Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
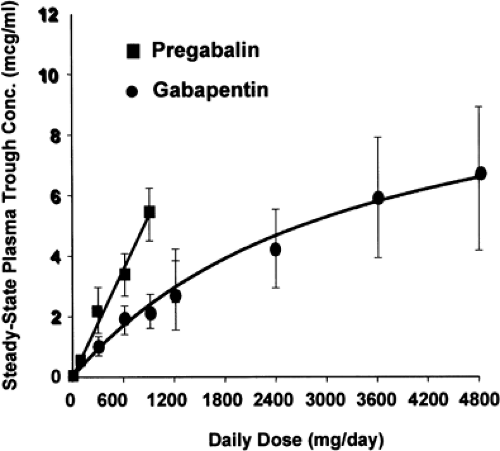
The particular NNTs for pregabalin and gabapentin were 7.71 and 7.16, respectively. 10 A more recent meta-analysis in 2022 specifically focused on post-herpetic neuralgia and found greater efficacy with pregabalin in alleviating pain and improving global perception of pain and sleep. 15 Another meta-analysis published in 2021 reported similar Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed in the small intestine, pregabalin is also absorbed in the proximal colon. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. Pregabalin offers key advantages over gabapentin, including improved absorption, faster onset / titration, more predictable dose-response relationship, and more convenient dosing. While the prospect of reduced drug costs with generic pregabalin is encouraging, it remains more expensive than gabapentin — the most significant roadblock in Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed in the small intestine, pregabalin is also absorbed in the proximal colon. Absorption of gabap-entin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily satura-ble, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. When comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin, pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and more fully by the body. Pregabalin is a controlled substance in every state, while gabapentin is controlled only in some states. Pregabalin and gabapentin are both used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and anxiety, but pregabalin has faster absorption, higher bioavailability, and requires lower doses for similar effects compared to gabapentin. Gabapentin (often sold under the brand name Neurontin) and pregabalin (brand name Lyrica) are two commonly prescribed medications that work in similar ways. While both belong to a class of drugs called gabapentinoids and are used to treat nerve-related conditions, they have distinct differences that can affect which one might be right for you. Gabapentin is more slowly and variably absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations around 3 hours post-dose. Pregabalin is quickly absorbed, with the maximum rate of absorption being 3 times that of gabapentin. It reaches peak blood concentrations within an hour after ingestion. First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. Introduction. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Lyrica (Pregabalin) are both medications commonly prescribed to treat various neurological conditions. While they belong to the same class of drugs and share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that set them apart. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations attained within 3–4 hours. Orally administered gabapentin exhibits saturable absorption — a nonlinear (zero-order) process — making its pharmacokinetics less predictable. Both Lyrica and gabapentin are used as anti-epileptic medications and to treat nerve pain. But there are several differences between them. The main differences between Lyrica and gabapentin are: Lyrica is a brand name for pregabalin. Gabapentin is a generic name - brands of gabapentin include Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. Pregabalin and gabapentin both show dose-response relationships in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. For neuropathic pain, a pregabalin dosage of 450 mg/day appears to reduce pain comparably to the predicted maximum effect of gabapentin. A progression from gabapentin to pregabalin originated from its rapid peak in blood concentration (3 hr to 1 hr) resulting from an increased absorption area expanding from the small intestine into the ascending colon, resulting in linear absorption . Even though it is indicated for PHN and DPNP currently, it is also available for all types of Pregabalin is rapidly absorbed, with peak concentrations occurring within one hour; plasma concentrations increase linearly with increasing dose. Gabapentin, however, is slowly absorbed, with peak concentrations occurring 3–4 hours post-dose; plasma concentrations increase non-linearly (less than proportional) with increasing dose. Some studies suggest gabapentin and pregabalin effectively reduce postoperative pain and opioid consumption, while other studies highlight pregabalin's higher addictive potential and adverse events, and gabapentin's benefits in specific conditions like vasomotor symptoms. Pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and has a higher bioavailability than gabapentin, with a peak concentration reached within 1 hour compared to 3-4 hours for gabapentin. Pregabalin also has a more predictable dose-response relationship and a faster onset of action. Absorption: Absorbed more slowly and variably 4: Results of comparison of analgesic benefits of gabapentin vs pregabalin for postoperative analgesia 7: Gabapentin In terms of pharmacokinetics, pregabalin demonstrates higher oral bioavailability, faster absorption, and a more predictable dose-response relationship than gabapentin (6, 7). Pregabalin also undergoes minimal metabolism and is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine, while gabapentin undergoes significant renal elimination and requires Pregabalin vs Gabapentin â What is the Difference? Pregabalin and gabapentin can both provide relief from pain and be effective ways to manage seizure disorders. However, it’s important to consider the differences between them. Pregabalin is more rapidly absorbed compared to gabapentin, which has a slower absorption rate.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |