Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 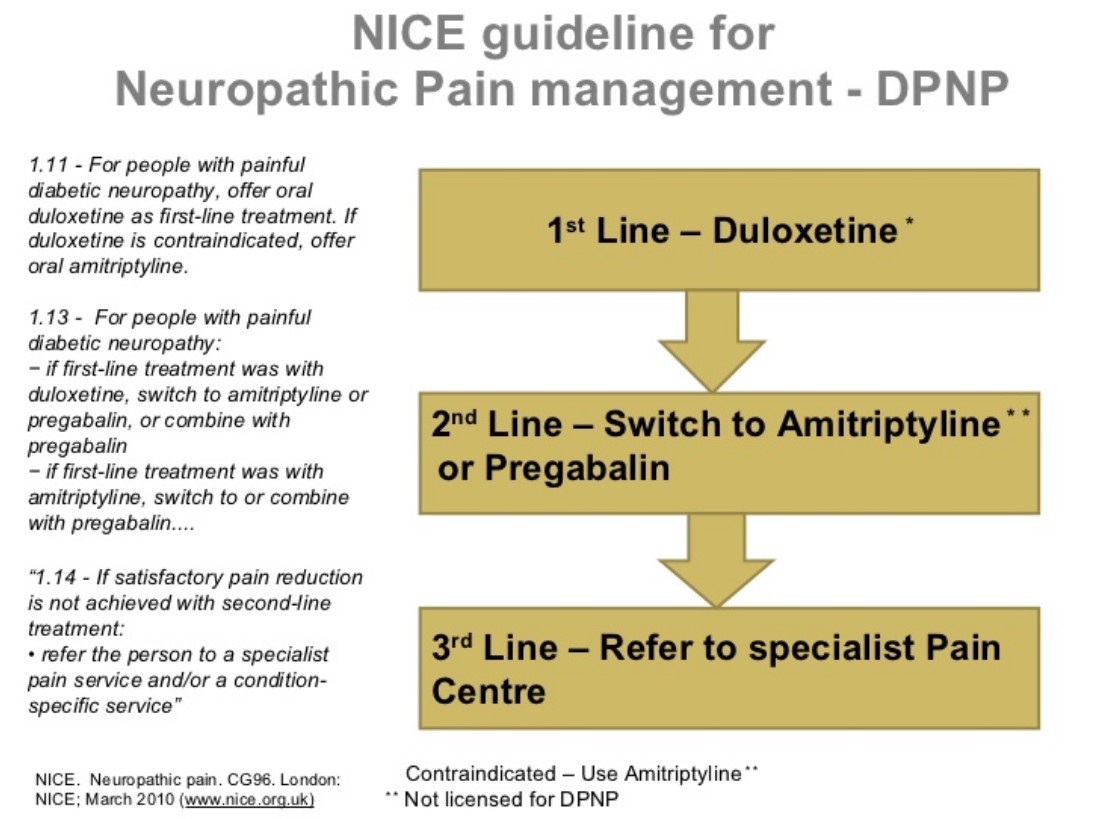 |
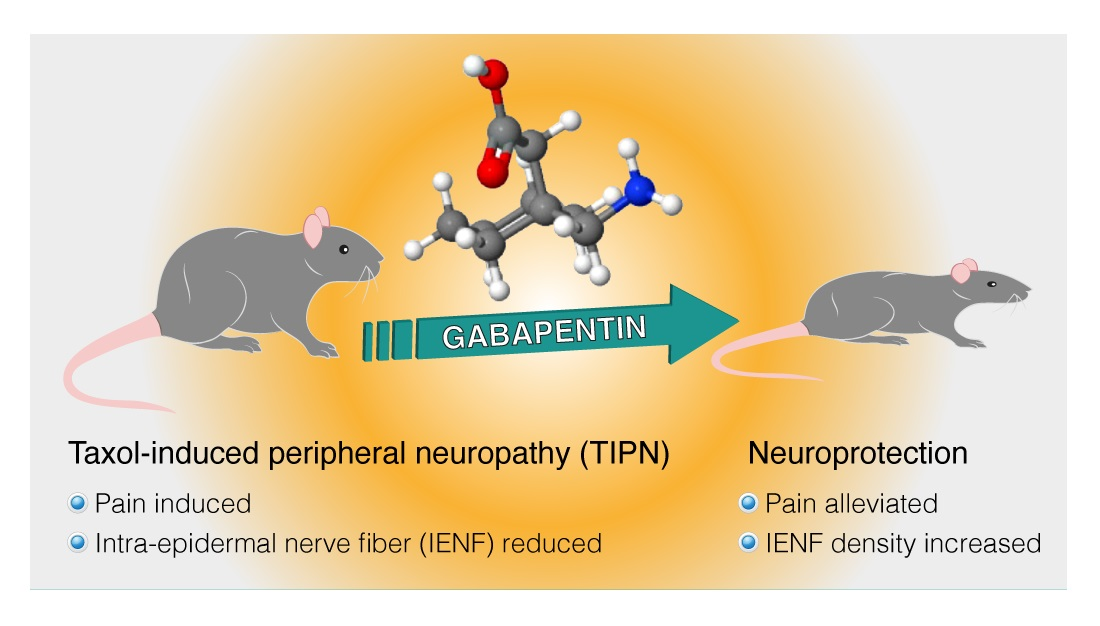
Keywords: Peripheral neuropathic pain, Post-herpetic neuralgia, Diabetic neuropathy, Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Cost-effectiveness analysis. Background. Neuropathic pain (NeP) is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as “Pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system”. Conclusion: In conclusion, pregabalin demonstrated superior and faster efficacy in alleviating neuropathic pain than gabapentin did. Additionally, it improved patient-reported outcomes, resulted in lower opioid consumption, and led to fewer adverse events. Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are recommended as the first-line treatment for neuropathic pain due to SCI [18, 19]. Both drugs have been shown to be effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia [20 – 26] and diabetic peripheral neuropathy [24 – 29]. Pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (except in older adults), or duloxetine (Cymbalta) should be used as first-line treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A 1 Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. There are limited studies directly comparing the efficacy of gabapentin to pregabalin. Based on the few studies examined, both drugs improve neuropathic pain but there is no clear difference between the two when it comes to pain reduction. However, pregabalin seems to result in quicker pain relief than gabapentin, which may be advantageous. For instance, Solak et al. observed that pregabalin improved pruritus to a greater extent than gabapentin in patients with uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients with documented peripheral neuropathy. It is divided into central or peripheral NeP according to the site of the lesion. 3 NeP encompasses a range of clinical conditions: from peripheral NeP conditions such as peripheral diabetic neuropathy (PDN) to central NeP conditions, for example, central post-stroke pain. Among the most prescribed antiepileptic medications for neuropathic pain management, pregabalin therapy and gabapentin therapy are widely used to treat conditions such as painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy, herpes zoster infection, and peripheral neuropathic pain. Conclusion: Our study revealed that Pregabalin is found to be more efficacious when compared to Gabapentin among Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with painful peripheral neuropathy. Hence, we conclude that Pregabalin provided significant improvement in pain relief and other perspectives. Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. Researchers compare four treatments for neuropathy. Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. After 12 weeks, each person rated their neuropathy Gabapentin and pregabalin reduce the calcium-dependent neurotransmitters in the neuronal membrane, thus inhibiting the neuronal excitability.[15,16] Pregabalin, in contrast to gabapentin, has a higher bioavailability (90% vs. 33–66%), rapid absorption (peak: 1 h) with plasma concentration increasing linearly with increasing dose, which In this context, the objective of this meta-analysis is to evaluate and compare pregabalin vs. gabapentin in terms of efficacy and safety in the treatment of neuropathic pain, aiming to provide a solid foundation for clinical decision-making and improve the management of this condition in medical practice. 2 Methods 2.1 Eligibility criteria The average number of pills per day by a patient in the gabapentin group was 1.8 pills higher than the pregabalin group which was statistically significant (p = 0.01). The results of this analysis support the notion that there is no significant difference in meaningful pain reduction with gabapentin versus pregabalin. Gabapentin is not the same as pregabalin, even though they both belong to the same class of medicine, called gabapentinoids, and work similarly. Lyrica and Lyrica CR are the only brands of pregabalin. Neurontin is a brand name for gabapentin. Other brands of gabapentin include Gralise and Horizant. Gabapentin is indicated as adjunct therapy for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia. 4 Pregabalin is indicated for the same uses as gabapentin, plus the management of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain associated with diabetes, specifically diabetic neuropathy. 5 We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The particular NNTs for pregabalin and gabapentin were 7.71 and 7.16, respectively. 10 A more recent meta-analysis in 2022 specifically focused on post-herpetic neuralgia and found greater efficacy with pregabalin in alleviating pain and improving global perception of pain and sleep. 15 Another meta-analysis published in 2021 reported similar
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |