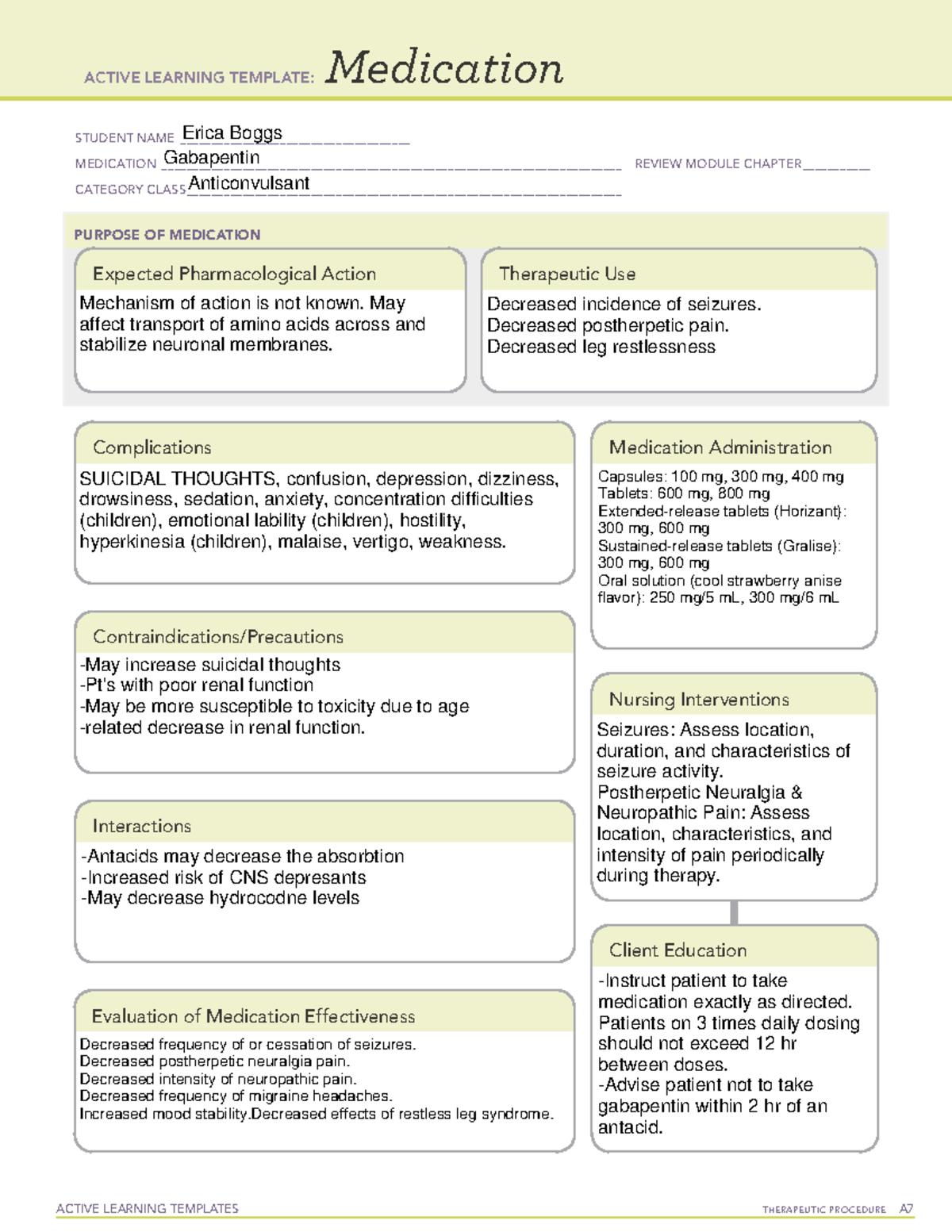
Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. NEURONTIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEURONTIN. NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 ----- Warnings and Pr ecautions, Respiratory Depression (5.7) 04/2020 Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization Initial: 300 mg PO q8hr May increase up to 600 mg PO q8hr; up to 2400 mg/day administered and tolerated in Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Gabapentin is indicated for the treatment of various conditions, including: 1. Epilepsy. It is commonly prescribed as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children. 2. Neuropathic pain. Larsen Burns M, Kinge E, Stokke Opdal M, Johannessen SI, Johannessen Landmark C. Therapeutic drug monitoring of gabapentin in various indications. Acta neurologica Scandinavica. 2019 May:139(5):446-454. doi: 10.1111/ane.13075. Epub 2019 Feb 19 [PubMed PMID: 30710348] In the United States, gabapentin is officially indicated for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults and for the adjunctive treatment of partial-onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, in patients 3 years of age and older. 16 In Europe, gabapentin is indicated for adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset Abstract. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly A 2017 systematic review of gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia or diabetic neuropathy found gabapentin (1800 to 3600 mg daily) was more effective than placebo. 10 Evidence for gabapentin’s analgesic effect in other neuropathic pain conditions was very limited. 10 Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. 14.2 Epilepsy for Partial Onset Seizures (Adjunctive Therapy) The effectiveness of gabapentin as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) was established in multicenter placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group clinical trials in adult and pediatric patients (3 years and older) with refractory partial seizures. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Discontinuation of therapy: In patients receiving gabapentin chronically, unless safety concerns require a more rapid withdrawal, gabapentin should be withdrawn gradually over ≥1 week to minimize the potential of increased seizure frequency (in patients with epilepsy) or other withdrawal symptoms (eg, confusion, irritability, tachycardia Despite variable pharmacokinetics, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is scarcely described in other indications than epilepsy. The aim of the study was to investigate the use and pharmacokinetic variability of gabapentin in epilepsy and non-epilepsy indications and to further evaluate the use of TDM in patients with restless legs syndrome (RLS). 300mg once on day 1, twice daily on day 2, and 3 times daily on day 3; may titrate up to usual max 1.8g/day in 3 divided doses (doses up to 3.6g/day have been used without added benefit). Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |