Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
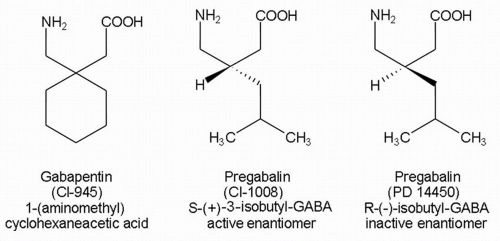
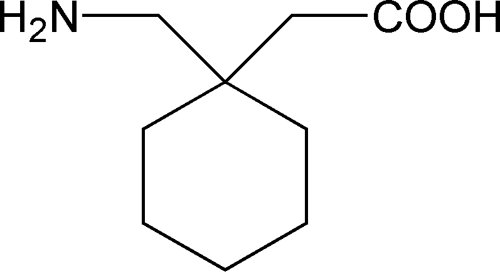
Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic medications that bare structural resemblance to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though neither agent has activity in GABA’s neuronal systems. Pregabalin and gabapentin are non-natural, branched-chain amino acids ().Both are chemical analogues of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA); however, neither drug has activity in GABAergic neuronal systems.[6–8] Functionally, they are similar to the essential, metabolizable, branched-chain amino acid, leucine, with regard to competitive binding to α 2 δ subunit types 1 and 2[] and facilitated First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. VET: In general, avoid the use of the commercially available human oral solution (Neurontin) in dogs as it reportedly contains 300 mg/mL xylitol.As the threshold dose that can cause hypoglycemia in dogs is approximately 100 mg/kg doses of up to 15 mg/kg in dogs using the solution should be safe, but further data is needed to confirm this Additionally, xylitol may be hepatotoxic in dogs. Lyrica is almost totally absorbed (~90%) very quickly after taking by mouth. It's maximum absorption rate is nearly three times gabapentin. This is why the dosage levels of Lyrica are so much lower than the dosage levels of gabapentin. Gabapentin You can see from the chemical structures how closely gabapentin and Lyrica are related. Gabapentin is composed of similar elements—carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. Its molecular structure is more complex than pregabalin, with a pyrrolidine ring attached to a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) derivative, which contributes to its ability to influence the central nervous system. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α2δ-1 and α2δ-2 auxiliary subunits of calcium channels, though only the former has been implicated in the development of The EC50 values of pregabalin and gabapentin were estimated to be about 9.77 and 23.9 mg/mL, respectively, based on studies in epilepsy, suggesting that pregabalin is about 2.4 times more potent than gabapentin. Chemical Structure and Pharmacokinetics: Gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic medications that are structurally similar to the brain chemical GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). They also have similar pharmacokinetic properties. Chemical structure of gabapentin, pregabalin, and gabapentin enacarbil. The mechanism of action of gabapentinoids differs from that of other antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Contrary to initial belief, they do not interact with GABA receptors. They are both structurally similar to GABA – though they have no GABAergic activity – and share functional similarities to the amino acid leucine. Pharmacokinetics: Gabapentin has a slow oral absorption following oral administration, reaching peak plasma concentrations after about 3-4 hours. Pregabalin and gabapentin are members of a unique class of compounds characterized by high affinity binding to the alpha-2-delta (α2δ) protein in the CNS. Both have been shown to be effective as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures and neuropathic pain disorders. Clinical pharmacology studies conducted to characterize the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and drug-drug interaction Pregabalin, like gabapentin, is a ligand of α2δ subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC) and reduces neuronal excitability. It remains to be determined, however, whether this mechanism is sufficient to account for the broad-spectrum pharmacodynamic activity of gabapentin and pregabalin (Sills 2006 ). Pregabalin is GABA derivative and analogue, but it works differently from GABA-ergic drugs. Its structure resembles a-amino acids naturally occurring in CNS -L-leucine and L-isoleucine. A chemical On the brighter side, the gabapentinoids, pregabalin and gabapentin, bind to a 2 d subunit of voltage-gated Ca ++ channel and inhibit the entry of Ca 2+ to the presynaptic afferents (Fig. 2), PGB can be considered as a successor to GBP, at least in terms of its basic chemical structure and therapeutic profile. Clinical experience with GBP encouraged the search for additional GABA derivatives with efficacy in both epilepsy and pain syndromes, and PGB emerged as one of the most promising candidate compounds [6]. The chemical structure of pregabalin is C 8 H 17 NO 2 and has a chemical name of (S)-3(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Pregabalin has a molecular weight of 159.23 grams per mole. Here’s what you need to know when comparing pregabalin vs. gabapentin: Pregabalin vs Gabapentin: What are They and How Do They Work? Pregabalin and gabapentin are medications that are primarily prescribed in the treatment of nerve pain and seizure disorders. These drugs work by blocking certain brain signals that are responsible for pain Pregabalin | C8H17NO2 | CID 5486971 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |