Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
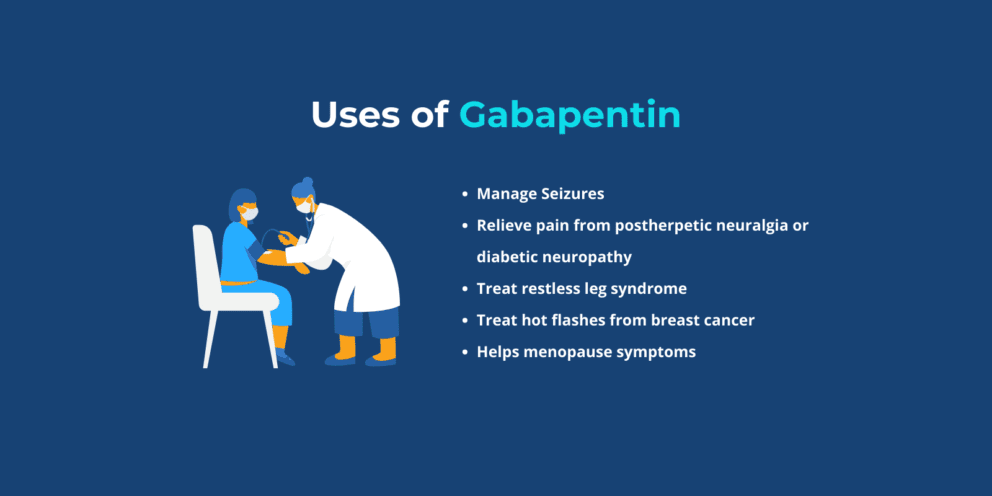
Gabapentin is an established pharmaceutical used to treat seizures and pain. Gabapentin is safe and well-tolerated when used as prescribed. However, misuse has skyrocketed among recreational and dependent opioid users to enhance effects and relieve withdrawal. Combined gabapentin and opioid use comes with a substantial risk of overdose and death. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Reports note that gabapentin is often used by people abusing other medicines, such as opioid painkillers like oxycodone, muscle relaxants, and anxiety medications such as Valium and Xanax to boost the high. What are the most common gabapentin withdrawal symptoms? Withdrawal symptoms after abruptly stopping gabapentin may include: agitation; anxiety Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. The Symptoms of gabapentin addiction may include Increased tolerance, needing higher doses for the same effect, and withdrawal symptoms when use is discontinued Objective: To identify case reports and studies regarding patients who abused, became dependent on, or experienced withdrawal from gabapentin. Data sources: A PubMed literature search (1993 to October 2015) was performed using the search terms gabapentin, withdrawal, dependence, and addiction. Additional references were identified from a review Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under a doctor's advice. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be reduced for kidney disease. Rarely do hypersensitivity reactions occur. Symptoms may include fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, swollen facial features, or throat swelling. People who develop physical dependence to gabapentin may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to come off it. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. Signs of addiction include taking higher doses and seeking more prescriptions. Symptoms of Gabapentin Withdrawal. Going through Gabapentin withdrawal can be challenging, but being aware of the potential withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin can help you prepare. Here are some common signs that may appear when you begin to taper off or stop taking Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Stop taking gabapentin and get help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction. Swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat Breathing problems or Continuing to use, despite awareness of negative consequences related to gabapentin use; Development of tolerance to gabapentin; Withdrawal symptoms when gabapentin use is discontinued; Someone who has an addiction to gabapentin may demonstrate some, or all, of the above-listed symptoms, depending on the stage of their addiction. Those who are Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. These symptoms may be the first signs of a serious reaction: Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms. If you think your symptoms are life threatening, call 911. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin is not likely to cause addiction, but it may lead to dependence or misuse under certain conditions. As such, doctors prescribe gabapentin carefully to avoid withdrawal symptoms and Gabapentin Detox and Treatment. Abruptly stopping gabapentin use can increase the likelihood of seizures, so it’s important to seek help when looking to quit using this drug. 4 If you are getting treatment for a gabapentin abuse problem, you will likely start with detox so that you can slowly eliminate the drug from your body in a controlled manner. Gabapentin (often prescribed under its brand name Neurontin) is an anti-convulsant/sedative medication used to treat a wide range of medical issues, ranging from partial seizures to shingles-related nerve pain and restless leg syndrome. 1 It is also commonly used off-label to treat an even wider variety of physical and mental health concerns, including fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain, and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |