Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
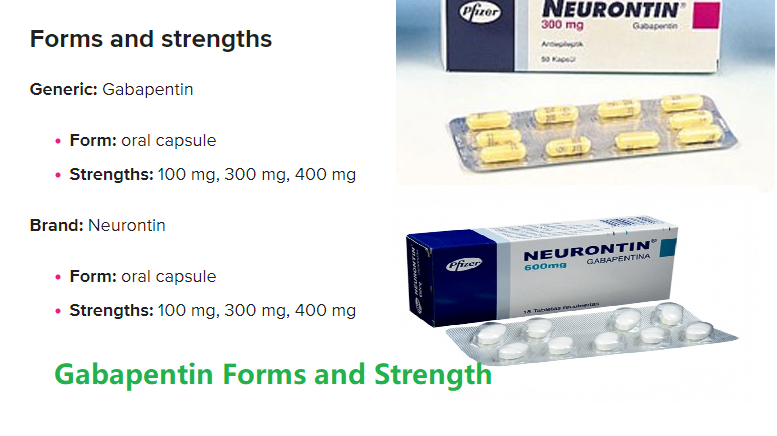
Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin appears to be effective and well tolerated for the short-term treatment of PHN. However, future controlled studies are needed to determine whether the effectiveness of gabapentin for PHN is maintained for > 2 months, to establish the optimal dose of gabapentin for PHN, and to compare t Conventionally, the treatments used for pain alleviation in acute herpetic neuralgia are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), oxycodone, morphine, amitryptyline, and nortryptyline having variable efficacy and side effects.[2,3] Gabapentin is used successfully in the treatment of post herpetic neuralgia (PHN) and other painful Previous trials have reported that gabapentin can relieve chronic neuropathic pain, but its effect on prevention of PHN is unclear. To assess the efficacy of a 5-week course of gabapentin on acute herpetic pain and on the prevention of PHN at 12 weeks in patients with acute HZ. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) can be used for treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Amitriptyline, nortriptyline (Pamelor), and desipramine can be used for pain relief in Gabapentin appears to exert its effect via the α2δ1 and α2δ2 auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. It is used to manage pain and provide sedation in neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is primarily used for the treatment of PHN. It has also been used to treatment the pain of acute zoster. Although herpes zoster can occur at any age, it is more commonly a disease of adults >50 years of age. In addition, the severity and complications of herpes zoster are much more common in this age group. The treatment of herpes zoster will be reviewed here. Two randomized controlled trials 18, 19 support the use of gabapentin (Neurontin) to treat postherpetic neuralgia with an NNT of 3 in one trial and 5 in the other. The dosage was started at 300 mg Adverse effects of gabapentin were minor and well tolerated, consisting primarily of somnolence and dizziness. These 2 adverse effects accounted for most of the adverse event–related withdrawals. Despite doses of gabapentin up to 3600 mg/d in a population with an average age of 73 years, no serious drug-related adverse events were reported. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain from shingles and herpes. It reduces pain by changing the pathway of pain sensation in post-herpetic neuralgic patients. In addition, it treats seizures by reducing hyperactivity or abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin immediate-release is commonly used for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. It is efficacious but is associated with a high incidence of dose-limiting side effects, namely dizziness (28% versus 8% for placebo) and somnolence (21% versus 5% for placebo). Previous trials have reported that gabapentin can relieve chronic neuropathic pain, but its effect on prevention of PHN is unclear. To assess the efficacy of a 5-week course of gabapentin on acute herpetic pain and on the prevention of PHN at 12 weeks in patients with acute HZ. Gabapentinoids (e.g., gabapentin and pregabalin) have been established as a treatment for postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), but their effects on the prevention of PHN are unclear. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy of gabapentinoids for acute herpes zoster (HZ) in preventing PHN. Gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia. Postherpetic neuralgia³ is a possible lasting consequence of a shingles infection. The condition causes a person to continue feeling the pain associated with blisters and skin lesions even after the skin lesions heal. Patients with herpes zoster who are at least 50 years old and have a pain score of 4 or higher on a visual analogue scale (VAS) will be recruited. The aim is to recruit 134 patients from the practices of general physicians. Participants will be randomized to receive gabapentin to a maximum of 1800 mg/day for 5 weeks or placebo. Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain that results from alterations of the peripheral nervous system in areas affected by the herpes zoster virus. The symptoms include pain, paresthesia, dysesthesia, hyperalgesia, and allodynia. The addition of gabapentin to valacyclovir within 72 hours of onset of a herpes zoster rash was not found to provide further relief from acute herpetic pain or to better prevent postherpetic Neurontin is used in adults to treat neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster). Neurontin is also used to treat seizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old. Use only the brand and form of gabapentin your doctor has prescribed. Our results indicate that the use of low-dose gabapentin in acute herpes zoster seems not effective in the prevention of PHN. Keywords: gabapentin; herpes zoster; postherpetic neuralgia. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Objective: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of acute herpes zoster (HZ) neuralgia, including pain control and the occurrence of adverse effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |