Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
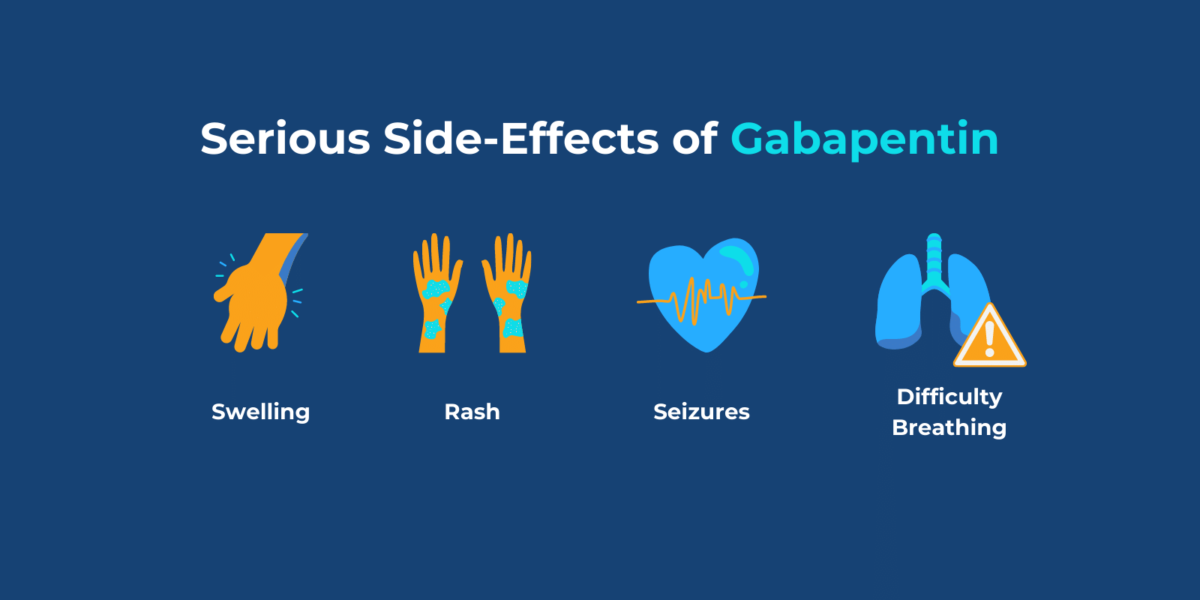 |  |
Gabapentin can be used to potentiate illicit opioids; data indicate gabapentin exposures associated with intentional abuse, misuse, or unknown exposures reported to U.S. poison centers increased by 104% from 2013 to 2017 (3). However, less is known about the drug’s role in fatal overdoses (4). The exact mechanisms through which gabapentin exerts its analgesic and antiepileptic actions are unknown however, according to ; information on the FDA-approved label for the gabapentin, gabapentin has no effect on GABA binding, uptake or degradation. In, vitro studies have shown that gabapentin binds to auxiliary α2-δ subunits of voltage- Gabapentin inadequate use can lead to toxicity and mortality. Gabapentin can induce diverse side effects such as teratogenicity, hypoventilation, respiratory failure, deficits in visual field, myopathy, self-harm behavior, suicidal behavior, mitochondrial toxicity, somnolence, dizziness and asthenia; these can be related to the route of The purpose of this study is to document the clinical manifestations and outcomes of gabapentin exposures reported to poison centers. Methods: A multicenter prospective observational study of all gabapentin exposures reported to three poisoncenters was conducted between 4/1/98 and 4/1/2000. Cases involving gabapentin only were evaluated. Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. Gabapentin toxicity is seen in those with chronic kidney disease or undergoing hemodialysis, showing symptoms like tremors, altered mental states, and respiratory depression requiring intubation. Reports of rhabdomyolysis due to gabapentin have been described. gabapentin was detected also involved an opioid, particularly (and increasingly) illicitly manufactured fentanyls. Although . gabapentin testing is recommended as part of comprehensive postmortem toxicology testing protocols for drug overdose death investigations in the United States, gabapentin is During that period, there were 62,652 overdose deaths, of which 58,362 had documented toxicology results. Of these, gabapentin was found in 9.7%. Gabapentin was judged to contribute to overdose death in 52.3% of those deaths—or 5.0% of the total deaths from overdose. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric properties. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. Neurontin (gabapentin) is a medication that is used for several different conditions such as nerve pain, epilepsy, and many others. While overdoses with gabapentin are rare, it is important to know the symptoms of an overdose and the risk factors that increase the likelihood of an overdose. This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified Objective: To raise awareness of serious toxicity, including respiratory depression and PRES (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) caused by gabapentin in the setting of overdose and abuse. Postmortem toxicology analyses have directly linked gabapentin as a cause of death, but most deaths observed occurred with concomitant use with opiates or benzodiazepines. Gabapentin when combined with these agents appears to be lethal at lower serum gabapentin concentrations than gabapentin alone. Gabapentin toxicity should be considered one of the differential diagnoses of altered consciousness in patients with compromised renal function, even after a single dose. We report a 57-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus and uraemia on regular haemodialysis who developed severe dizziness and lethargy after a single recommended dose of The best way to avoid an overdose is to get sober and avoid abusing drugs and alcohol altogether. Here is everything you need to know about gabapentin toxicity and treatment. What is Gabapentin (Neurontin)? Gabapentin is a muscle relaxer and an anticonvulsant that is used to help control partial seizures in people struggling with epilepsy. Routine gabapentin postmortem testing and linking of death certificate, medical examiner, coroner, toxicology, and prescription history data will provide more reliable information on the extent of gabapentin misuse, diversion, and implications for clinical care. In cases in which gabapentin was determined to be a cause of death, the blood concentrations ranged from 1.1 to 134.0 mg/L. Persons who died of a gabapentin-related drug death were prescribed the drug legitimately 91.4% of the time, with 84.2% of those also having a known prior history of abuse or misuse of prescription medications. ported with hemodialysis. The workgroup assessed gabapentin and pregabalin as “dialyzable” for patients with decreased kidney function (quality of the evidence grade as A and B, respectively). Limited clinical data were available (24 patients with gabapentin toxicity and 7 with pregabalin toxicity received ECTR). Thus, hydrocodone is observed to be present more frequently in cases with gabapentin toxicity than across the regular population of mixed drug fatalities, although these are not mutually exclusive groups so a chi-square test cannot be used to determine the significance of this observation. Gabapentin and Hydrocodone Concentrations Klein-Schwartz W, Shepherd JG, Gorman S et al. Characterization of gabapentin overdose using a poison center case series. Journal of Toxicology-Clinical Toxicology 2003; 41(1):11-15. Lofton AL, Klein-Schwartz W. Evaluation of lamotrigine toxicity reported to poison centers. Annals of Pharmaotherapy 2004; 38:1811-1815.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |