Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
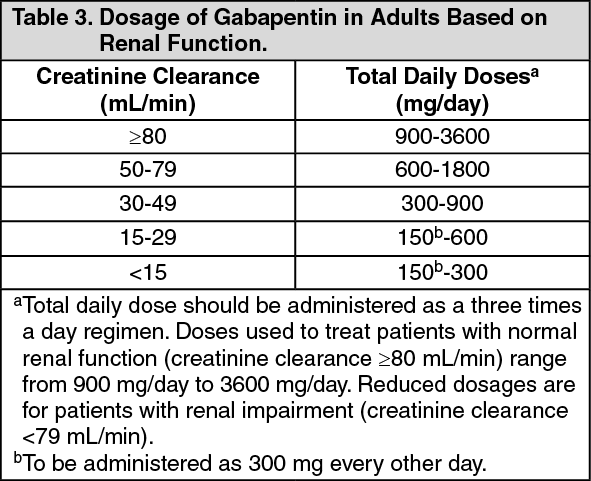
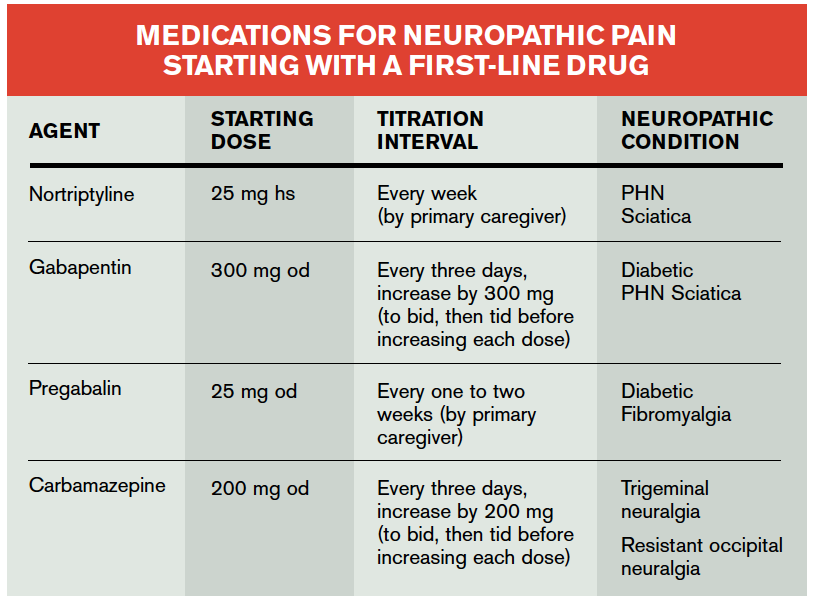
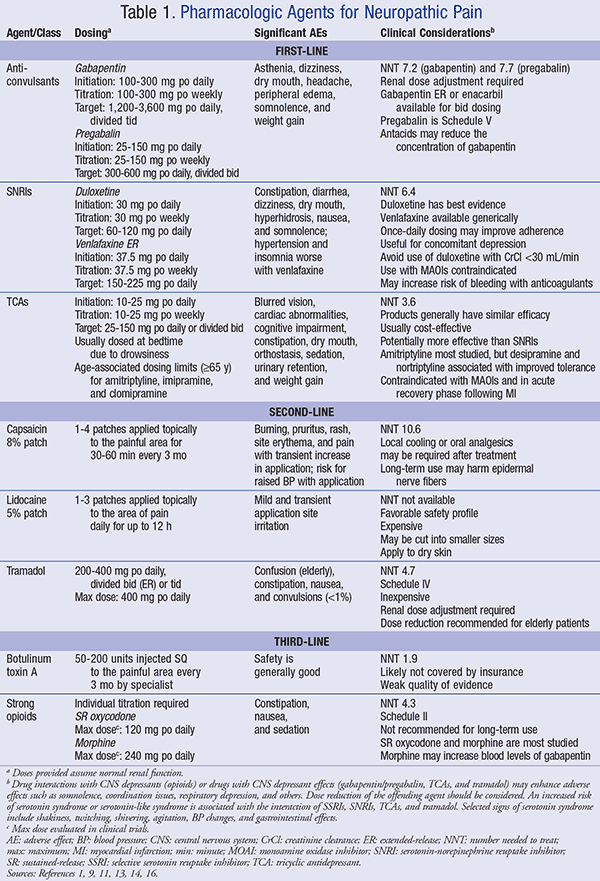
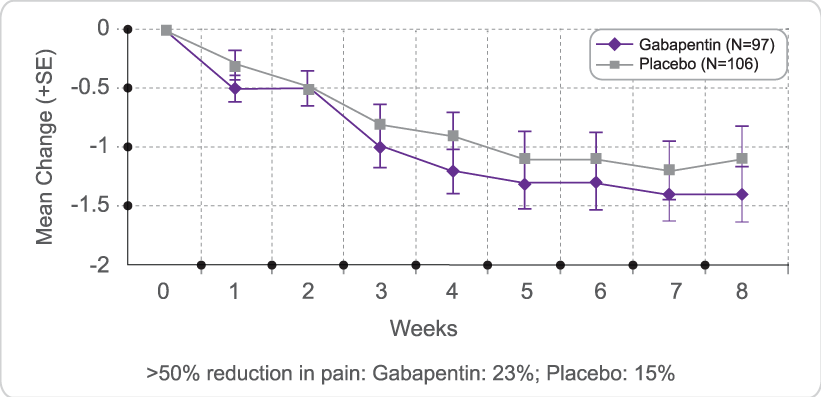
Administration of 4 different doses of gabapentin during the initial titration in outpatients with neuropathic pain resulted in a significant reduction in awakening from breakthrough pain and a reduction in the adverse effects of the medication. Background for FF #49: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiepileptic that has FDA indication to treat postherpetic neuralgia and partial onset seizures. This Fast Fact will review gabapentin’s role in neuropathic pain. See Fast Fact #289 for a comparison of gabapentin with pregabalin, a similar neuropathic analgesic. Methods: Randomized controlled studies of gabapentin for neuropathic pain were identified through a search of PubMed and MEDLINE from 1966 to the present using the search terms gabapentin, randomized, placebo, and pain. Abstracts of identified articles were screened for study size (>100 patients per treatment arm) and use of appropriate Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Slower titration of gabapentin may be appropriate for individual patients to improve tolerability. Once a patient is on a 900mg dose, the dose can be increased in 300mg increments every two to three days until tolerated. Pharmacologic therapy for neuropathic pain, or nociplastic or centralized pain — For most patients with chronic neuropathic pain, initial treatment involves either selected antidepressants (ie, tricyclic antidepressants [TCAs] or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors [SNRIs]), or antiseizure medications (ie, gabapentin or pregabalin Gabapentin Dosing for Neuropathic Pain: Evidence from Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials Miroslav Backonja, MD,1 and Robert L. Glanzman, MD2 l Departments of Neurology, Anesthesiology, and Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics, Madison, Wisconsin, and 2pfizer lnc, New York, New York ABSTRACT Background: Pain is one of the most common reasons for Additional titration to 1800 mg/d is recommended for greater efficacy. Doses up to 3600 mg/d may be needed in some patients. The effective dose should be individualized according to patient response and tolerability. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin. Please read the leaflet included in your prescription. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic / anti-convulsant drug that can be used in to treat pain caused by damage to the nerves (neuropathic). How to take Gabapentin Gabapentin needs to be gradually increased over a period of time until a maximum daily dose of 600mgs For management of localised neuropathic pain including superficial, small fibre neuropathies, post herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy, consider: Localised neuropathic pain CARBAMAZEPINE – Start dose at 100mg twice daily and slowly titrate the dose based on response in steps of Guideline for managing neuropathic pain in primary care Page 4 of 11 First Produced: January 2008 Reviewed: April 2023 Next review date: March 2026 Neuropathic pain treatment pathway (Adapted from PrescQIPP bulletin 216 Neuropathic pain, 2021) (approx. cost for 6 months, DT Feb2023) Trigeminal neuralgia Use carbamazepine first line second line treatments for peripheral neuropathic pain. The NHS Tayside guidance and algorithm for the treatment of neuropathic pain reflects the SMC advice and should be followed for the treatment of neuropathic pain within NHS Tayside. NICE clinical guidelines such as the guideline for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain, do Multidisciplinary conservative care and nonopioid medications (tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, gabapentanoids, topicals, and transdermal substances) are recommended as firstline therapy; combination therapy (firstline medications) and tramadol and tapentadol are recommended as secondline; serotonin-specif For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Start at 100mg twice daily and titrate the dose gradually until pain is relieved (increase by a maximum of 100mg every 3 days). A dose of 200mg 3 or 4 times daily is usually sufficient to maintain pain free state. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. The tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), amitriptyline and nortriptyline (unapproved indications), and the gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin, are all first-line pharmacological treatment options for neuropathic pain *. 4, 5 Duloxetine is often a first line choice for neuropathic pain in other countries, however, it is neither an approved
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |