Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
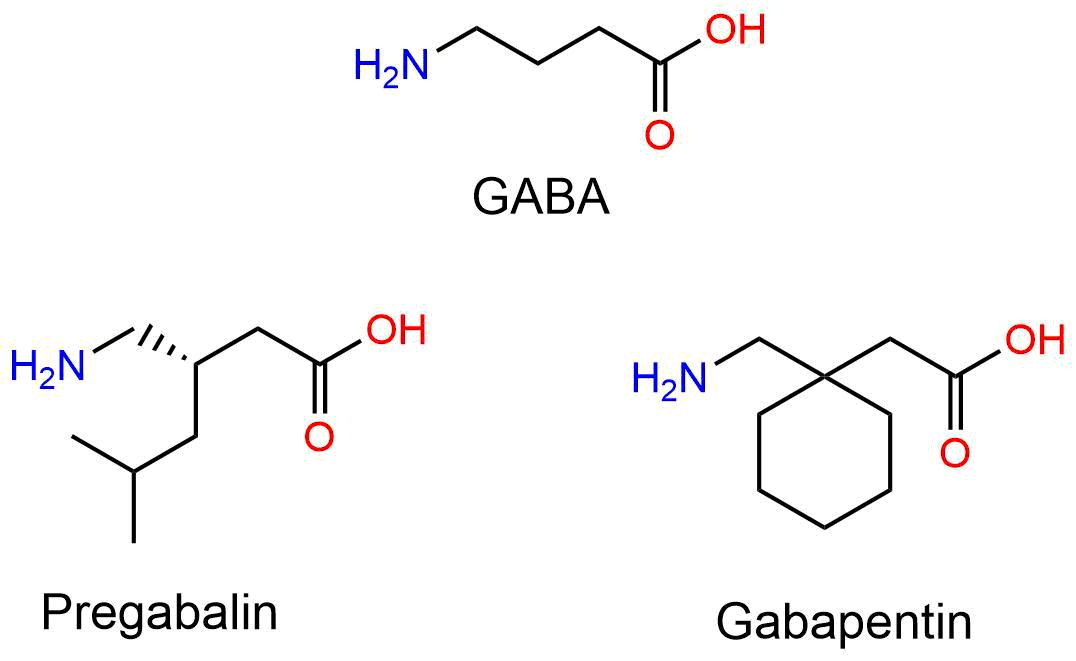
Gabapentin and pregabalin; Other antiseizure medications; OTHER ADJUVANT MEDICATIONS. Topical agents; Cannabis and cannabinoids - Use of cannabis or cannabinoids for pain - Efficacy - Adverse effects; Botulinum toxin; Adjuvants we do not recommend - Muscle relaxants - Benzodiazepines; OPIOIDS; INFUSION THERAPIES. Ketamine; Lidocaine infusion Compare Gabapentin vs Tizanidine head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Skeletal muscle relaxants; Generic Is Gabapentin a Muscle Relaxer? Understanding Its True Function. Gabapentin’s Primary Function: An Anticonvulsant and Neuropathic Pain Relief. What Does an Anticonvulsant Do? Gabapentin’s Indirect Effects on Relaxation; Understanding the Difference: Muscle Relaxers vs. Gabapentin; Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin. 1. Flexeril is a muscle relaxant that may be used short-term in addition to rest and physical therapy to treat muscle spasms caused by musculoskeletal conditions. Sedation is a common side effect more. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It was initially developed as a muscle relaxer and anti-spasmodic medication, but its anticonvulsive properties were discovered later. Gabapentin is used as a nerve relaxer besides what it was intended for seizures. I have a lot more things wrong just from this one pill. It's up to you if you'd want to try it, but I wouldn't recommend it to anyone for muscle pain when there was nothing wrong with my nerves until now. Flexeril (cyclobenzaprine): Another muscle relaxant commonly used to relieve muscle spasms and pain. Soma (carisoprodol): A muscle relaxant that works by blocking pain sensations between nerves and the brain. Zanaflex (tizanidine): A muscle relaxant that can help alleviate muscle spasticity due to conditions such as multiple sclerosis. flammatory drugs for low back pain. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses support using skeletal muscle relaxants for short-term relief of acute low back pain when nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory Muscle relaxers, or muscle relaxants, are medications used to treat muscle spasms or muscle spasticity. Muscle spasms or cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of a muscle or group Gabapentin slows this neuronal firing down to rates that make having a seizure impossible. That’s different than cyclobenzaprine, the most frequently studied skeletal muscle relaxer for pain, Key Takeaways: Gabapentin and Muscle Relaxation Primary Use: Gabapentin is mainly prescribed for managing nerve pain. Indirect Muscle Relaxation: It may help relax muscles by alleviating discomfort. Mechanism of Action: Gabapentin inhibits neurotransmitter release, reducing pain. Gabapentin is not a muscle relaxer. The mechanism by which Gabapentin exerts its analgesic action is unknown, but in animal models of analgesia, Gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a normally innocuous stimulus) and hyperalgesia (exaggerated response to painful stimuli). In some cases, muscle relaxers can help relieve this pain and get you through these tough days. With so many muscle relaxers to choose from, you may be wondering which one works best. Let’s take a closer look at a list of commonly used muscle relaxers for neck and back pain, as well as their potential side effects. What do muscle relaxers do? Gabapentin primarily targets overactive nerve signals, making it effective for managing nerve-related pain, while muscle relaxers like Carisoprodol focus on reducing muscle tension and spasms. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Methocarbamol (Robaxin) is a muscle relaxer. It's used to treat muscle pain and discomfort, like back pain, in people ages 16 years and older. It works best when used along with non-medication treatments, such as rest and physical therapy. Methocarbamol is taken by mouth, typically 3 or 4 times daily. Muscle relaxers, also known as skeletal muscle relaxants, are medications used to treat muscle spasms or muscle pain. They work by reducing muscle tension and improving range of motion. These medications are typically prescribed for short-term use, as they can be habit-forming and have the potential for abuse. Combining muscle relaxers and gabapentin can increase the risk of overdose, especially when taken in high doses or with other central nervous system depressants. It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions and never exceed the recommended dosage. How Skeletal Muscle Contracts. A single α-motor neuron can innervate up to 200 muscle fibers, forming a complex called motor unit (Figure 1).¹⁰ With movement, an action potential originates from the UMN in the motor cortex.⁹ This action potential depolarizes the motor neuron terminal, resulting in the opening of voltage-gated calcium (Ca²⁺) channels and the subsequent release of the
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |