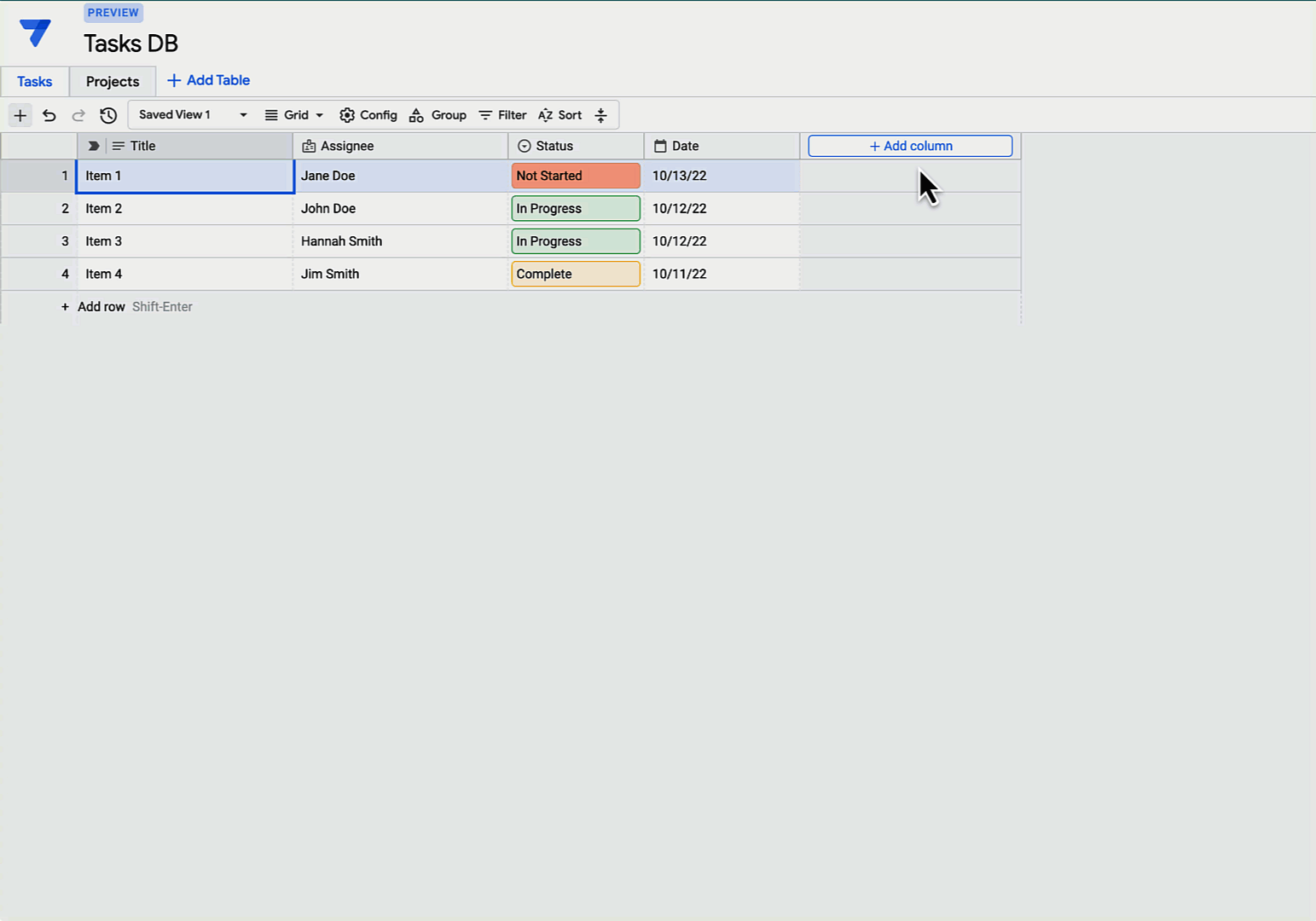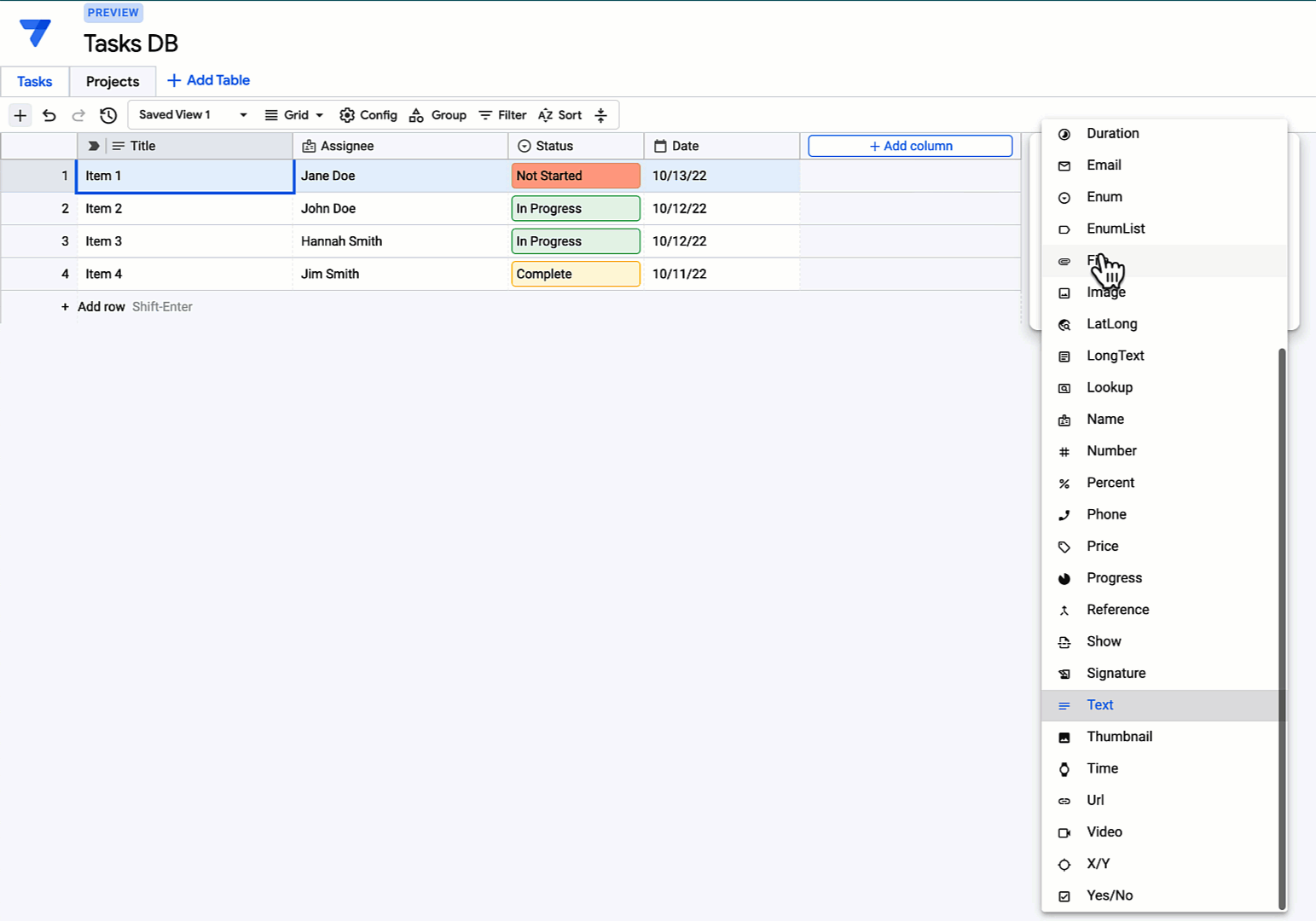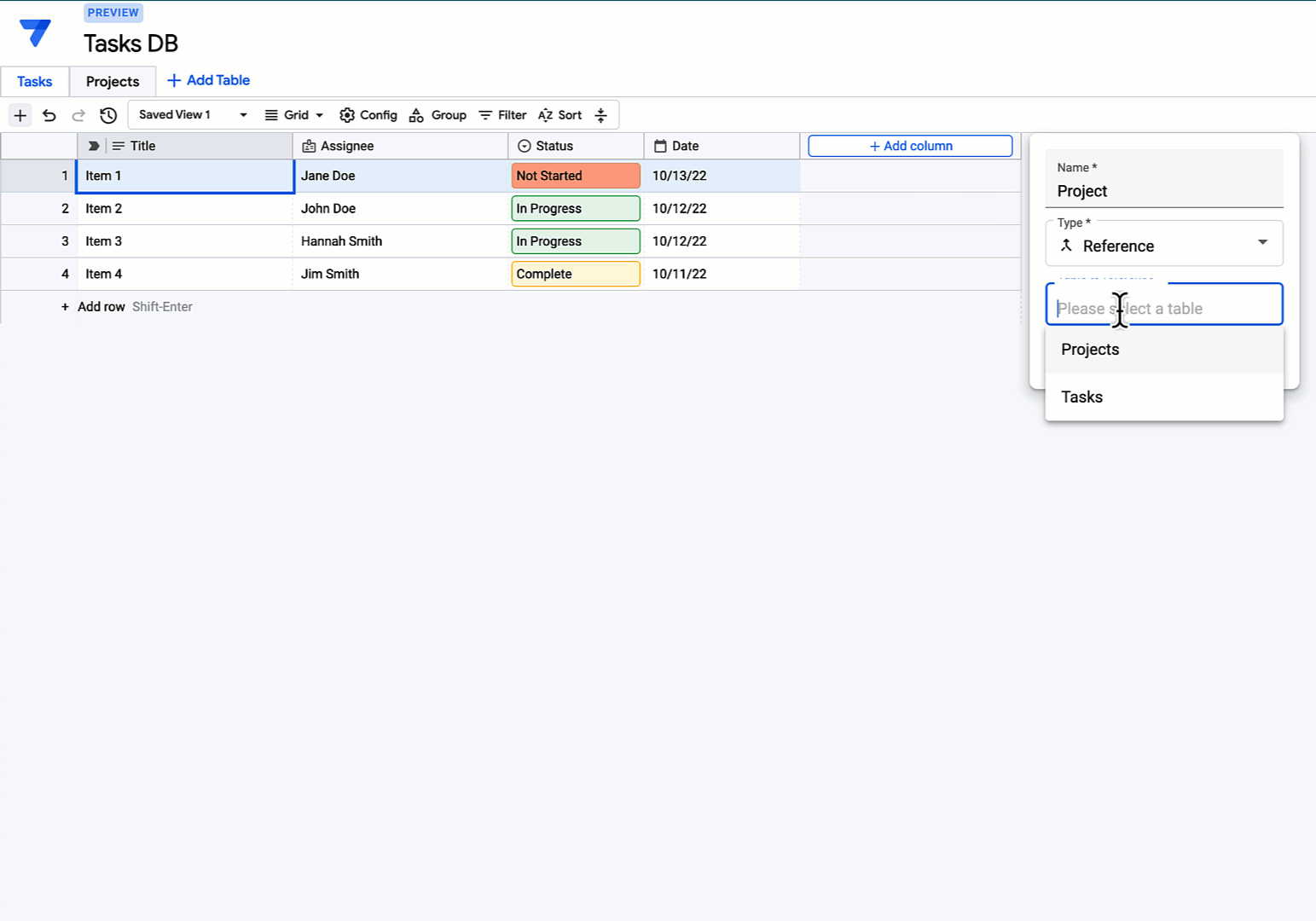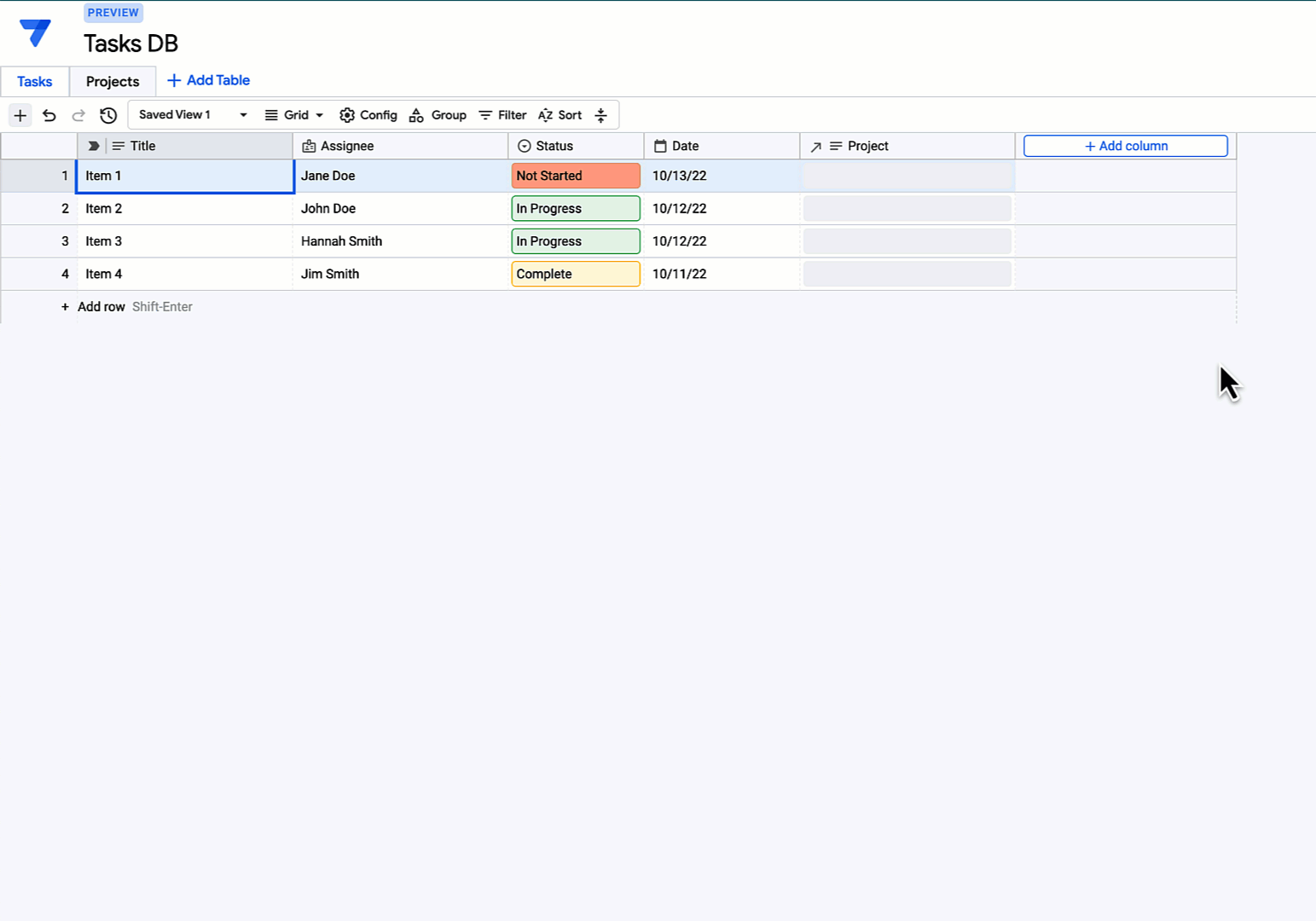
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 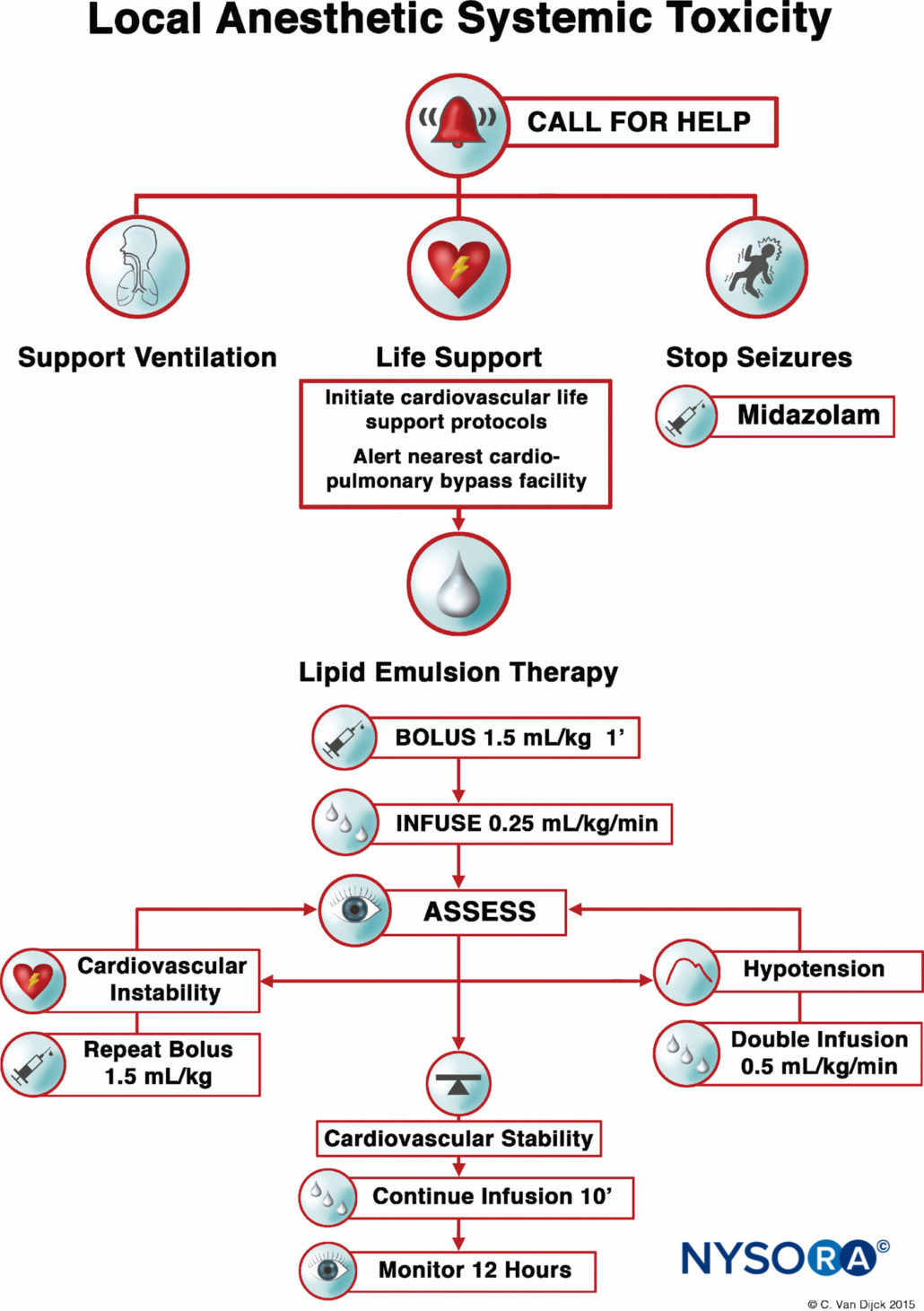 |
The purpose of this study is to document the clinical manifestations and outcomes of gabapentin exposures reported to poison centers. Methods: A multicenter prospective observational study of all gabapentin exposures reported to three poisoncenters was conducted between 4/1/98 and 4/1/2000. Cases involving gabapentin only were evaluated. Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. The management of a gabapentin overdose primarily involves supportive care, as there is no specific antidote. In some cases, hemodialysis has been used to remove gabapentin from the system, particularly in severe instances of toxicity. Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose. Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. The objective of this review is to provide a repository of standard and emerging treatment modalities for loperamide, gabapentin and modafinil for the emergency medicine team. Expert opinion: Loperamide, gabapentin, and modafinil are becoming drugs of abuse, and as such, should be on the radar of healthcare providers. Recognizing their unique These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. A summary table to facilitate emergency management is provided . Their therapeutic use and a general Treatment for Gabapentin Overdose. Once medical services arrive, they can begin treating the symptoms of a gabapentin overdose. If the person has combined gabapentin with opioids, the person may be given naloxone to help reverse the overdose. If no opioids are suspected, other treatment will happen. Understanding how to treat gabapentin toxicity is crucial for healthcare providers and those who may encounter or experience it. The immediate management of gabapentin overdose focuses on stabilizing the patient and supporting vital functions. This typically involves: Airway Maintenance: Ensuring a clear airway is the first priority. Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. Thirty-three Gabapentin overdose can be serious and may result in many symptoms, from mild drowsiness to life-threatening complications. Understanding the signs, risks, and proper management of gabapentin overdose is crucial for medical professionals and individuals using the medication. Prevention and Management of Gabapentin Overdose. Preventing gabapentin overdose involves careful monitoring of the patient’s condition, adherence to the prescribed dosage, and awareness of potential interactions with other medications. In cases of suspected overdose, immediate medical attention is necessary. A gabapentin overdose is rare, but it is possible. The likelihood of an overdose increases when you abuse gabapentin with other drugs like opioids and alcohol. If you or someone you know is experiencing a gabapentin overdose, seek medical help immediately. Neurontin (gabapentin) is a medication that is used for several different conditions such as nerve pain, epilepsy, and many others. While overdoses with gabapentin are rare, it is important to know the symptoms of an overdose and the risk factors that increase the likelihood of an overdose. To avoid an overdose, take gabapentin as directed. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Toxicity / Risk Assessment Management - Lone Pregabalin or Gabapentin exposures are usually well - Supportive care is the mainstay of management tolerated - Coma with loss of airway reflexes is rare and may require intubation The gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin are among the most prescribed drugs in the United States, 1 and are increasingly misused recreationally. 2, 3 Treatment of patients with gabapentinoid toxicity is supportive, but the role of extracorporeal treatment (ECTR) is debated. The patient improved symptomatically and his tremors subsided. In this case report, we describe the successful management of gabapentin toxicity with continuous renal replacement therapy and calculate the clearance of gabapentin which will enable future treatment of gabapentin toxicity by CVVHD. Keywords: Clearance, dialysis, gabapentin, toxicity These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |