Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | -Cap-100mg-UK-1.jpg) |
 |  |
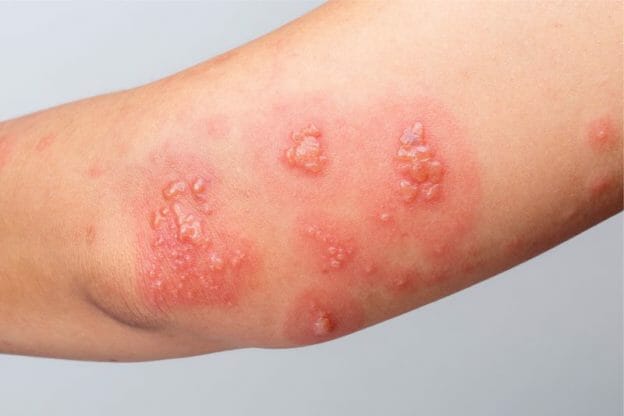 |  |
Gabapentin and Lyrica are generally considered 'first-line' agents for treating the pain associated with shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Alternative treatment options include tricyclic antidepressants, lidocaine, anticonvulsants, SNRI antidepressants and tramadol. Shingles can cause severe pain, so your health care provider also may prescribe: Capsaicin topical patch (Qutenza) Anticonvulsants, such as gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) Reach out to your doctor if you have received a shingles diagnosis, are undergoing treatment, and experience any of the following: if your rash is more painful than before if the rash becomes infected Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant initially developed and approved as adjunctive therapy for treatment of partial seizures, often used for the treatment of neuropathic pain. It is an analogue of gamma aminobutyric acid and binds to the α 2 -δ site of voltage-dependent calcium channels, thereby reducing neurotransmitter release [ 18 ]. Gabapentin does not work to treat the virus-causing shingles, but rather it is used to address the pain from nerve damage that can occur in certain individuals at higher risk of developing complications from shingles, termed postherpetic neuralgia. Antiviral Medications: Help reduce severity and duration of shingles. OTC Pain Relievers: Provide temporary relief for mild nerve pain cases. Prescription Options: Gabapentin and pregabalin are effective for chronic pain. Topical Treatments: Lidocaine patches and capsaicin cream target localized pain. Gabapentin, a structural analogue of γ-aminobutyric acid, has been used for the treatment of PHN for decades, and the results of several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) show that it is a well-tolerated and efficacious treatment in patients with PHN . However, gabapentin used for the prevention of PHN has shown contradictory results. Treatment includes antiviral drugs and pain relief options like gabapentin and lidocaine to manage symptoms and accelerate healing. Comprehensive patient education and timely vaccination are essential in reducing the burden of shingles and preventing complications. Roughly 30% to 60% of people over age 60 who get shingles go on to develop a chronic pain syndrome called post-herpetic neuralgia. Learn about treatment options from a pain management specialist. Duration of Treatment: Gabapentin is taken for 7 to 14 days for shingles pain. Dosage Guidelines: Initial doses start low, increasing based on tolerance. Consult Healthcare Providers: Always discuss treatment options and adjustments. Pain Management: Gabapentin effectively reduces postherpetic neuralgia pain. Lifestyle Modifications:Lifestyle Only six-percent developed PHN, compared to 26-percent who were not taking gabapentin ahead of time. The bottom line is that gabapentin can help with nerve pain from shingles, and might work well for those who develop post-herpetic neuralgia after the shingles rash disappears. In summary, I recommend speaking to your doctor about medications like gabapentin or pregalbin and whether to get the shingles vaccine to perhaps decrease the risk of future episodes. Robert Ashley, MD , is an internist and assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Gabapentin is used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type nerve pain that can occur due to an outbreak of shingles, and restless legs syndrome (RLS), an uncomfortable urge to move your legs around, often at night. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) can be used for treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Amitriptyline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), and desipramine can be used for pain relief in Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications. This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. These may include gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica). A doctor will prescribe a low dose and adjust as needed. You may experience side effects from the medication, and it can take a Patient global impression of change at endpoint: intent-to-treat population. Adapted from Sang et al. 17 The clinical efficacy seen with gabapentin extended-release parallels that shown in studies using three times daily dosing of gabapentin immediate-release in the 1800–3600 mg total daily dose range. 20, 21 A meta-analysis by Edelsberg et al 22 evaluated data from randomized controlled Some studies show that various alternative treatments, from acupuncture to supplements, can offer relief. The research isn’t complete, but some show promise. Check with your doctor before you try Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that is most commonly used to treat seizures. However, it can also treat postherpetic neuralgia or pain that persists after an attack of shingles. and gabapentin, or oxycontin and gabapentin have demonstrated superior efficacy17,18. Guidelines for General Practitioners on Treatment of Pain in Post-Herpetic Neuralgia From The Shingles Support Society. 41 North Road, London N7 9DP – created 24-2-2010; revised 2-10-2018
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | -Cap-100mg-UK-1.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |