Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
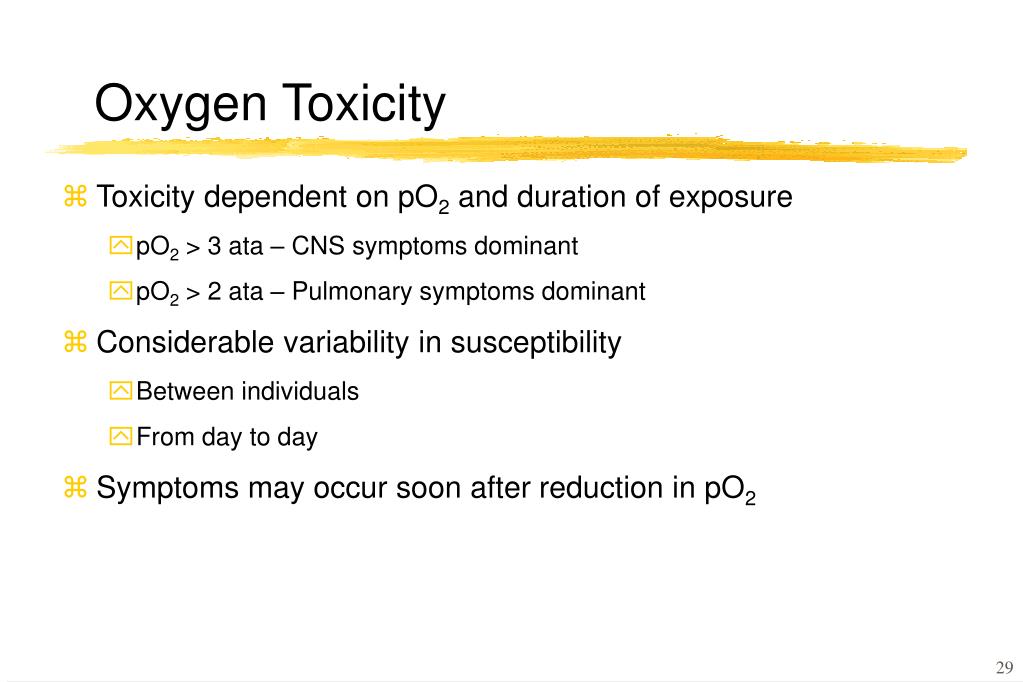
The lethal dose of gabapentin has not been determined. In an FDA study, no lethal dose was found in mice and rats receiving doses as high as 8,000 milligrams per kilogram of body weight (mg/kg). A regular dosage of gabapentin for children aged 3 to 11 years is up to 50 mg/kg per day. Our literature search found only 2 population-based studies examining the association between gabapentin use and risk of toxicity in patients with CKD (our search strategy is shown in Table S2 and the results in Table S3). 11, 14 Only one study examined the risk of toxicity by initial gabapentin dose in new users, 14 and, in a subgroup analysis Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is prescribed for both FDA-approved and multiple off-label conditions, and has a relatively safe side-effect profile. Rare cases of overdose-related adverse effects have been reported in the literature. Described herein are the circumstances and autopsy findi Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose include drowsiness, muscle weakness, and respiratory depression. There is no specific antidote for gabapentin overdose; treatment is supportive care and may consist of hemodialysis. Preventing overdose involves safe prescribing practices, patient education, and proper medication storage and disposal. Gabapentin is widely prescribed. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication, with about 3.9 million prescriptions filled in Canada in 2015. 1 Gabapentin is approved by Health Canada as adjunctive therapy in the management of epilepsy. 1 However, the most common recommendations and prescribing internationally are for off-label conditions, including anxiety, alcohol use disorder and chronic Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures. Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally once Day 2: 300 mg orally 2 times day Day 3: 300 mg orally 3 times a day. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: Toxicity / Risk Assessment Management - Lone Pregabalin or Gabapentin exposures are usually well - Supportive care is the mainstay of management tolerated - Coma with loss of airway reflexes is rare and may require intubation Compared with some drugs, such as opioids, gabapentin appears to be relatively non-lethal in overdose situations, meaning the morbidity associated with a toxic dose is low. 8 However, the primary danger of gabapentin overdose appears when individuals use gabapentin in conjunction with other drugs, such as alcohol or opioids. 9,10 However, people taking gabapentin should be aware that it does have particularly unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, even after taking it for a relatively short amount of time and at low doses. Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose. Most side effects of a gabapentin overdose will be related to an overall deceleration of the body’s systems. Taking anything above the recommended dose of gabapentin can be considered too much. The maximum dosage depends on your condition and age: Although the lethal dosage of gabapentin is not yet known, researchers found that people who consumed 49 grams of Gabapentin experienced unpleasant symptoms. 6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin Overdose in Dogs 1. Can a dog die from a gabapentin overdose? While a gabapentin overdose can cause significant distress and discomfort, it is rarely fatal in dogs. The primary risks involve the side effects like extreme sedation, incoordination, and gastrointestinal issues. What are the symptoms of a gabapentin overdose? Common symptoms of gabapentin overdose are drowsiness, fast heartbeat, dizziness, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, lethargy, coma, and death may occur. What to do if someone takes too much gabapentin or takes it by accident How Much Gabapentin to Overdose? The lethal dose of gabapentin ranges from 49 grams or more. Gabapentin overdose side effects like ataxia, labored breathing, diarrhea, and sedation have been reported by the FDA in people who took 49 grams or more of the drug. Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Taking too much of a drug like gabapentin can result in a potentially fatal overdose. And, by the time a person realizes he or she is experiencing a gabapentin overdose, it may be too late to call for help and receive treatment in time. The best way to avoid an overdose is to get sober and avoid abusing drugs and alcohol altogether. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose. A gabapentin overdose can be dangerous or even deadly. Some factors can increase the risk of a fatal overdose, such as taking several substances at once. Gabapentin overdose symptoms can include: Drowsiness; Movement difficulties; Dizziness; Nausea or vomiting; Rapid heartbeat; Low blood pressure Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |