Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) | 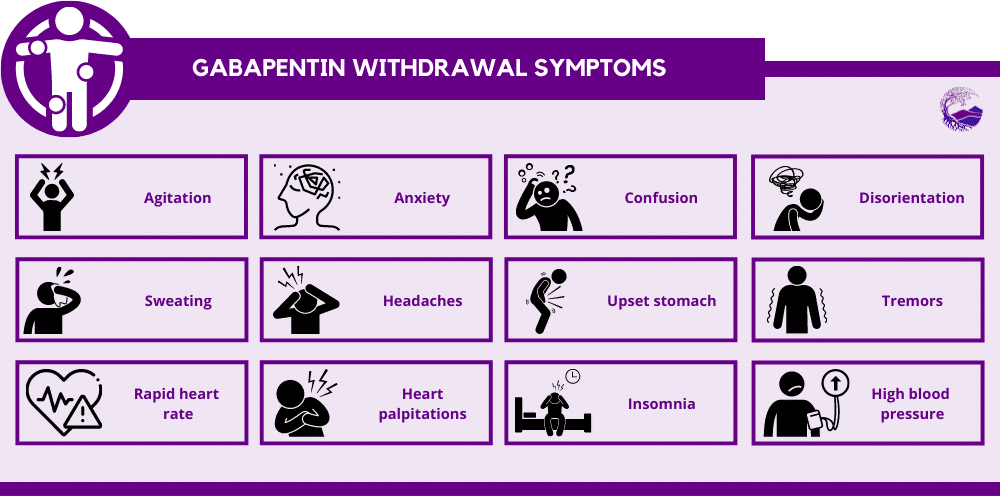 |
 |  |
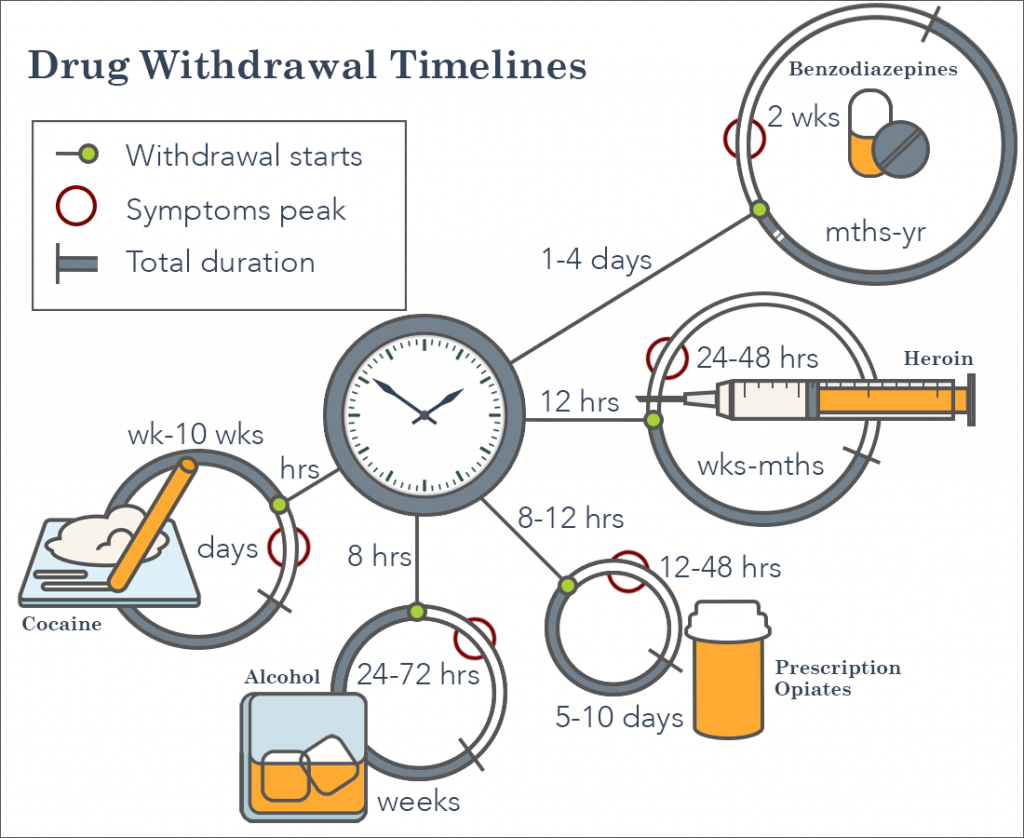
Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Specifically, it is useful in treating withdrawal and maintaining abstinence in people struggling with alcohol, benzodiazepine, and opioid addiction. A research review from Pharmacology & Pharmacy indicates that multiple studies show gabapentin as a positive support to alcohol detox and withdrawal. Abstract. There is an increasing interest in anticonvulsants for the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, and among the newer substances gabapentin seems particularly promising due to its gabaergic and its glutamate-antagonistic activity. There is no consensus on a treatment protocol for benzodiazepine withdrawal but it is beneficial to place patients on a CIWA protocol to allow for symptom-triggered treatment with long-acting benzodiazepines as tolerated with slow tapers over time as well as other adjunctive therapies such as phenobarbital, propranolol, haloperidol, and The evaluation and management of benzodiazepine and other substance use disorders (see "Benzodiazepine use disorder" and "Substance use disorders: Clinical assessment" and "Substance use disorder in adolescents: Treatment overview") Withdrawal syndromes from other agents with sedative properties (see "Management of moderate and severe alcohol Overall, Neurontin Gabapentin is a valuable treatment option for benzodiazepine withdrawal. Its ability to reduce withdrawal symptoms, stabilize mood, prevent seizures, improve sleep quality, and minimize discomfort make it an effective and supportive medication for individuals navigating the challenges of benzodiazepine withdrawal. related to withdrawal, benzodiazepines are sant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should treatment of benzodiazepine dependence: summary of Gabapentin works by showing a high affinity for binding sites throughout the brain corresponding to the presence of the voltage-gated calcium channels, especially α-2-δ-1, which seems to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the presynaptic area that participate in epileptogenesis.” The results provide preliminary evidence that gabapentin may be a helpful adjunct to benzodiazepines in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Patients in the Axis I category “other” received a significantly lower amount of benzodiazepines than those with a primary mood disorder. Benzodiazepine withdrawal may involve nausea, sweating, tremors, and increased anxiety. Some medications may also help treat your withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carbamazepine Gabapentin withdrawal lasts between 5 to 10 days, with symptoms such as anxiety, headaches, and nausea peaking during the first few days. According to Krebs and Tzeng (2019), in their study “Gabapentin Withdrawal: A Case Series,” withdrawal symptoms begin within 24 to 72 hours after the last dose and intensify over the next 1 to 5 days Benzodiazepines are currently the gold standard for treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has growing evidence to support its use in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, however there is limited evidence regarding its role in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Current studies examining the inpatient treatment of alcohol withdrawal with gabapentin versus benzodiazepines are low-quality with design flaws. Randomized, controlled studies of gabapentin to treat hospitalized patients suffering alcohol withdrawal syndrome are required. USA: Gabapentin and benzodiazepine combination is safe for the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to findings from a recent study. The results were presented at the American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting (virtual meeting) held from May 1-3, 2021. The best way to prevent benzodiazepine dependence for high-risk patients is to adhere to treatment recommendations and emphasize nonpharmacologic therapies for anxiety and insomnia. 6, 9 If In general, the prognosis for patients who undergo withdrawal treatment for benzodiazepine dependence is fairly good. 6 However, additional therapeutic approaches may be necessary, depending on In 2021, the American Psychiatric Association presented a study on the possibility of treating benzodiazepine dependence, abuse, and withdrawal with gabapentin. According to the psychiatrists, the two drugs share similar mechanisms, making gabapentin an effective adjunct treatment. Most people I was in treatment with took Gabapentin to ease withdrawal symptoms. since you’re doing a more gradual taper you probably wouldn’t need it, but I don’t think you’re gonna screw anything up by taking it if you think it helps. The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) recommends gabapentin for treating withdrawal symptoms as follows: (I) Gabapentin is an appropriate alternative to benzodiazepines for mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal. (II) Gabapentin is a suitable choice for treating alcohol withdrawal when the physician also intends to utilize it for a The combination of gabapentin and benzodiazepine can be safe in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to data presented at American Psychiatric Association annual meeting,
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) |  |
 |  |