Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
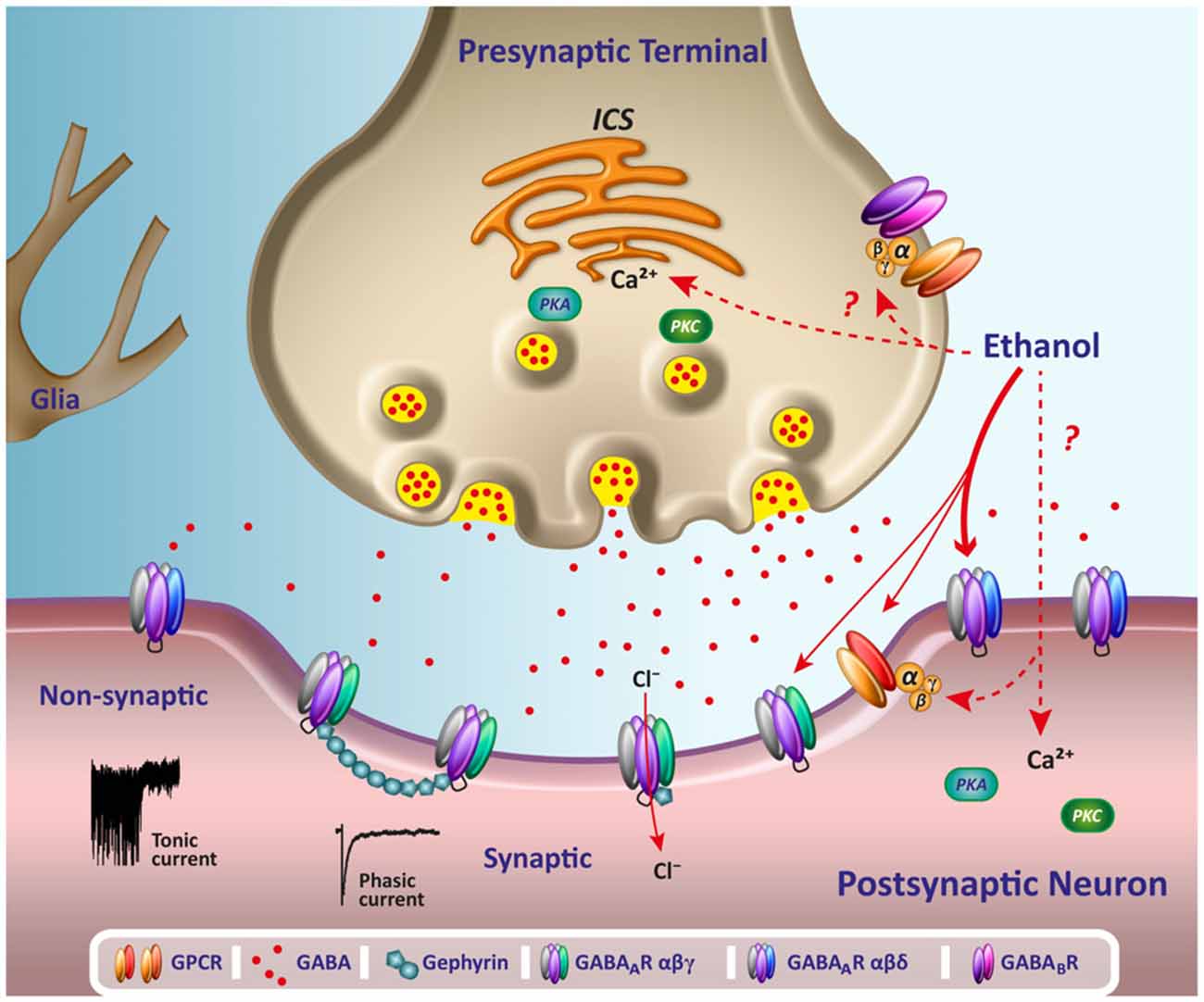
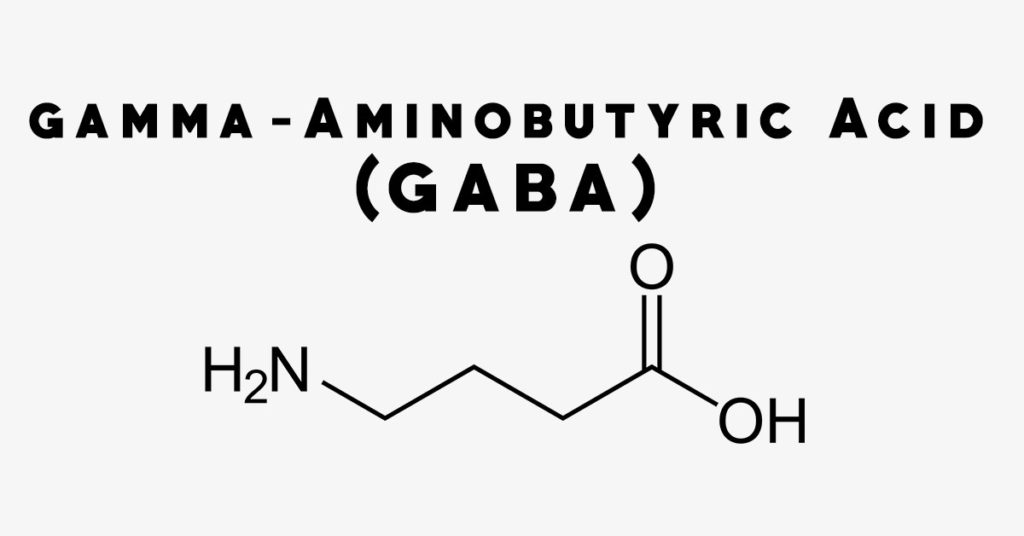
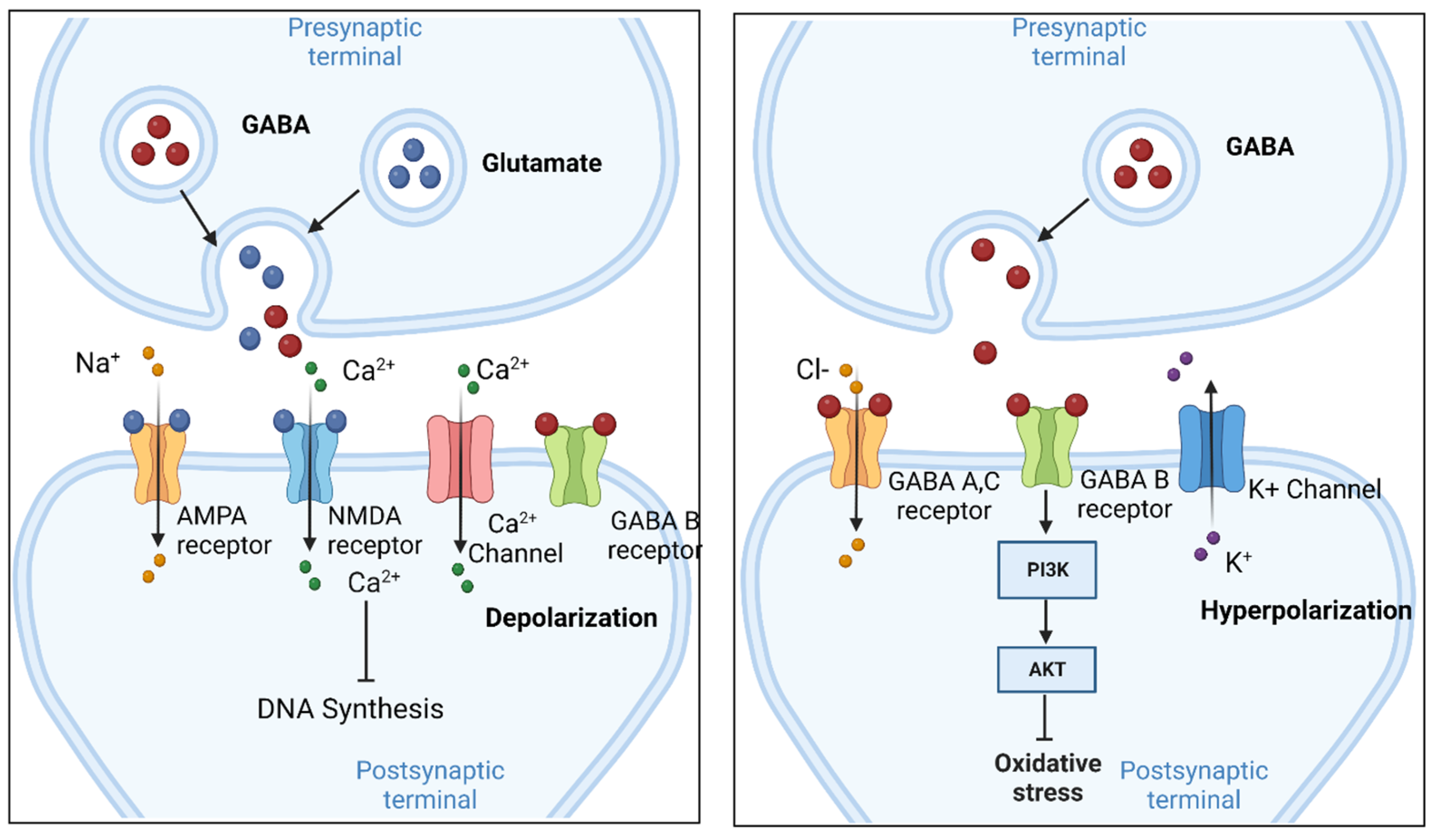
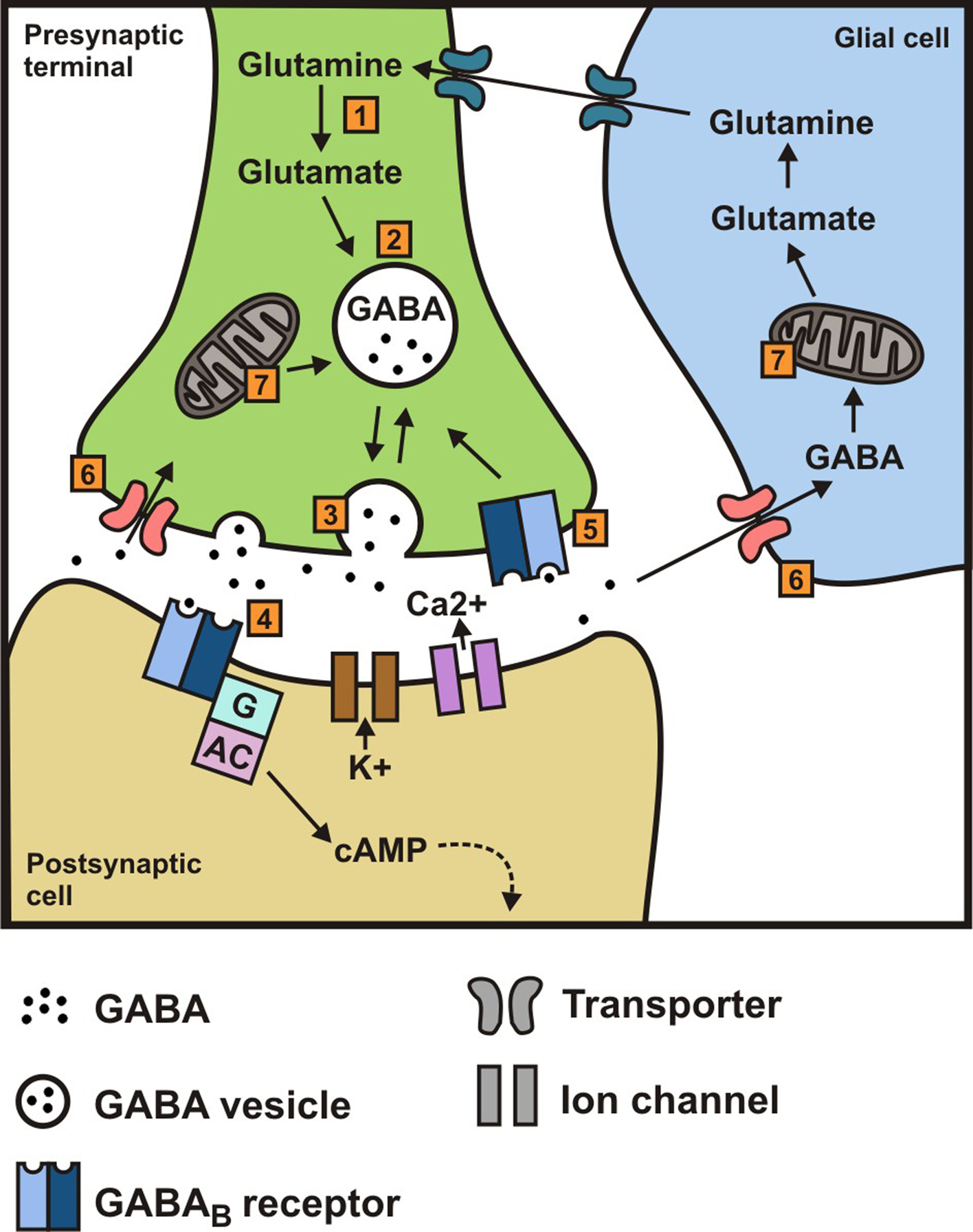
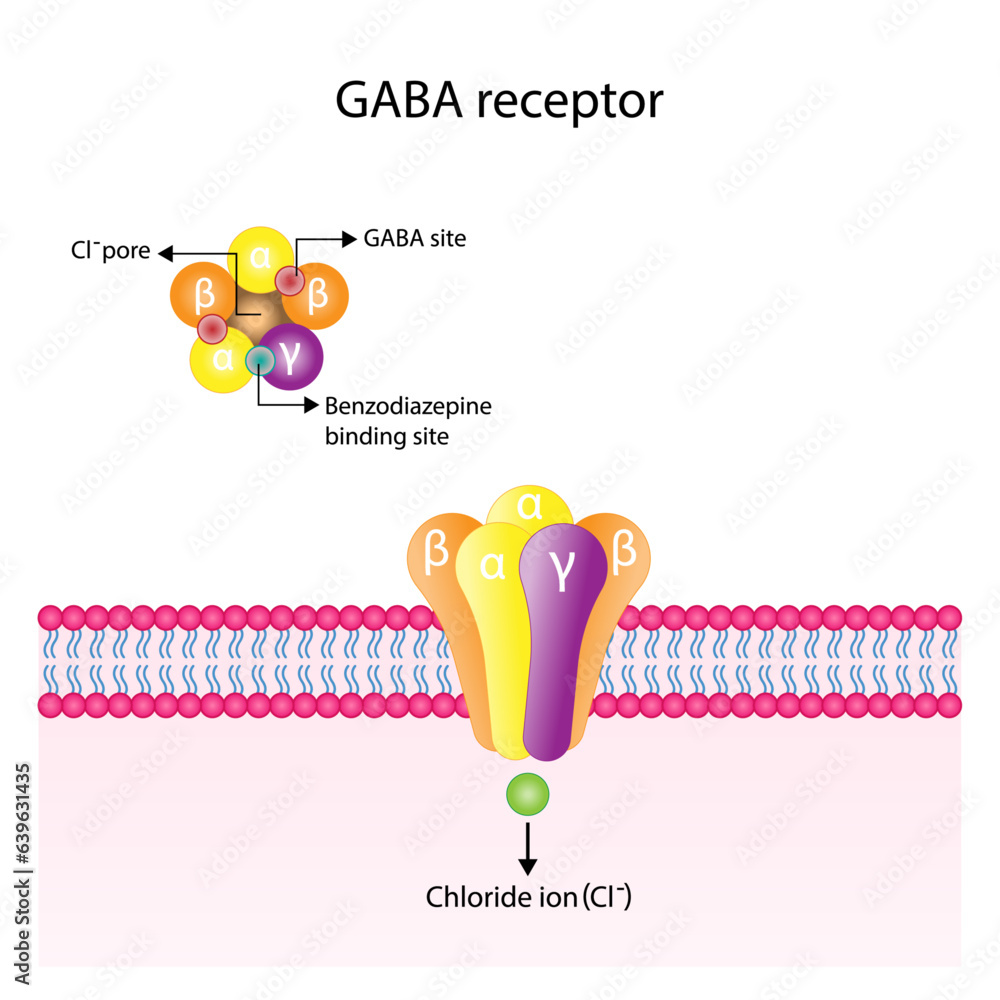
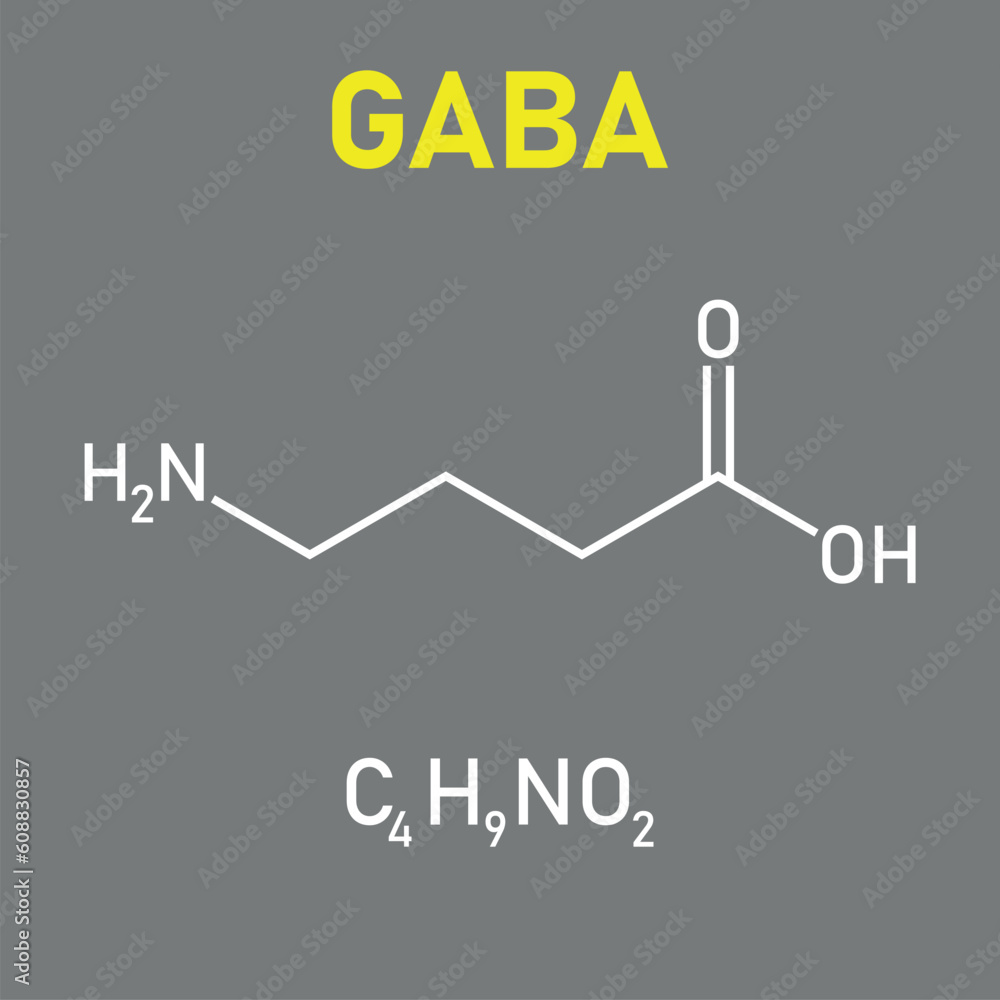
If you supplement GABA, nothing happens in your brain as the GABA cannot cross the blood brain barrier. This means fhat taking extra GABA does nothing. The substance gabapentin is modeled after GABA, but contains a group that helps it cross the BBB (blood brain barrier). It works similarly to GABA in some ways but doesn't do exactly the same thing. GABA, an abbreviation for gamma-aminobutyric acid, serves as the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter within the central nervous system (CNS). Its pivotal role involves the regulation of neuronal activity by diminishing excitation and fostering relaxation. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. While GABA and gabapentin share structural similarities, their mechanisms of action and clinical applications differ significantly. GABA functions as a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, while gabapentin modulates calcium channels to reduce neuronal excitability. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: GABA is a neurotransmitter that directly inhibits neuronal activity, whereas gabapentin is a GABA analog that modulates calcium channels to achieve its therapeutic effects. Understanding these differences is crucial for their effective use in clinical practice. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. GABA and gabapentin are two fundamentally different compounds that share some important similarities. The first, gamma- or γ-aminobutyric acid (or GABA), is a neurotransmitter that serves as a chemical messenger in the brain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major neurotransmitter for fast inhibitory synaptic transmission and tonic inhibitory control, is present in 25–50% of all synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000).L Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both compounds that play important roles in the functioning of the central nervous system. While GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, Gabapentin is a synthetic drug that is structurally similar to GABA. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) was first synthesized in 1883. It was first identified as a biochemical substance in 1910 by Ackermann and Kutscher who showed that putrefactive bacteria could produce it by decarboxylation of glutamic acid. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. These studies suggest that gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and gabapentin are not the same, as gabapentin does not act through GABA(B) receptors and has different therapeutic effects. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Considering both GABA and Phenibut, it is best to let your doctor recommend which drug can be taken as a supplement. What is GABA? GABA is an abbreviation for Gamma-aminobutyric acid. GABA is the neurotransmitter that blocks nerve impulses in your brain. GABA is naturally found in your body and boosts your mood, and gives an overall calm feeling. Scientists also call GABA a non-protein amino acid neurotransmitter. How does gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) work? GABA is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in your central nervous system. Inhibitory neurotransmitters prevent or block chemical messages and decrease the stimulation of nerve cells in your brain. Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) and Gabapentin are two terms that are often mentioned in the context of neurological research and treatment. While they may sound similar and are both associated with the nervous system, they are fundamentally different in their nature and function. Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) and Gabapentin are two substances that often come up in discussions about neurological health, anxiety disorders, and pain management. While they share some similarities in their names and have certain overlapping functions, they are distinctly different in their nature, mechanisms of action, and applications. Gaba (269 reports) Gabapentin (313,472 reports) How the study uses the data? The study is based on gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin (the active ingredients of Gaba and Gabapentin, respectively). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs or brand names) are also considered.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |