Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
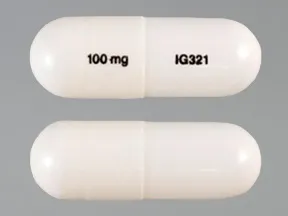
For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic. But certain products are brand-only. Each tablet contains 600mg or 800mg of gabapentin. If you're taking gabapentin as a liquid, 2ml is usually the same as taking a 100mg tablet or capsule. Always check the label. The usual dose for: The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. Initial dose: 300 mg on day one, 300 mg twice daily on day two, and 300 mg three times daily on day three. Maintenance dose: 900-1800 mg per day, divided into three doses. Treatment is typically long-term. Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose Neurontin: Gabapentin belongs to the class of medications called anti-epileptics. It is used in combination with other seizure control medications to manage and prevent seizures associated with epilepsy. Gabapentin does not cure epilepsy and only works to control seizures as long as the medication is taken. Gabapentin works by affecting the transmission of nerve signals in the brain. Take gabapentin by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once a day with the evening meal. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Swallow gabapentin whole. Do not crush or chew sustained-release tablets. Doing so can release all of the drug at once, increasing the risk of side effects. How is gabapentin supplied (dosage forms)? Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. Pharmacodynamics. Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 This article discusses gabapentin and its uses, how long it takes to treat nerve pain, dosage recommendations, side effects, and more. Safety Warning Taking antiepileptic drugs like gabapentin can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription. This product is available in the following dosage forms: In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. Gabapentin is used to: Prevent and control partial seizures. Gabapentin can be used in adults and children age 3 and older who have partial seizures. Relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults. Shingles is a painful rash that develops many years after you've had chickenpox. Data from a limited number of clinical trials support the use of ER gabapentin in reducing pain by more than 50% and improving sleep in diabetic neuropathy Sandercock 2009, Sandercock 2012. A meta-analysis of trials evaluating the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia supports the use of gabapentin in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia Yuan 2016. Additional smaller gabapentin dosage groups (600 mg/day, N=53; 1800 mg/day, N=54) were also studied for information regarding dose response. Responder rate was higher in the gabapentin 1200 mg/day group (16%) than in the placebo group (8%), but the difference was not statistically significant. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CNS depressants can result in serious, life-threatening, and fatal respiratory depression. Use lowest dose possible and monitor for respiratory depression and sedation. diazepam intranasal and gabapentin both increase sedation Administer gabapentin three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 11 Years. 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Gabapentin use in elderly patients. Gabapentin can be used in elderly patients, but caution should be exercised due to age-related changes in renal function. A lower starting dose may be necessary to prevent overdose and accumulation of the drug in the body. Monitoring of kidney function is recommended. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients Effective Dose: Reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days; the effective dose in patients 5 years of age and older is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day in divided doses (3 times a day). The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (3 times a day). Additional smaller gabapentin dosage groups (600 mg/day, N=53; 1800 mg/day, N=54) were also studied for information regarding dose response. Responder rate was higher in the gabapentin 1200 mg/day group (16%) than in the placebo group (8%), but the difference was not statistically significant. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |