Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
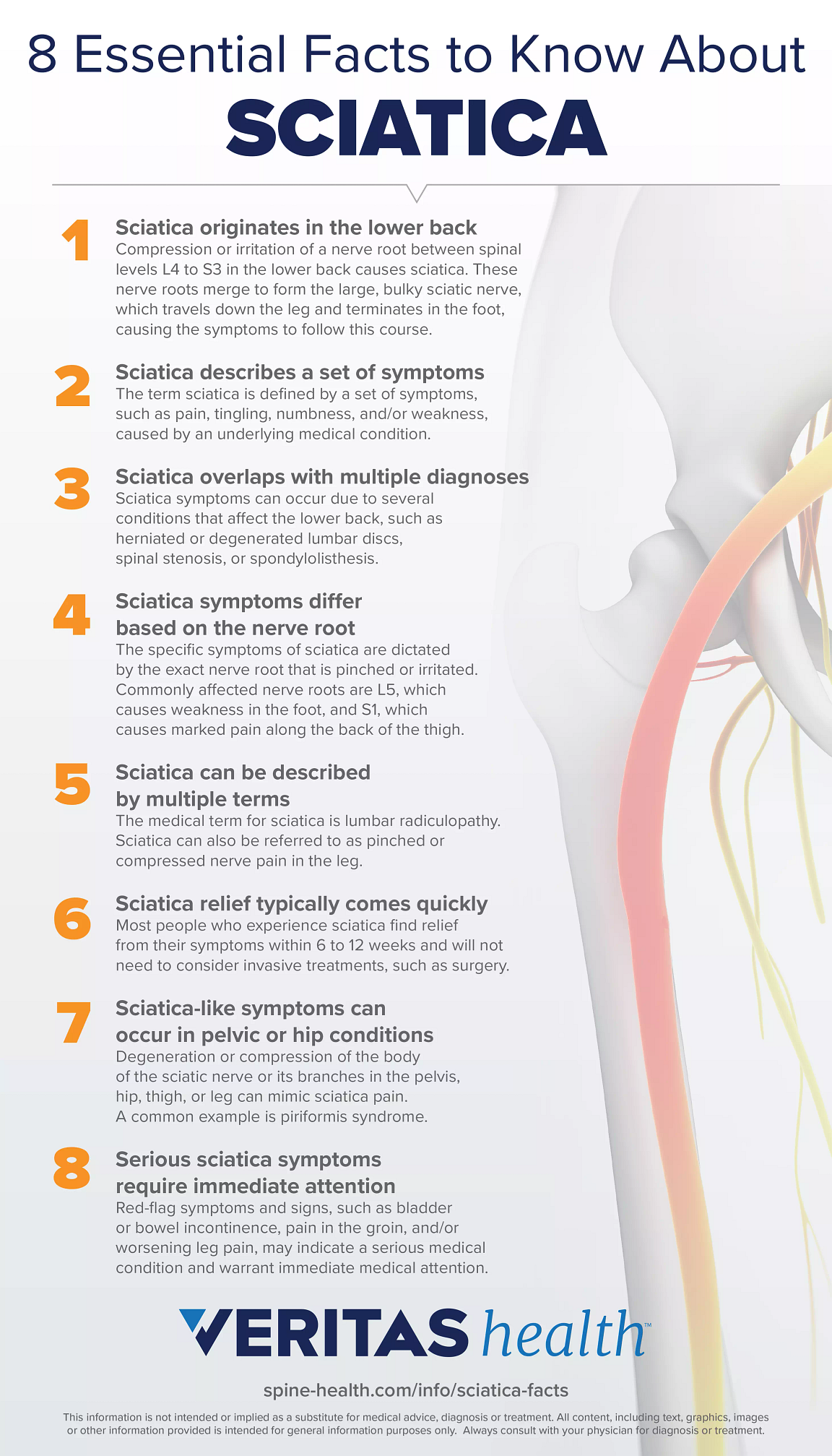
Gabapentin belongs to the anticonvulsant class of medications that treat pain due to convulsions or nerve damage, especially in the lower back and legs. It works for sciatic pain in several ways, from binding to calcium channels on nerve endings to calming the nerve signals that are hyperactive due to pain and eventually improving pain Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gralise (gabapentin) is only used for pain after having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It should not be used for any other medical condition. Esta revisión sistemática ofrece evidencia clara de la falta de pruebas sobre la efectividad de pregabalina o gabapentina para el manejo del dolor derivado de la ciática. Por tanto, su uso clínico rutinario no está avalado. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. Gabapentin (Neurontin, 900 to 3,600 mg per day) Verbaan D, Jacobs WC, et al. Surgery versus prolonged conservative treatment for sciatica: 5-year results of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Both gabapentin (GBP, Neurontin) and pregabalin (PGB, Lyrica) are used to treat chronic sciatica (CS). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an important pain-related neurotransmitter, although neither GBP nor PGB affect the GABA receptor. Gabapentin can help relieve sciatica, intense pain that runs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back through the hips and buttocks (12). Sciatica affects one side of the body and is usually caused by disk herniation or spinal stenosis (12). How Gabapentin Helps with Sciatica Pain. Gabapentin’s ability to alleviate sciatica pain lies in its mechanism of action. By modulating the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception, Gabapentin can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain signals traveling from the sciatic nerve to the brain. For those at their wits end with endless sciatica flare ups, gabapentin could provide much needed respite. In this article, we’ll explore the growing body of research on gabapentin for sciatica and how this medication is giving new hope to sciatica sufferers. Treatment of back pain has undergone a recent sea change. Experts now appreciate the central role of exercise to build muscles that support the back. This Special Health Report, Back Pain: Finding solutions for your aching back, helps you understand why back pain occurs and which treatments are most likely to help. This report describes the There is currently an absence of high-grade evidence regarding the treatment of chronic sciatica (CS). Whilst gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are both currently used to treat CS, equipoise exists regarding their individual use. In particular, no head-to-head study of GBP and PGB in CS exists. Whilst pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are both used to treat neuropathic pain, their relative role in sciatica is unclear. Our aim was to extensively review the roles of PGB and GBP in treating sciatica. The efficacy, side effects (SE) profile and cost of PGB and GBP in neuropathic pain state No evidence supports the use of pregabalin or gabapentin for sciatica pain or low back pain, as their effectiveness is not superior to placebo. Additionally, reported adverse effects raise concerns, making their routine clinical use unsupported. Treatment. For pain that doesn't improve with self-care measures, some of the following treatments might help. Medications. The types of medicines that might be used to treat sciatica pain include: Anti-inflammatories. Corticosteroids. Antidepressants. Anti-seizure medications. Opioids. Physical therapy Sciatica is commonly seen in primary care. Its prevalence in the general population varies between 3% and 14%, depending on the definition used. 1 The prognosis of acute sciatica is generally favourable: data from a prospective study of 183 patients with a median disease duration of 16 days show that in approximately one third of patients, symptoms improve greatly (ie, measured on a 4 point Gabapentin is widely prescribed for management of peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes. To our knowledge, however, these two case reports are the first to describe sciatica successfully controlled with gabapentin. But it’s also commonly used off-label to treat other types of nerve pain, including back pain. Although healthcare professionals often prescribe gabapentin, high-quality studies show that gabapentin doesn’t work well to treat all types of back pain. Evidence suggests that gabapentin works best for nerve pain caused by diabetes and shingles. Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are both used to treat neuropathic pain, but their precise role in sciatica has been under-explored. The amount and quality of evidence for their use is low. Weak evidence suggests efficacy and side effect profiles of PGB and GBP in sciatica are similar. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is commonly used to treat nerve pain caused by diabetes (diabetic neuropathy). It’s also been studied for treatment of chronic sciatica. Early evidence suggested that gabapentin was more effective at reducing sciatic nerve pain when compared with placebo. But further evidence shows it’s not as helpful as initially
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |