Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
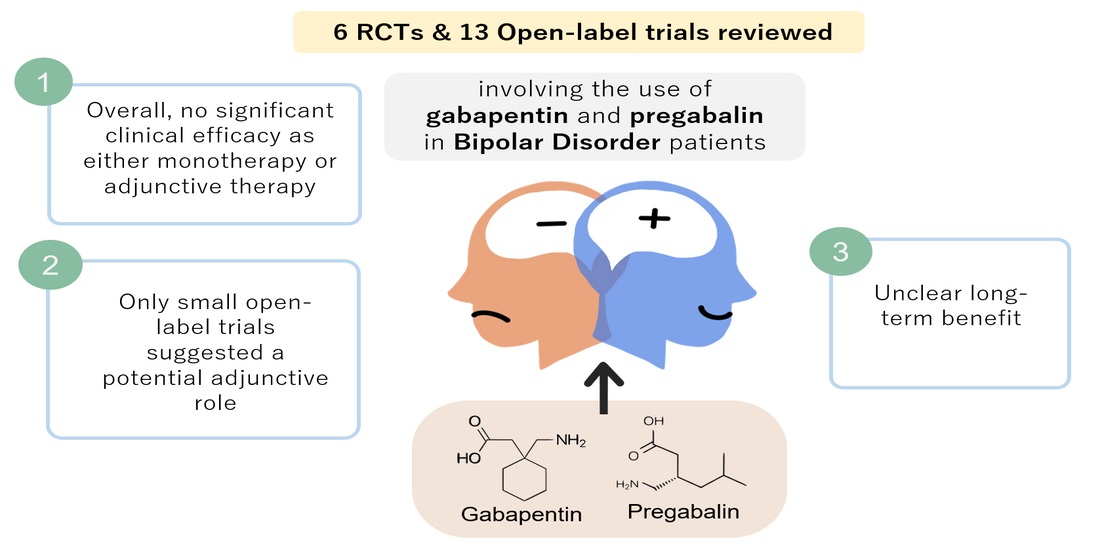
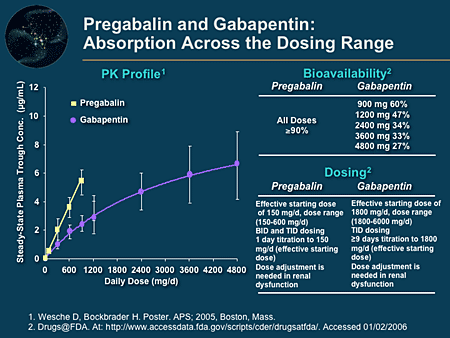
How Do These Drugs Work? Lyrica vs Gabapentin. Lyrica is the brand name for the drug pregabalin, and gabapentin is the name of the medication that is used in drugs such as Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant. All of these drugs are prescribed as anticonvulsant or antiepileptic medications. Gabapentin is indicated as adjunct therapy for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia. 4 Pregabalin is indicated for the same uses as gabapentin, plus the management of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain associated with diabetes, specifically diabetic neuropathy. 5 Abstract. This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified and scrutinized with the goal to define the problem, identify risk factors, and discuss possible methods to reduce the potential for Pregabalin is a Schedule V controlled substance that carries risks of misuse, abuse, or addiction. Gabapentin is not considered a controlled substance. In a research study comparing the potential for addiction, neither gabapentin nor pregabalin were found to be particularly addictive. Though gabapentin and pregabalin share a similar mechanism of action, pregabalin’s higher bioavailability and faster absorption may account for its perceived potency in managing symptoms more quickly than gabapentin. Gabapentin vs. Pregabalin for Anxiety Disorders Pregabalin, also known as Lyrica, has been linked to a higher risk of addiction compared to Gabapentin, also known as Neurontin. According to studies, Pregabalin has a higher potential for abuse and dependence, with some users developing a physical and psychological need for the medication. Pregabalin appeared to be somewhat more addictive than gabapentin regarding the magnitude of behavioral dependence symptoms, transitions from prescription to self-administration, Despite their inherent abuse potential, gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) may be safer than presumed and offer prescribers an effective opioid-alternative treatment for certain types of neuropathic pain. Pregabalin appeared to be somewhat more addictive than gabapentin, taking into consideration that the pregabalin use was more frequently associated with behavioral ICD-10-dependence symptoms, switches from prescription to self-administration and self-administrations themselves (Table 2). The principal population at risk for addiction of gabapentinoids consists of patients with other current or past substance use disorders (SUD), mostly opioid and multi-drug users, who preferred pregabalin. Gabapentin and Addiction Gabapentin is a medication that is used to treat a variety of conditions‚ including seizures‚ nerve pain‚ and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is not a controlled substance‚ but it can be habit-forming in some people. People who abuse gabapentin may take it in high doses to get high. There is some evidence that Lyrica may have a higher addiction potential than gabapentin due to its faster absorption and onset of action; Although both drugs have similar interactions, gabapentin may also interact with NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac. Differences Between Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both anticonvulsants used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but they have key differences in potency, absorption, and usage. Potency and Effectiveness. Pregabalin binds more strongly to calcium channels, making it more potent and requiring lower doses for the same effects. Here’s what you need to know when comparing pregabalin vs. gabapentin: Pregabalin vs Gabapentin: What are They and How Do They Work? Pregabalin and gabapentin are medications that are primarily prescribed in the treatment of nerve pain and seizure disorders. These drugs work by blocking certain brain signals that are responsible for pain Addiction Potential: Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin. A medication's efficacy must be weighed against its addictive potential when treating chronic pain or neurological disorders. Pregabalin and gabapentin, known as gabapentinoids, are widely used as interventional therapies which are used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. Pregabalin appeared to be somewhat more addictive than gabapentin regarding the magnitude of behavioral dependence symptoms, transitions from prescription to self-administration, and the durability of the self-administrations. One of the biggest differences between gabapentin and Lyrica is that the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) labels Lyrica a controlled substance. This means it has a higher potential for dependence and addiction. Gabapentin And Pregabalin Side Effects. Both gabapentin and pregabalin have various side effects. Some are the same, but there are Considering the higher occurrence rates of euphoria among pregabalin users (relative to gabapentin users) and the stronger action of pregabalin on α2δ subunit-containing VDCCs (relative to gabapentin users), one would expect pregabalin (Lyrica) to exhibit greater abuse/addiction potential than gabapentin (Neurontin) when administered at Gabapentin and pregabalin are structurally similar drugs acting via the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. The mechanism by which the drugs may induce dependence is not well worked out. Gabapentin and pregabalin are associated with significant euphoric effects. Pregabalin appeared to be somewhat more addictive than gabapentin, taking into consideration that the pregabalin use was more frequently associated with behavioral ICD-10-dependence symptoms, switches from prescription to self-administration and self-administrations themselves (Table 2).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |