Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
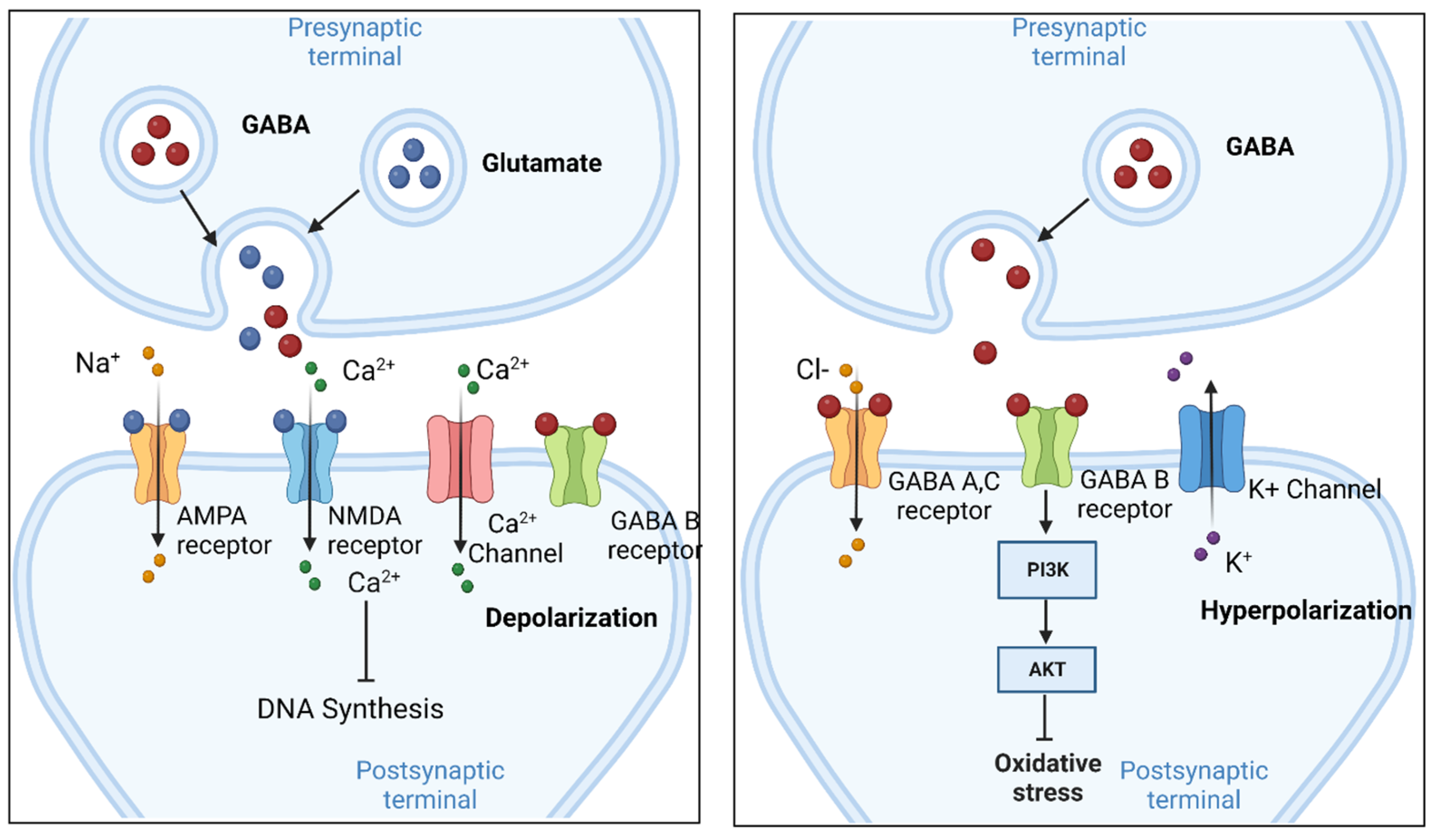
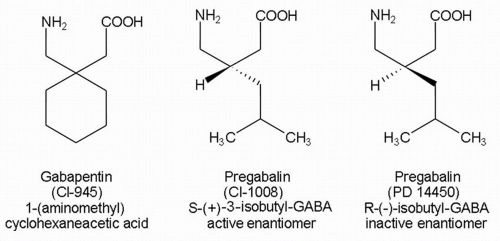
GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Learn the differences between GABA, a natural inhibitory neurotransmitter, and Gabapentin, a synthetic anticonvulsant drug. Find out how they act, what they are used for, and what side effects they may cause. What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. While both relate to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), they are fundamentally different in their origin, mechanism of action, and legal status. In short, over-the-counter (OTC) GABA is a dietary supplement, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. GABA supplements are classified as dietary supplements and can be purchased over-the-counter, while gabapentin requires a doctor's prescription and medical oversight due to its potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Gaba (269 reports) Gabapentin (313,472 reports) How the study uses the data? The study is based on gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin (the active ingredients of Gaba and Gabapentin, respectively). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs or brand names) are also considered. According to a 2020 review, about 1 to 10% of people may experience a sense of euphoria when taking gabapentin, which may increase the likelihood of misuse.And data suggest that 40-65% of people You can take 100 to 300mg sublingual GABA to treat pain flares, or 100 to 200mg of GABA simultaneously with an opioid medication or GABA surrogate for added pain relief. Forest Tennant is retired from clinical practice but continues his research on intractable pain and arachnoiditis. Gabapentin stimulates GAD at drug concentrations of 1.0 to 2.5 mM (Silverman et al, 1991; Taylor et al, 1992) and inhibits the GABA-catabolizing enzyme, GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) at high concentrations (23-25 mM; Taylor et al, 1992) with relatively weak effects on GABA-T at lower concentrations of 10 mM (Goldlust et al, 1995). Neurontin: Gabapentin · Oral capsule: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg · Oral tablet: 600 mg, 800 mg · Oral solution: 50 milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL) Gralise: Gabapentin · Oral tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Horizant: Gabapentin enacarbil · ER tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Lyrica: Pregabalin The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Gabapentin stimulates GAD at drug concentrations of 1.0 to 2.5 mM (Silverman et al, 1991; Taylor et al, 1992) and inhibits the GABA-catabolizing enzyme, GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) at high The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Ativan vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? Ativan and Gabapentin are both medications commonly used to treat anxiety and seizures, but they work in different ways. Ativan is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain, leading to a calming effect. GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners GABA y gabapentina son químicamente similares, pero existen diferencias entre ellos. por ejemplo, composición estructural de los compuestos químicos, aplicaciones, etc. La principal diferencia entre GABA y gabapentina es que GABA es un neurotransmisor inhibidor que puede regular la excitabilidad neuronal en el sistema nervioso central While GABA and gabapentin share structural similarities, their mechanisms of action and clinical applications differ significantly. GABA functions as a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, while gabapentin modulates calcium channels to reduce neuronal excitability. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Gabapentin is a GABA analog that mimics some of the effects of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. Learn how they differ in structure, function, side effects, and uses for epilepsy and pain. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |