Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 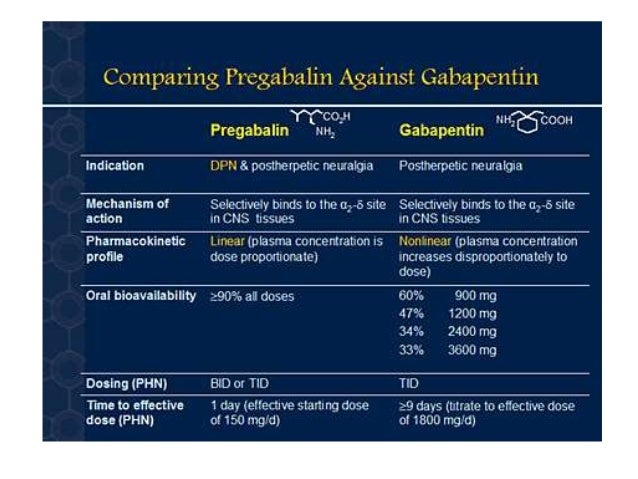 |
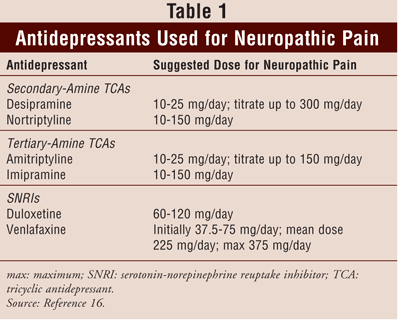
Both gabapentin and amitriptyline are good nerve pain relievers. Amitriptyline can be better for some patients because of the convenient dosing schedule. On the other hand, most patients prefer gabapentin (the relatively newer medication) over amitriptyline due to less anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, constipation) and less sedation. To assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin and amitriptyline along with opioids in patients suffering from neuropathic pain in malignancy. Eighty-eight adult patients between 18 and 70 years of age with neuropathic pain in stage III malignant We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. No statistically significant differences were found between each weekly pain score within each treatment group, ie, amitriptyline at week 0 vs gabapentin at week 7, amitriptyline at week 1 vs gabapentin at week 8, etc (by 1-way analysis of variance and Fisher Protected Least Significant Difference post hoc test for comparing weekly mean pain Gabapentin produced greater improvements than amitriptyline in pain and paresthesia associated with diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, gabapentin was better tolerated than amitriptyline. Further controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results. Gabapentin is less than 3% bound to any plasma proteins. Amitriptyline is greater than 90% bound to α-glycoprotein. Therefore, amitriptyline carries a higher risk of drug interactions owing to protein displacement and is not easily dialyzable in overdose compared with gabapentin. Both gabapentin and amitriptyline provided effective pain control in peripheral neuropathic pain. Additionally gabapentin was more effective especially in paroxysmal shooting pain than other pain qualities. And also gabapentin was tolerated well. The web page discusses a study that compared four medications for idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy, a condition of unknown cause that damages nerve fibers. It mentions gabapentin and amitriptyline as two commonly prescribed drugs, but they were not included in the trial. The first amitriptyline brand was Elavil, which was FDA-approved on April 7, 1961, and has since been discontinued. Other amitriptyline brand names include Vanatrip and Endep, which have also been discontinued. Amitriptyline is now available as a generic medication. Amitriptyline is from the drug class tricyclic antidepressants (TCA). Amitriptyline may be used to treat depression or off-label to relieve chronic pain, fibromyalgia, or insomnia. Experts are unsure exactly how amitriptyline works, although historically it was believed that amitriptyline’s effects for depression were due to its ability to rebalance chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin and/or norepinephrine. However, Amitriptyline is used at a low dose to manage neuropathic pain. Amitriptyline is available as tablets of various strengths (10mg, 25mg and 50mg) and as a liquid oral solution (25mg/5ml that is, every 5ml of liquid contains 25mg of the active ingredient). Thirteen patients received gabapentin and 12 received amitriptyline. All 25 patients completed the trial. Gabapentin produced greater pain reductions than amitriptyline (mean final scores were 1.9 vs. 1.3 points below baseline scores; P = 0.026). Decreases in paresthesia scores also were in favor of gabapentin (1.8 vs. 0.9 points; P = 0.004). Gabapentin produced greater improvements than amitriptyline in pain and paresthesia associated with diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, gabapentin was better tolerated than amitriptyline. Further controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results. Gabapentin produced greater improvements than amitriptyline in pain and paresthesia associated with diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, gabapentin was better tolerated We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Practical insight: Gabapentin is widely favored for nerve-related conditions, while amitriptyline is known for its potency in both pain relief and mood regulation. The latter, though, may not be suitable for individuals sensitive to anticholinergic effects. Compare Amitriptyline vs Gabapentin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and amitriptyline demonstrate similar effectiveness in alleviating neuropathic (NeP) pain. In terms of NPRS score, gabapentin is superior to both pregabalin and amitriptyline. Gabapentin has been reported to have fewer adverse effects, leading to improved patient adherence for long-term use. Amitriptyline alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy. It is recommended by a variety of guidelines as a first or second-line treatment. [14] It is as effective for this indication as gabapentin or pregabalin but less well tolerated. [29] Amitriptyline is as effective at relieving pain as duloxetine. We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gabapentin and Amitriptyline hydrochloride. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 536,141 people who take Gabapentin and Amitriptyline hydrochloride, and is updated regularly.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |