Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
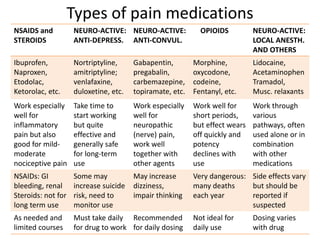
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may more. Nortriptyline is an effective antidepressant but it may cause drowsiness initially and a withdrawal syndrome with abrupt discontinuation. In a **Nortriptyline vs Gabapentin** comparison, it's also worth noting that **nortriptyline** is often more effective in managing pain associated with fibromyalgia, while **gabapentin** is often more effective in managing pain associated with nerve damage. Combined gabapentin and nortriptyline seems to be more efficacious than either drug given alone for neuropathic pain, therefore we recommend use of this combination in patients who show a partial response to either drug given alone and seek additional pain relief. Future trials should compare other combinations to their respective monotherapies for treatment of such pain. Find patient medical information for Nortriptyline on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Neuropathic pain is relieved more effectively by combination treatment with the anticonvulsant gabapentin and the antidepressant nortriptyline than by treatment with either drug alone, a study published online in The Lancet has shown. In 2010, an evidence-based guideline sponsored by the International Association for the Study of Pain recommended nortriptyline as a first-line medication for neuropathic pain. [56] However, in a 2015 Cochrane systematic review the authors did not recommend nortriptyline as a first-line agent for neuropathic pain. Patients showed significant improvement in sleep scores in both the treatment groups nortriptyline (46.0%) and gabapentin (52.0%). The VAS and the SF-MPQ scores for pain were significantly reduced in both the groups. Gabapentin was, however, better tolerated as compared to nortriptyline. Do not use nortriptyline with buspirone (Buspar®), fentanyl (Abstral®, Duragesic®), lithium (Eskalith®, Lithobid®), tryptophan, St. John's wort, or some pain or migraine medicines (eg, sumatriptan, tramadol, Frova®, Maxalt®, Relpax®, Zomig®). Check with your doctor first before using any other medicines with nortriptyline. Combined gabapentin and nortriptyline seems to be more efficacious than either drug given alone for neuropathic pain, therefore we recommend use of this combination in patients who show a partial response to either drug given alone and seek additional pain relief. Future trials should compare other combinations to their respective monotherapies for treatment of such pain. Gabapentin vs Nortriptyline for nerve pain involves two different approaches: gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, stabilizes nerve activity, while nortriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, helps by increasing certain neurotransmitters to reduce pain. Nortriptyline is not recommended for use in children. Warnings. You should not use nortriptyline if you recently had a heart attack. Do not use nortriptyline if you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days, such as isocarboxazid, linezolid, methylene blue injection, phenelzine, tranylcypromine and others. Interpretation: Combined gabapentin and nortriptyline seems to be more efficacious than either drug given alone for neuropathic pain, therefore we recommend use of this combination in patients who show a partial response to either drug given alone and seek additional pain relief. Interpretation: Combined gabapentin and nortriptyline seems to be more efficacious than either drug given alone for neuropathic pain, therefore we recommend use of this combination in patients who show a partial response to either drug given alone and seek additional pain relief. There was no indication that either nortriptyline or gabapentin was more effective in postherpetic neuralgia (very low quality evidence). Two studies reported the number of people with at least moderate pain relief, and one reported the number who were satisfied with their pain relief and had tolerable adverse effects. Serious side effects of nortriptyline. Along with its needed effects, nortriptyline may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking nortriptyline: Incidence not known Participants were prescribed one of four medications commonly used to treat CSPN: nortriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant; duloxetine, a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; pregabalin, an anti-seizure drug; or mexiletine, an anti-arrhythmic medication. The most effective treatment was nortriptyline. Of the study subjects taking this medication, 25% reported their discomfort improved by at least 50%. The least effective treatment was pregabalin: only 15% of study subjects reported that much improvement. Source Reference: Gilron I, et al "Nortriptyline and gabapentin, alone and in combination for neuropathic pain: a double-blind, randomised controlled crossover trial." Lancet 2009; DOI: 10.1016 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Nortriptyline oral capsule is available as a generic drug and as the brand-name drug Pamelor. Learn about side effects, warnings, dosage, and more. pain or pressure in your upper body; Stroke
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |