Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
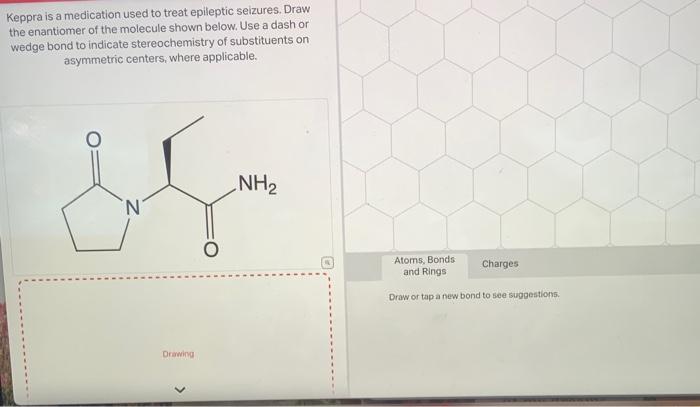
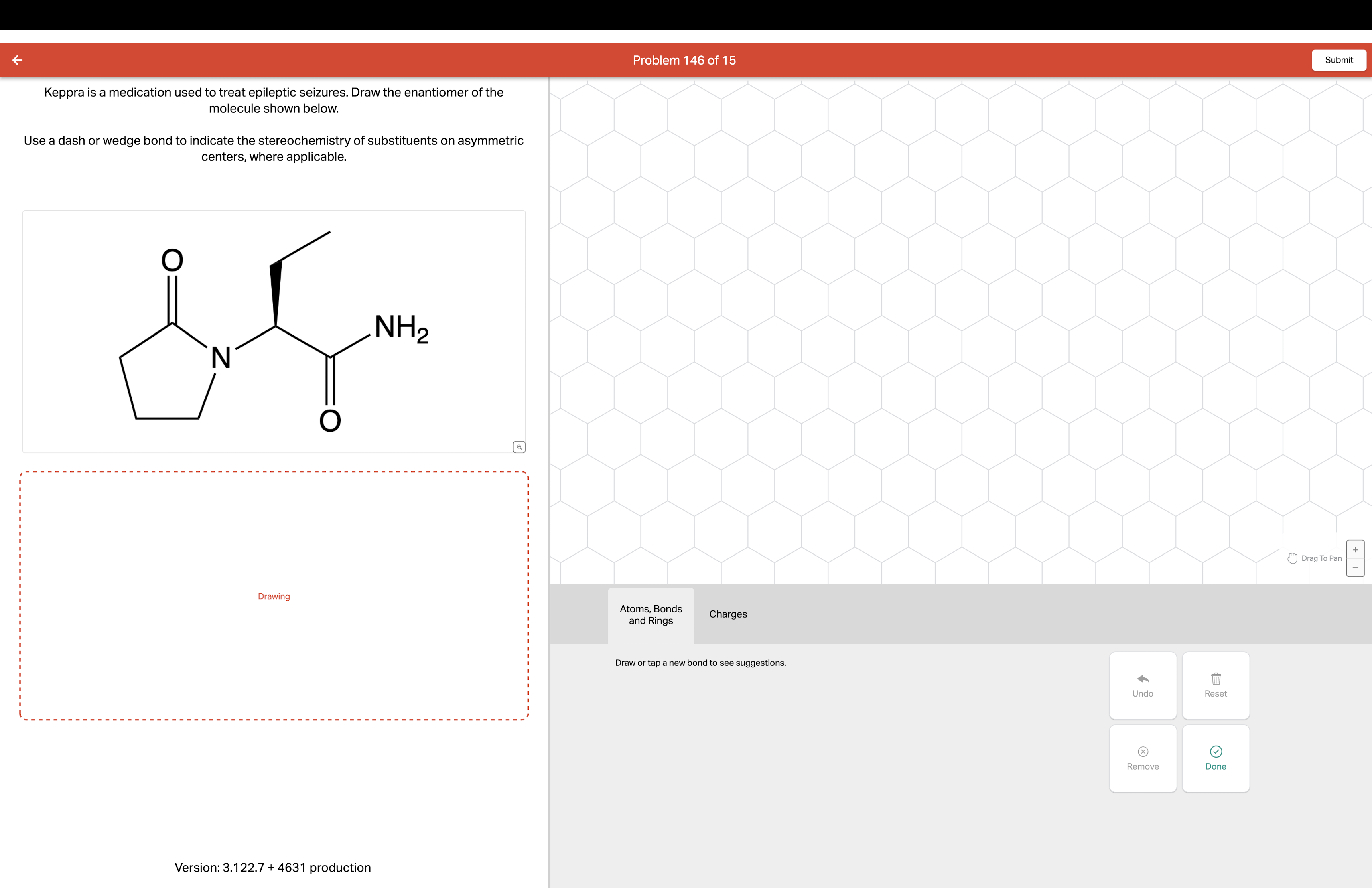
Abstract. Many studies investigated the use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) in several neurological diseases other than epilepsy. These neurological disorders, usually, involve neuronal excitability through the modulating of ion channels, receptors and intracellular signaling pathways, and are the targets of the AEDs. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Levetiracetam (Keppra) are both antiepileptic medications, but they have some key differences. Gabapentin is used to treat certain seizures and nerve pain, while Levetiracetam is used for various types of seizures, including partial-onset, myoclonic, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Studies have shown that Keppra is more effective in reducing seizure frequency and severity compared to Gabapentin. One of the key advantages of Keppra is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier quickly, allowing it to reach therapeutic levels rapidly. This makes it an ideal choice for emergency situations where time is of the essence. Usually, a single medication can help people with epilepsy keep their seizures under control. But if one medication is only partially effective for you, your doctor may sometimes add another drug. Or your doctor may choose to combine your medication with surgery, an implanted device, or a special diet. 238 medications are known to interact with Keppra. Includes gabapentin, trazodone, sertraline. This review focused on the use of gabapentin in drug‐resistant focal epilepsy and the results could not be generalised to add‐on treatment in people with generalised epilepsy. Likewise, no inference can be made about the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin when used as monotherapy. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may Two studies have examined the use of gabapentin in refractory canine epilepsy. The first study involved 11 dogs administered gabapentin (10 mg/kg t.i.d.) in addition to phenobarbital and potassium bromide.8 A positive response to gabapentin, defined as ≥ 50% reduction in seizure frequency, was reported in six of the 11 dogs. Results: Both levetiracetam (25-100 mg/kg) and gabapentin (6.25-25 mg/kg) significantly reduced PBBI-induced seizure frequency by 44% to 73% and 61% to 69%, and seizure duration by 45% to 64% and 70% to 78%, respectively. However, the two drugs manifested different dose-response profiles. It is legal (and common) to prescribe medicines for so-called off-label uses even though the FDA has not formally approved such use. So gabapentin is often used "off-label" for many types of pain as well as for some mood disorders, such as anxiety. In fact, more people have taken gabapentin to treat pain than to control seizures. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Keppra is an anticonvulsant that is used in conjunction with other medications for the treatment of certain types of seizures. Gabapentin. Gabapentin is used as a pain-relieving medication and anticonvulsant. A 2005 study investigated gabapentin as an add-on anticonvulsant in dogs with refractory seizures and found that in a 4-month period, 3 of 17 dogs were seizure-free and 4 other dogs had a 50% reduction in seizure frequency. Gabapentin has been used in cats at 5–10 mg/kg, bid-tid. Felbamate: Felbamate is a dicarbamate AED that exerts its anticonvulsant effects through multiple mechanisms, including potentiating GABA-mediated neuronal inhibition, inhibiting voltage-sensitive neuronal calcium and sodium channels, and blocking N-methyl- d -aspartate–mediated We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gabapentin and Keppra. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 565,459 people who take Gabapentin and Keppra, and is updated regularly. Gabapentin < Back to All Medications. Brand Names: Neurontin, generics What is Gabapentin used for? Gabapentin (GA ba PEN tin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. Drug interactions are reported among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) and Keppra (levetiracetam). Common drug interactions include weight decreased among females and asthenia among males. The phase IV clinical study analyzes what interactions people have when they take Gabapentin and Keppra, and groups them by gender, age and more. Keppra vs Gabapentin: Keppra (levetiracetam) is primarily used to treat seizures, while Gabapentin targets nerve pain and some seizure types. Keppra has fewer drug interactions, but Gabapentin may cause more sedation. In patients with epilepsy, steady-state predose (C min) concentrations of gabapentin in cerebrospinal fluid were approximately 20% of the corresponding plasma concentrations. Elimination Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin has been used in randomized control trials (RCTs) of neuropathic pain and was proven effective.40 Its use and effectiveness were also reported in several TN studies.41,42 Gabapentin showed adequate efficacy in only one RCT, where it was used in combination with ropivacaine.43 This combination was found to be safe and effective. Applies to: gabapentin and Keppra (levetiracetam) Using gabapentin together with levETIRAcetam may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |