Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
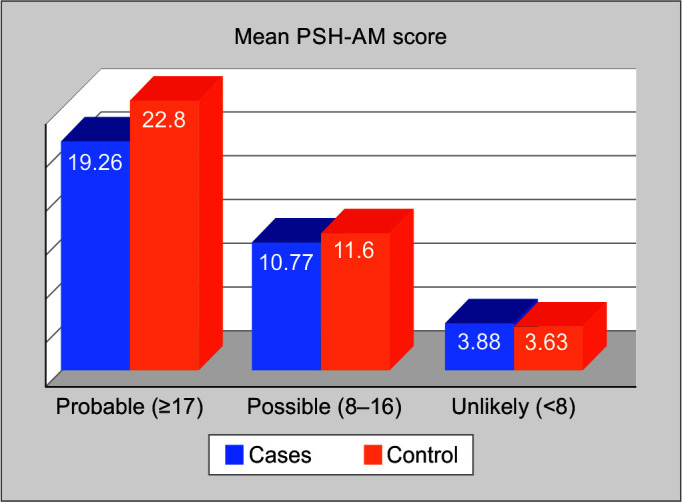
This study represents the first prospective investigation aimed at assessing the impact of gabapentin on TBI patients, focusing on the prevention of secondary brain injury and brain edema while enhancing the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). 38. Massagli T. Neurobehavioral effects of phenytoin, carbamazepine, and valproic acid: Implications for use in traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med and Rehabil 1991;72:219-225. 39. Dikmen S, Machamer J, Winn H, et al. Neuropsychological effects of valproate in traumatic brain injury. Neurology 2000;54:895-902. 40. Chatham-Showalter P, Kimmel DN. Keywords: traumatic brain injury, pharmacologic therapies, psychopharmacology, neuroprotectants. 1. Introduction. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a sudden injury that causes damage to the brain. Sixty-nine million individuals worldwide are estimated to sustain a TBI each year . Pharmacologic therapies play important roles in mild to severe TBI. Keywords: neurorecovery, dose exploration, spinal cord injury, gabapentin, traumatic. Introduction. Gabapentin is an FDA-approved medication initially indicated for the treatment of seizures. Its action as an anticonvulsant is related to its ability to bind to the α2δ subunits of voltage-sensitive calcium channels . This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such as with peripheral neuropathy, various types of nerve damage, nerve pain following shingles, injury, or multiple sclerosis. This paper presents six subjects with dysautonomia following extremely severe traumatic brain injury where gabapentin controlled paroxysmal autonomic changes and posturing in the early post‐acute phase following limited success with conventional medication regimens. (1997). Psychomotor agitation following gabapentin use in brain injury. Brain Injury: Vol. 11, No. 7, pp. 537-540. Intracranial hypertension, anxiety, agitation, pain, paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity (PSH) and seizures lead to use of prolonged and large dosages of sedating intravenous infusion medication (SIIM) in severe TBI (sTBI). Gabapentin (GBP) is a potential adjunct or alternative for this role. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major public health problem worldwide that is associated with increased mortality and morbidity. Posttraumatic epilepsy (PTE) is one of the sequelae of TBI. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) as an adjuvant on the efficacy of Here, we showed that gabapentin reduced brain tissue injury in ICH through suppressing NFκB-mediated neuroinflammation. ICH was induced by injecting collagenase IV into the right striatum of Sprague–Dawley rats. PC12 and BV2 cells injury induced by Hemin were used to simulate ICH in vitro. Two patients with a traumatic brain injury who presented to a neurorehabilitation unit complaining of pain that was diagnosed as neurologically mediated are described, and within one week of receiving a daily 900 mg dose of gabapentin, both patients complained of heightened anxiety and restlessness. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant structurally related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was RESULTS: The mean values of GCS and GOS before and after the treatment were not significantly different between the groups. This study showed significant changes in EEG patterns after treatment We conducted this prospective study to primarily investigate the impact of gabapentin on TBI. The study focuses on the role of gabapentin to avert secondary brain injury, mitigating brain edema, and improving the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Prospective observational cohort study. To assess the effects of gabapentin on neuropsychological variables including memory, attention, and executive function in individuals with spinal cord injury. The study focuses on the role of gabapentin to avert secondary brain injury, mitigating brain edema, and improving the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Additionally, our research delves into the effects of gabapentin on preventing dysautonomia/PSH stemming from secondary injury and any associated drug side effects. TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINES Gabapentin, Lamotrigine -Not as well studied -Reports of negative effects, such as anxiety and agitation [38],[39],[40] Patients recover from a concussion with time, regardless of medication. Gabapentin and TCAs appear to have immediate effects on improving symptom burden, but long-term outcomes show similar improvement compared to those who are not prescribed medication. More rigorous prospective studies are require In the present study we administered gabapentin intravenously 20 minutes before brain injury induced by transient MCA occlusion/reperfusion and found a significant reduction in infracted area in the 5 mg/kg gabapentin group. These two cases suggest that gabapentin may cause agitation in cognitive impaired patients. Physicians treating brain-injured patients and prescribing gabapentin for neuropathic pain may wish to closely monitor patients for similar signs of restlessness or anxiety. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in brain tissue injury during intracerebral hemorrhage. Gabapentin can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signals. Here, we showed that gabapentin reduced brain tissue injury in ICH through suppressing NFκB-m
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |