Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 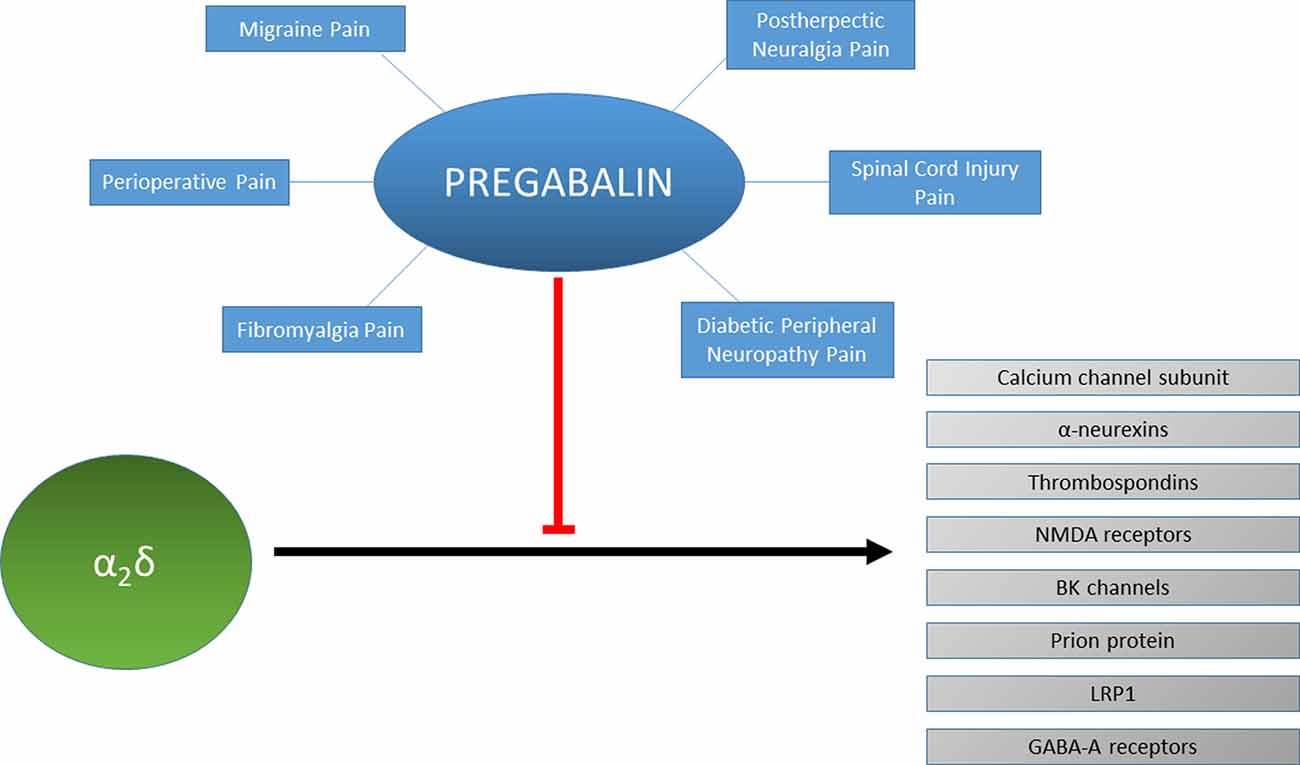 |
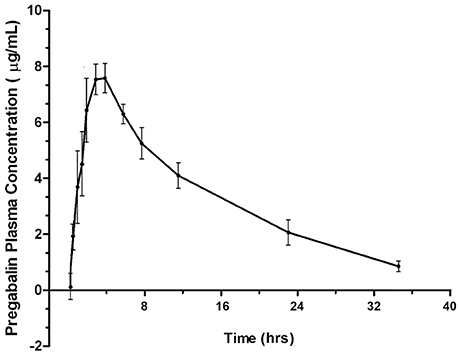
Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and phar-macodynamic characteristics. Pharmacokinetics of Pregabalin and Gabapentin. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic medications that bare structural resemblance to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though neither agent has activity in GABA’s neuronal systems. Pregabalin and gabapentin both show dose-response relationships in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. For neuropathic pain, a pregabalin dosage of 450 mg/day appears to reduce pain comparably to the predicted maximum effect of gabapentin. There is little evidence to guide conversion between gabapentin and pregabalin. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin . Pharmacokinet 2010; Pregabalin shows higher affinity to the α2-δ protein subunit than gabapentin , suggesting that pregabalin is more potent than gabapentin. Pregabalin has been shown to be effective and well-tolerated as an add-on anticonvulsant medication in people with partial (focal) seizures (6, 7), and for management of neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. Although pregabalin and gabapentin share similarities in their mechanisms of action, they exhibit some pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences. In terms of pharmacokinetics, pregabalin demonstrates higher oral bioavailability, faster absorption, and a more predictable dose-response relationship than gabapentin (6, 7). Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are similar medications that treat similar conditions. But pregabalin is approved to treat more conditions than gabapentin. Both medications, though, are often used off-label. When comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin, pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and more fully by the body. Gabapentin AUC exposure was less than dose-proportional in a PK study evaluating dose proportionality of Horizant® vs gabapentin AUC in blood after single oral doses. Gabapentin blood levels were shown to reach a maximum value independent of the dose. This is consistent with saturation of absorption. Pregabalin is administered BID or TID, gabapentin TID. Pregabalin is approximately 2.5 times more potent than gabapentin based on plasma concentrations. Distinct pharmacokinetic advantages exist for the second generation alpha-2-delta ligand, pregabalin. Differences Between Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both anticonvulsants used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but they have key differences in potency, absorption, and usage. Potency and Effectiveness. Pregabalin binds more strongly to calcium channels, making it more potent and requiring lower doses for the same effects. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinic Gabapentin vs. Pregabalin: A Comparative Analysis Introduction to Gabapentin and Pregabalin. Gabapentin and pregabalin are both antiepileptic drugs that have found extensive use in the treatment of various types of pain, including neuropathic pain and postoperative pain. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles can have implications for clinical practice. This article has summarised these key differences. In addition to their use in managing ne In terms of pharmacokinetics, pregabalin demonstrates higher oral bioavailability, faster absorption, and a more predictable dose-response relationship than gabapentin (6, 7). Pregabalin also undergoes minimal metabolism and is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine, while gabapentin undergoes significant renal elimination and requires Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Expert opinion: The higher intrinsic potency of pregabalin compared to gabapentin is associated with an increased antiepileptic efficacy both in animal models of epilepsy and in clinical applications. In randomized add-on trials, seizure reduction compares favorably with other second-generation AED. The main difference between gabapentin and pregabalin is their pharmacokinetics. Pregabalin has advantages over gabapentin because it is absorbed more efficiently and has a linear dose-response relationship, meaning a single dose achieves predictable pain reduction. The EC50 values of pregabalin and gabapentin were estimated to be about 9.77 and 23.9 mg/mL, respectively, based on studies in epilepsy, suggesting that pregabalin is about 2.4 times more potent than gabapentin. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed in the small intestine, pregabalin is also absorbed in the proximal colon. Absorption of gabap-entin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily satura-ble, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |