Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
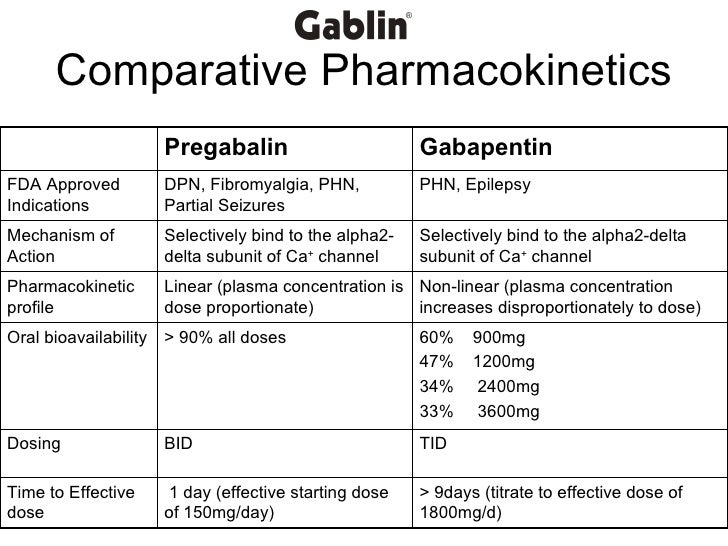
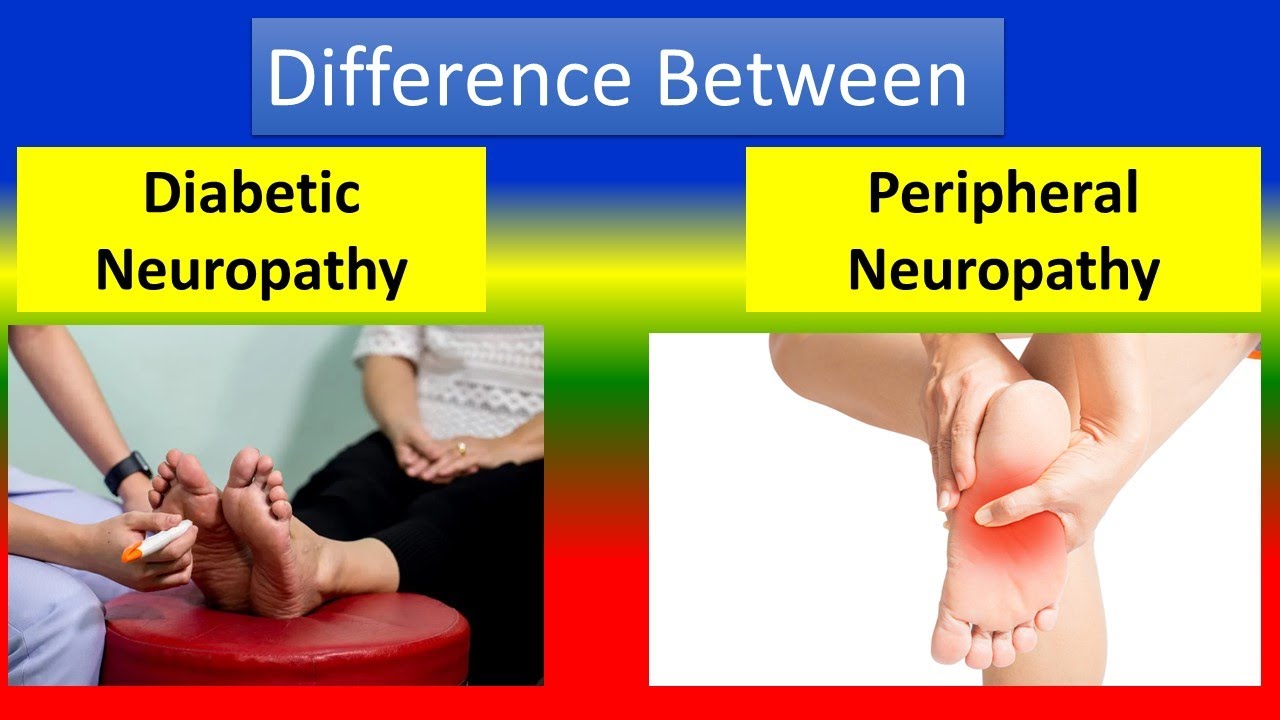
Keywords: Peripheral neuropathic pain, Post-herpetic neuralgia, Diabetic neuropathy, Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Cost-effectiveness analysis. Background. Neuropathic pain (NeP) is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as “Pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system”. Lyrica and gabapentin are two prescription drugs that treat some seizures and nerve pain. Here's a comparison of how the drugs are similar and different. Studies show Lyrica tends to work faster and more predictably for nerve pain, especially for FDA-approved conditions like fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathy. Both medications can cause similar side effects like dizziness and weight gain, require gradual dose adjustment, and should never be stopped suddenly due to withdrawal risks. Gabapentin and Lyrica are similar drugs, but they do have some differences. For example, both drugs come as a capsule or liquid solution that you swallow. But gabapentin also comes as a tablet Pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (except in older adults), or duloxetine (Cymbalta) should be used as first-line treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A 1 Several studies have evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, yielding contradictory results. On one hand, it has been observed that gabapentin is more effective, especially at higher doses, compared to pregabalin (8, 9). Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. %PDF-1.5 %âãÏÓ 1095 0 obj > endobj xref 1095 78 0000000016 00000 n 0000002874 00000 n 0000003245 00000 n 0000003281 00000 n 0000003367 00000 n 0000003447 00000 n 0000003521 00000 n 0000003598 Methods: The analysis was based on a dynamic simulation model which estimated and compared the costs and outcomes of pregabalin and gabapentin in a hypothetical cohort of 1,000 patients suffering from painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) or Post-Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN). In the model, each patient was randomly allocated an average Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are recommended as the first-line treatment for neuropathic pain due to SCI [18,19]. Both drugs have been shown to be effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia [20–26] and diabetic peripheral neuropathy [24–29]. Gabapentin is indicated as adjunct therapy for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia. 4 Pregabalin is indicated for the same uses as gabapentin, plus the management of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain associated with diabetes, specifically diabetic neuropathy. 5 A prospective, randomized, open label, 12-week study that compared the safety and efficacy of gabapentin, duloxetine, and pregabalin in 152 patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Each drug demonstrated a significant reduction in VAS pain scores from baseline over the 12-week period with no significant difference between groups. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. However, pregabalin may also be used to treat nerve pain from diabetes (diabetic neuropathy), nerve pain from spinal cord injuries, and fibromyalgia. Gabapentin may be used for these conditions as well, and it’s viewed as a first-choice medication for diabetic neuropathy. In addition to pain management, in cases of diabetic neuropathy, it is crucial to recommend proper glucose control, as poor control can increase nerve damage and, consequently, neuropathic pain. Fortunately, it has been observed that pregabalin does not affect glucose levels or hemoglobin A1c in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy . Researchers compare four treatments for neuropathy. Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. After 12 weeks, each person rated their neuropathy The particular NNTs for pregabalin and gabapentin were 7.71 and 7.16, respectively. 10 A more recent meta-analysis in 2022 specifically focused on post-herpetic neuralgia and found greater efficacy with pregabalin in alleviating pain and improving global perception of pain and sleep. 15 Another meta-analysis published in 2021 reported similar Compare Lyrica vs Gabapentin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Abstract. Pregabalin is a first-line treatment in all major international guidelines on the management of painful diabetic neuropathy (pDPN). Treatment with pregabalin leads to a clinically meaningful improvement in pain scores, offers consistent relief of pain and has an acceptable tolerance level. Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |