Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
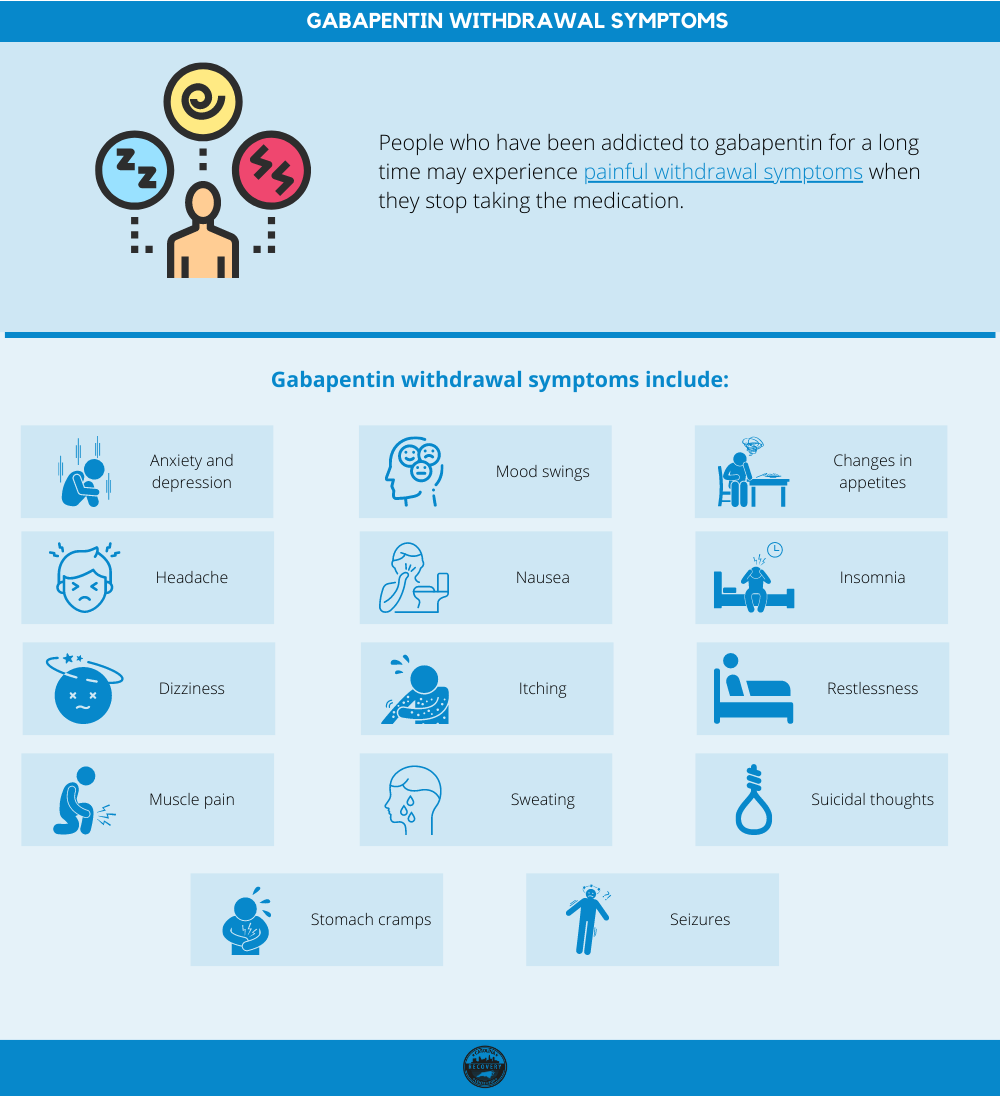
We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease which resolved with discontinuation of gabapentin and treatment with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Gabapentin and pregabalin toxicity can manifest as myoclonus. While myoclonus can present in multiple ways – focal or multifocal, positive, negative, and rest, cortical or subcortical – it most often occurs in a positive or rest, multifocal, and subcortical fashion. Results: A 68-year-old male presented with hand tremors starting 2 weeks after the initiation of 1800 mg daily gabapentin recommended for distal neuropathic pain. Examination revealed bilateral action-induced clonus in the hands. His mental status was normal, and there was no weakness. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease which resolved with discontinuation of gabapentin and treatment with hemodialysis Sixth, myoclonus has multiple etiologies [25].Pertinent to these cases are azotemia and toxic effects of medications. Azotemia was present in both cases; however, in Case 2, the patient had chronic stable renal function with the development of myoclonus only after initiation of gabapentin. Three patients developed focal myoclonus, contralateral to their epileptic focus. Two patients had an exacerbation of preexistent myoclonus. An EEG performed during myoclonus on three patients showed no correlate. The myoclonus tended to persist as long as GBP was maintained, whereas discontinuance of GBP resulted in rapid cessation of the Myoclonus is a sudden, abrupt, brief, 'shock-like' involuntary movement caused by muscular contractions ('positive myoclonus') or a sudden brief lapse of muscle contraction in active postural muscles ('negative myoclonus' or 'asterixis'). Various disorders can cause myoclonus including neurodegenera Myoclonic activity may occur as a complication of gabapentin toxicity, especially with acute kidney injury or end-stage renal disease. We report 2 cases of myoclonic activity associated with gabapentin toxicity in the setting of renal disease which resolved with discontinuation of gabapentin and treatment with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Gaba- pentin (GBP) is a drug recently introduced for the treat- ment of partial seizures. We observed a relatively high incidence of myoclonus associated with GBP therapy. Clinic charts of 104 consecutive patients treated with GBP were reviewed. Negative myoclonus is a jerky, brief, and sudden interruption of voluntary muscle contraction. Although gabapentin and pregabalin have been reported to induce positive myoclonus in some patients with impaired renal function, there are only a few studies describing pregabalin- or gabapentin-induced negative myoclonus. This study reviewed patients who had developed pregabalin- or gabapentin Acute hyperkinetic movement disorders such as multifocal or segmental myoclonus in elderly patients warrant a prompt review of recent drug history, especially gabapentin, even in the background of normal renal function. Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are FDA approved for adjunctive treatment of partial seizures and for treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. Both drugs are primarily eliminated by renal excretion. However, PGB or GBP induced myoclonus has only been reported infrequently in case reports/series. Myoclonus is a rare side effect of gabapentin (GBP) and has been reported in patients with preexisting myoclonus, mental retardation, chronic static encephalopathy, diffuse brain damage, impaired renal function, or end stage renal disease. We report Myoclonus is a well-reported complication of gabapentin toxicity especially in patients with renal impairment. As gabapentin is solely excreted by the kidneys, renal dose adjustment is recommended in the literature. Gabapentin is used as an anti-epileptic and for neuropathic pain. Adverse effects with gabapentin include severe myopathy, severe myoclonus, neutropenia, hypoglycaemia episodes and altered consciousness. Gabapentin is renally excreted; dose adjustments are required to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Acknowledgments Abstract. A wide variety of drugs can cause myoclonus. To illustrate this, we first discuss two personally observed cases, one presenting with generalized, but facial-predominant, myoclonus that was induced by amantadine; and the other presenting with propriospinal myoclonus triggered by an antibiotic. Gabapentin and pregabalin toxicity can manifest as myoclonus. While myoclonus can present in multiple ways – focal or multifocal, positive, negative, and rest, cortical or subcortical – it most often occurs in a positive or rest, multifocal, and subcortical fashion. The most crucial co-morbidity to consider is renal insufficiency. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. An increased risk of myoclonus has been associated with its use in patients with ESRD and a patient with renal failure was noted to have coma attributed to gabapentin toxicity. Toxins that are water soluble are easily removed by hemodialysis and tend to have a smaller volume of distribution.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |