Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
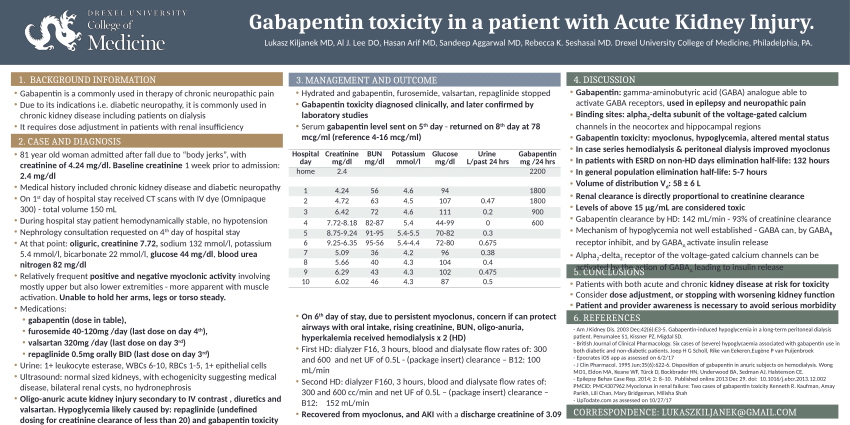
This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabapentin toxicity has been underrecognized. Gabapentin (C 9 H 17 NO 2 ) is a water-soluble 1-(aminomethyl)-cyclohexaneacetic acid and a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Myoclonic activity may occur as a complication of gabapentin toxicity, especially with acute kidney injury or end-stage renal disease. We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease which resolved with discontinuation of gabapentin and treatment with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. Myoclonus is a well-reported complication of gabapentin toxicity especially in patients with renal impairment. As gabapentin is solely excreted by the kidneys, renal dose adjustment is recommended in the literature. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Gabapentin toxicity in kidney failure hasn't been clearly proved till now. We want to emphasize the gabapentin toxicity on fi ve cases with chronic kidney diasease at the present study. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. including chronic kidney disease. However, gabapentin is eliminated solely through the kidney, and kidney impair-ment poses a significant risk for gabapentin accumulation and toxicity. To date, published literature on gabapen-tin toxicity in chronic kidney disease is limited to case reports.11-17 To determine the gabapentin dosage and risk of Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. However, current guidance is based on pharmacokinetic and toxicity studies, but studies confirming efficacy of these dosing strategies are lacking. Zand L, McKian KP, Qian Q. Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease: a preventable cause of morbidity. Am J Med. 2010;123(4):367–373. 23. Yoo L, Matalon D, Hoffman RS, Goldfarb DS. Treatment of pregabalin toxicity by haemodialysis in a patient with kidney failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54(6):1127–1130. 24. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |